Sugar Intake Calculator
Calculate your optimal daily sugar intake limit based on age, gender, activity level, and health goals. Get personalized recommendations for managing sugar consumption and improving your diet.
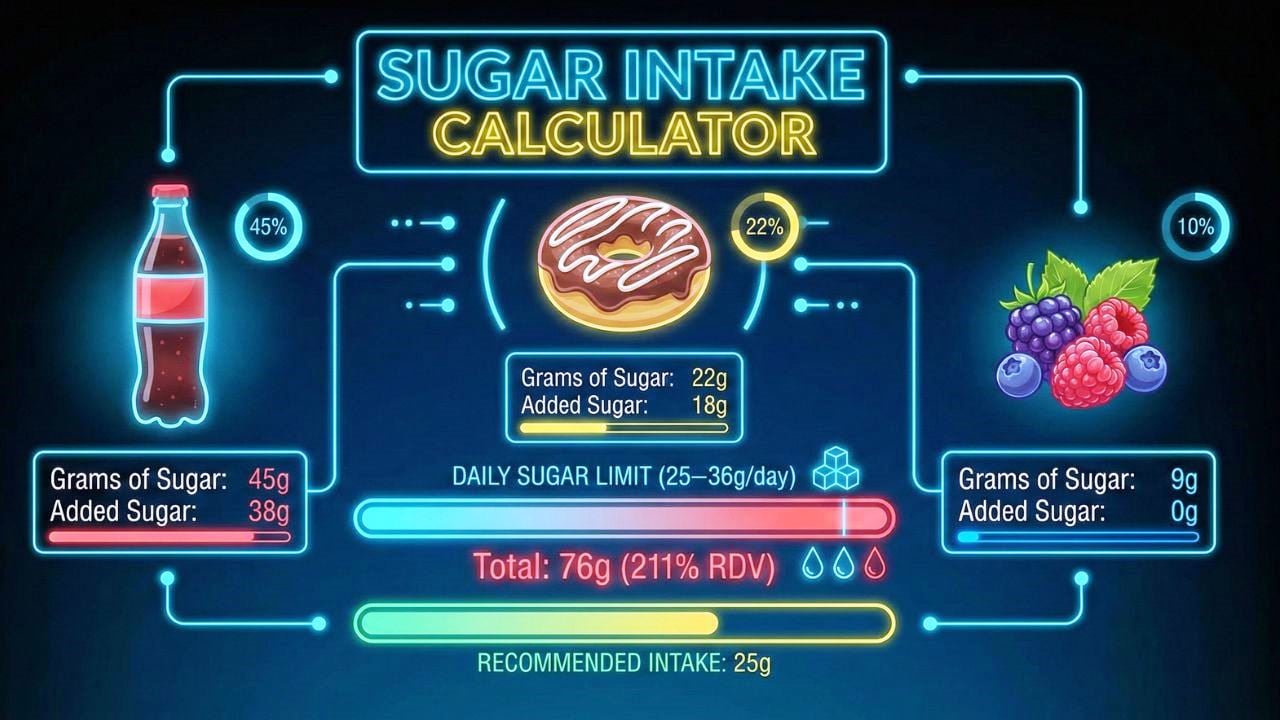
What is the Recommended Daily Added Sugar Intake?
The World Health Organization (WHO) and American Heart Association (AHA) recommend limiting added sugars to less than 10% of total daily energy intake. For optimal health benefits, a reduction to below 5% of total energy intake is suggested. Unlike natural sugars found in whole foods, added sugars provide empty calories without nutritional benefits. Our calculator provides personalized added sugar limits based on your estimated daily calorie needs and health conditions.
Natural vs Added Sugars: What’s the Difference?
Natural sugars occur naturally in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. These sugars come packaged with fiber, vitamins, and minerals that slow sugar absorption. Added sugars, however, are sugars and syrups added to processed foods and beverages during manufacturing. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugars to no more than 6 teaspoons (25 grams) per day for women and 9 teaspoons (36 grams) per day for men.
Age-Based Sugar Intake Recommendations
Sugar intake needs change throughout life. Children and adolescents require adequate carbohydrates for growth and development, while older adults may need to reduce sugar intake due to metabolic changes and health conditions. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans provide specific recommendations based on age groups, with younger children having the lowest recommended intakes and active teenagers having higher allowances.
Health Conditions and Sugar Intake
Certain health conditions require more restrictive sugar intake limits. People with diabetes need to carefully manage carbohydrate intake to control blood sugar levels. Those with prediabetes, metabolic syndrome, or cardiovascular conditions may also benefit from reduced sugar consumption. Our calculator automatically adjusts recommendations based on selected health conditions for safer, more appropriate guidance.
Added Sugar Intake Calculation Methodology
| Organization | Added Sugar Guideline | Scientific Basis | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| WHO | <10% of total energy intake | Reduces risk of overweight, obesity, tooth decay | Global public health recommendation |
| AHA | 6 tsp (25g) women, 9 tsp (36g) men | Reduces cardiovascular disease risk | Evidence-based for heart health |
| ADA | Individual assessment for diabetes | Blood sugar control and metabolic health | Personalized for diabetes management |
| Dietary Guidelines | <10% of calories from added sugars | Overall dietary pattern improvement | National nutrition policy |
Calculation Formula: Added Sugar Limit = (Estimated TDEE × 0.10) ÷ 4
Where TDEE is calculated using Mifflin-St Jeor equation with activity level adjustments.
Health condition multipliers applied for medical conditions requiring stricter limits.
Common Sources of Added Sugars
| Food/Beverage | Sugar Content (per serving) | % Daily Limit (50g) | Healthier Alternative |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soda (12 oz) | 39g | 78% | Sparkling water |
| Fruit Juice (8 oz) | 30g | 60% | Whole fruit |
| Yogurt (plain with added sugar) | 25g | 50% | Greek yogurt |
| Cereal (with added sugar) | 20g | 40% | Oatmeal |
| Candy Bar | 30g | 60% | Nuts or fruit |
Note: Sugar content can vary by brand and preparation method. Always check nutrition labels. The % Daily Limit is calculated based on a 50g daily sugar allowance for adults.
