
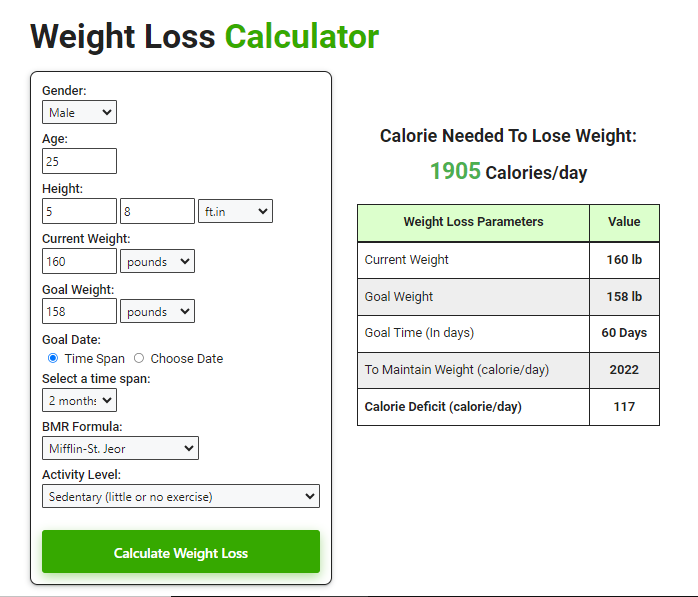
Weight Loss Calculator
Calorie Needed To Lose Weight:
_____ Calories/day
| Weight Loss Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Current Weight | |
| Goal Weight | |
| Goal Time (In days) | |
| To Maintain Weight (calorie/day) | |
| Calorie Deficit (calorie/day) |
Looking for an online calorie deficit weight loss calculator that accurately estimates the time (in weeks or months) needed to achieve a specific weight loss goal? Look no further.
Our calorie deficit calculator can determine the time needed for both healthy and rapid weight loss, as well as the required daily or weekly calorie intake. It is suitable for both men and women.
The calculator will provide precise results and even generate a weight loss chart to help you better understand how calorie intake affects weight loss.
Note: It is not advisable to limit daily caloric intake to less than 1,200-1,600 for men and 1,000-1,200 for women.
To Know Your Body Fat %: Use Our Body Fat % Calculator
What Is A Calorie Deficit Weight Loss Calculator?
A weight loss calculator is a digital tool designed to help people estimate various metrics associated with weight loss.
These calculators consider factors such as age, gender, height, current weight, and the frequency of exercise to help you lose weight. They can advise on how many calories to consume, how much exercise to engage in, and how long to do it.
Basic Features of Weight Loss Calculators
- Caloric Intake Estimation: Estimate the number of calories you should consume daily to achieve a specific weight loss goal within a specified period.
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): the number of calories your body requires to maintain basic physiological functions.
- Physical Activity Level (PAL): Your activity level is considered when adjusting your recommended caloric intake, depending on whether you are sedentary, lightly active, or highly active.
- Timeframe for Weight Loss: Estimate how long it will take for you to reach your weight loss goal based on the information you provide and the caloric deficit you are willing to maintain.
- Exercise Recommendations: offer exercise suggestions to help you burn extra calories. This can be helpful for individuals who prefer to consume more calories and balance them out with regular physical activity.
How to Use a Calories Deficit Weight Loss Calculator
To use a calorie deficit weight loss calculator, follow these steps:
- Please enter your current weight and your goal weight accurately. Weigh yourself under consistent conditions.
- Be honest about your activity level. Sedentary, moderately active, active, or very active. This affects your calorie needs.
- Use your actual height, age, and gender. The calculator uses these to estimate your basal metabolic rate.
- Start with a modest calorie deficit of 500 calories per day to achieve approximately 1 lb of weight loss per week. Avoid extreme deficits.
- If you find that your calorie target is too aggressive or is not leading to expected weight loss, you should adjust it.
- Re-calculate your calories every 10 lbs as you lose weight to account for your new weight.
- Focus on nutritious whole foods that align with your target calories and macronutrient goals.
- Use a food-tracking app consistently to ensure you stick to your calorie target.
- Weigh yourself weekly under the same conditions and adjust your calories if needed.
- Don’t rely solely on the calculator. Listen to your body’s hunger and fullness signals.
- Be patient! Steady weight loss of 1–2 lbs per week is healthier and more sustainable in the long term.
Calculate Weight Loss Calorie Requirement Per Week
Here is how you can calculate your weight loss calories:
1. Determine Your BMR
Use an online BMR calculator or the Mifflin-St. Jeor Equation to estimate your BMR based on your age, gender, weight, and height.
- For men: BMR = (10 x weight in kg) + (6.25 x height in cm) – (5 x age in years) + 5
- For women: BMR = (10 x weight in kg) + (6.25 x height in cm) – (5 x age in years) – 161
2. Estimate Your Activity Level
Based on your daily routine and exercise habits, estimate the number of calories you burn through physical activity.
There are several ways to do this, but a standard method is to use an activity multiplier:
Activity Level
- Sedentary (little or no exercise): BMR x 1.2
- Lightly active (1-3 days of exercise per week): BMR x 1.375
- Moderately active (3-5 days of exercise per week): BMR x 1.55
- Very active (6-7 days of exercise per week): BMR x 1.725
- Extra active (very intense exercise or physical job): BMR x 1.9
3. Calculate Your TDEE
- TDEE = BMR + Activity Level
4. Calculator Calories For Weight Loss
Once you have calculated your TDEE, you can adjust your calorie intake to achieve your desired weight loss or gain.
- To lose weight, you must create a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories than your TDEE. A deficit of 500–1000 calories per day is recommended for safe and sustainable weight loss.
- Keep track of your calorie intake and make gradual adjustments to ensure you’re on track towards your goal.
- Approximately 1 kg of body fat contains 7,700 calories.
- One pound (0.45 kg) of body fat contains approximately 3500 calories.
To Lose Weight, 0.25 Kg/Week
- = (0.25 kg x 7700 calories/kg ÷ 7 days/week).
- You need a 275-calorie deficit per day.
- If your TDEE is 2000 calories per day, you should consume 1725 calories per day (2000 – 275) to lose 0.25 kg per week.
To Lose Weight, 0.5 Kg/Week
- = (0.5 x 7700 ÷ 7).
- You need a 550-calorie deficit per day.
- If your TDEE is 2000 calories per day, you should consume 1450 calories per day (2000 – 550) to lose 0.5 kg per week.
To Lose Weight, 1 Kg/Week
- = (1 x 7700 ÷ 7).
- You need a 1100-calorie deficit per day.
- If your TDEE is 2000 calories per day, you should consume approximately 1100 calories daily (2000 – 900) to lose 1 kg per week.
5. Calculate Zig Zag Diet Calories
To calculate Zigzag calories, you must determine your weekly calorie target and alternate between high and low-calorie days to meet that target.
- Determine your weekly calorie target based on your weight loss.
- Daily Calorie Target = Weekly Calorie Target / 7
- Alternate between low and high-calorie days to create a calorie deficit for weight loss.
- On low-calorie days, consume 300–500 calories less than your daily target,
- On high-calorie days, consume 100–300 calories more than your daily target to prevent weight loss plateaus.
6. Track Your Weekly Weight Loss Calories
Choose a way to track your calories and weight loss progress. Several tools can help:
- Smartphone apps: Many user-friendly apps track your food intake, exercise, and weight loss journey.
- Estimating calories: While calorie counting can be tedious, learning to estimate the calorie content of everyday meals can help you make informed food choices without constant tracking.
- Manual tracking: An Excel spreadsheet or a simple journal is a perfectly good option if you prefer a traditional approach.
7. Track Your Progress
Take time to track your progress and adjust your plan accordingly. When determining your health and fitness, consider weight loss, muscle gain, or fat loss.
Furthermore, measurements should be taken over more extended periods, such as a week (rather than daily), as significant variations in weight can occur due to variations in water intake or time of day.
For consistent measurements, weigh yourself every day at the same time, such as immediately after waking up and before breakfast.
Keynote:
Remembering that a proper diet and regular exercise are widely recognised as the most effective ways to achieve weight loss is essential.
Decreasing your daily calorie intake by over 1,000 calories is not recommended, as losing more than 2 pounds (0.91 kg) per week can be detrimental to your health. This may lead to a decreased metabolism in the future due to the loss of muscle mass.
Losing weight too quickly can lead to dehydration, a potentially unhealthy consequence. In addition, maintaining a healthy diet is crucial when exercising and dieting to support the body’s metabolic processes and replenish itself.
Severely restrictive diets can have serious adverse effects by depriving the body of necessary nutrients. They are unsustainable, with regained weight typically resulting in the accumulation of fat. This leaves the individual in a worse state than they were in when they started.
Thus, monitoring calorie and fibre intake is essential while ensuring the body receives all other necessary nutrients.
Please consult a doctor when losing 1 kg or more per week, since it requires that you consume less than the minimum recommendation of 1,200 calories a day.
Calculate Weight Loss Calories Per Day
Let’s say a 40-year-old female weighs 70 kilograms (154 pounds) and is 170 centimeters (5 feet 7 inches) tall.
To calculate her estimated BMR using the Mifflin-St.. Jeor equation, we need to use the following formula:
- BMR = (10 x weight in kg) + (6.25 x height in cm) – (5 x age in years) – 161
Substituting the values into the equation to get BMR:
- = (10 x 70) + (6.25 x 170) – (5 x 40) – 161
- = 700 + 1062.5 – 200 – 161
- = 1,401.5 calories per day
TDEE for Lightly active (1-3 days of exercise per week): BMR x 1.375
- TDEE =1401.5 x 1.375
- TDEE = 1927.06
TDEE is the total number of calories you can consume every day to maintain your weight.
To lose weight, you must consume fewer calories daily, increase your physical activity level, or do both.
To Lose Weight, 0.25 Kg/Week
- = (0.25 kg x 7700 calories/kg ÷ 7 days/week).
- You need a 275-calorie deficit per day.
- Your TDEE is 1927 calories per day; to lose 0.25 kg per week, you should consume 1652 calories per day (1927 – 275).
Weight Loss Calculator By Goal Date
A weight loss calculator by date is a tool that estimates how much weight you can lose within a specific time frame based on the number of calories you consume and the amount of physical activity you engage in.
To use a weight loss calculator by date, you typically input information such as your current weight, height, age, and activity level. You may also need to enter your gender, as well as your target weight and the date by which you aim to achieve it.
Once you have entered this information, the calculator will estimate the number of calories you need to consume each day to lose weight at a safe and healthy rate. This rate is typically 1–2 pounds per week.
It is a helpful tool for setting realistic weight loss goals and tracking progress, but it should be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and a regular exercise regimen.
Weight Loss Percentage Calculator
Tracking your weight loss progress can be a motivating factor. To calculate your weight loss percentage, your current weight is subtracted from the weight you were at when you began your efforts to lose weight.
This figure is then divided by your starting weight, and the resulting number is multiplied by 100. This will give you your weight loss percentage. This formula can be presented as follows:
- Weight Loss Percentage (%) = [ (Starting Weight − Current Weight) / Starting Weight ] × 100
- Percentage of weight lost = (Total pounds lost ÷ Starting weight) x 100
For example, if you weighed 200 pounds originally and have lost 10 pounds, your calculations would be:
- (10 pounds lost ÷ 200 original pounds) x 100 = 5%
- So you have lost 5% of your starting body weight.
Stay motivated and continue reaching your goals by setting clear, achievable goals and maintaining your dedication. You can do it!
Weight Loss Calculator by Calories
Determining the appropriate daily caloric intake is crucial for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. However, there is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of how many calories a person needs to maintain a healthy weight.
Several factors include age, weight, height, sex, physical activity levels, and overall health status.
For instance, A teenage athlete who plays basketball for several hours each day will require more calories than a sedentary office worker of the same age and gender.
The athlete’s body will need more energy to sustain the physical demands of their sport and maintain optimal health, while the office worker’s body will require fewer calories to maintain basic bodily functions.
The 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans state that the daily calorie requirements for:
- Women typically range from 1,600 to 2,400,
- Men typically require between 2,000 and 3,000 calories per day.
However, these figures can vary based on various factors such as age, body size, height, overall health, lifestyle, and activity level.
The body requires a minimal number of calories to survive, but consuming too few calories can lead to poor bodily function, as the body will prioritise essential functions necessary for survival over those vital for general health and well-being.
According to Harvard Health Publications, women should consume at least 1,200 calories per day, and men should consume at least 1,500 calories per day, unless advised otherwise by a medical professional.
For example, to lose 1 to 2 pounds a week — a rate experts consider safe — your food consumption should be 500 to 1,000 calories less than your total weight-maintenance calories.
Calculate Your Daily Calories Requirement
While adhering to a rigorous weight loss regimen can help you achieve your desired weight, many people struggle to understand their daily caloric needs and plan a diet accordingly. That’s where our Weight Loss Calculator comes in handy.
This helpful tool is ideal for anyone seeking to lose weight. It calculates your daily and weekly calorie requirements and estimates how long it will take to achieve your weight loss goals healthily and safely.
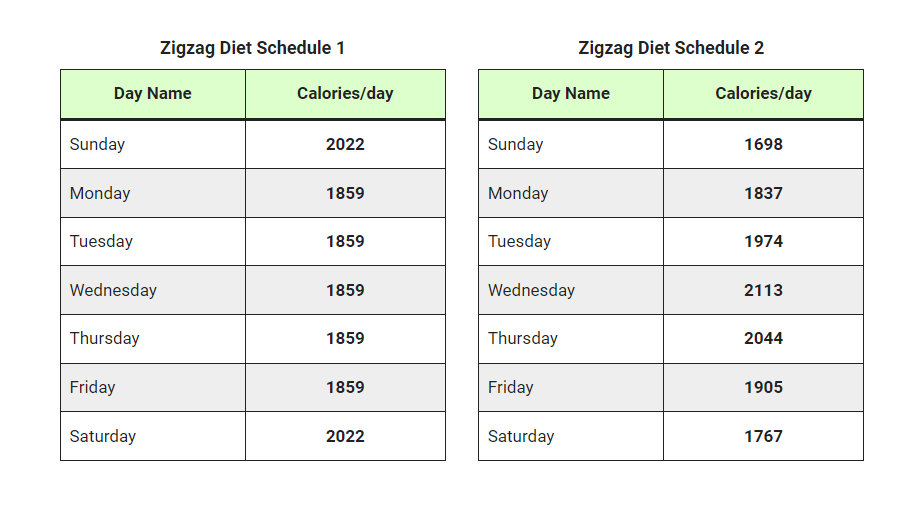
Zigzag Calorie Cycling to Lose Weight
Zigzag calorie cycling is an approach to weight loss that aims to counteract the body’s tendency to adapt to a lower-calorie intake.
Counting and restricting calories can be effective, but over time, the body may adapt to the lower-calorie environment, leading to a plateau in weight loss that can be challenging to overcome. Zigzag calorie cycling helps to prevent this adaptation by alternating the number of calories consumed on a given day.
With zigzag calorie cycling, a person alternates between high and low-calorie days to meet the same weekly calorie target. For example, a person with a weekly calorie target of 14,000 could consume 2,300 calories three days a week and 1,775 calories the other four days, or they could consume 2,000 calories each day.
Zigzag calorie cycling also provides flexibility in the diet, allowing a person to plan for occasions where they may consume more calories, such as family gatherings or work events. By consuming fewer calories on other days, a person can make up for these excess calories without feeling guilty.
There is no concrete rule for varying calorie intake with zigzag calorie cycling, as it largely depends on personal discretion and activity level.
Generally, the high and low-calorie days should vary by approximately 200–300 calories, with the high-calorie day being the number of calories needed to maintain the current weight. The calorie difference should be larger for those with a higher activity level.
The calculator offers two zigzag diet schedules: one with two high-calorie days and five low-calorie days, and another that gradually increases and reduces calories. However, finding an approach that works for you and fits your lifestyle is essential.
Calorie counting and zigzag calorie cycling are just two methods among many for achieving weight loss, and there are many possible approaches within these methods. The best result will come from finding a strategy that you can consistently adhere to.
How To Calculate Zigzag Calorie Cycling
- Daily Calorie Target (Weight Loss) = Weekly Calorie Target / 7
- Plan low-calorie days by consuming 300–500 calories less than your daily calorie target.
- Low-Calorie Day Target = Daily Calorie Target – (300-500) calories.
- Plan high-calorie days by consuming 100–300 calories more than your daily calorie target. This helps to prevent your metabolism from slowing down and can help to avoid weight loss plateaus.
- High Calorie Day Target = Daily Calorie Target + (100-300) Calories
- Create a schedule for your low and high-calorie days, and stick to it consistently.
- Example: Monday – Low Calorie Day
- Tuesday – High Calorie Day
- Wednesday – Low-Calorie Day, and so on.
- Monitor your progress by regularly weighing yourself and taking body measurements. Adjust your calorie intake as needed based on your progress.
- If your progress is slower than expected, you can reduce your calorie intake on high-calorie days or increase your calorie deficit on low-calorie days.
- If your progress is faster than expected, you may need to increase your calorie intake on high-calorie days or decrease your calorie deficit on low-calorie days.
- Remember to maintain a balanced and nutritious diet, regardless of your daily calorie intake. It’s essential to consume various nutrient-dense foods to support your overall health and well-being.
Benefits of Using a Weight Loss Calculator
Using a weight loss calculator can offer a range of benefits to help you on your weight loss journey. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Personalised Information
Weight loss calculators can provide personalised recommendations based on your age, gender, height, weight, and activity level. This allows for a more targeted approach than generic diet and exercise plans.
2. Goal Setting
Having a number for your caloric needs and potential weight loss helps you set achievable and realistic goals. This, in turn, can increase your chances of sticking to your weight loss plan.
3. Increased Awareness
Understanding the numbers behind your weight loss journey can make you more conscious of your dietary choices and activity levels, thereby fostering healthier habits.
4. Time-Saving
A weight loss calculator can provide instant estimates that serve as a starting point for your weight loss plan, eliminating the need to spend hours researching or consulting experts.
5. Enhanced Motivation
Seeing potential weight loss numbers is a good way to get motivated. Having a sense of direction or needing adjustments can keep you focused and committed.
Regularly updating your information in a weight loss calculator can be a form of self-monitoring. Consequently, you’ll be more accountable and likely to stick to your weight reduction plan.
To Stay Motivated: 150+ Gym Workout Motivational Quotes To Stay Fit
6. Informed Decision-Making
The insights gained from using a weight loss calculator can help you make informed choices about food, exercise, and lifestyle changes. This leads to a more effective and sustainable weight loss strategy.
7. Versatility
Many weight loss calculators offer additional options, such as tracking calories from exercise or identifying the nutritional content of food. Like our calorie-deficient weight loss calculator.
This makes them valuable tools that can be changed in many ways.
8. Cost-Effectiveness
Weight loss calculators are available for free or for a nominal fee, making them an affordable tool that can provide invaluable insights.
Weight Loss Calculator By Calorie Intake
1. Calories In Fruits
| Fruit | Serving Size | Calories |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | 1 medium | 72 |
| Banana | 1 medium | 105 |
| Orange | 1 medium | 62 |
| Grapefruit | 1/2 medium | 52 |
| Peach | 1 medium | 59 |
| Pear | 1 medium | 101 |
| Pineapple | 1 cup | 82 |
| Watermelon | 1 cup | 46 |
| Strawberries | 1 cup | 49 |
| Blueberries | 1 cup | 84 |
| Raspberries | 1 cup | 64 |
| Blackberries | 1 cup | 62 |
| Mango | 1 medium | 135 |
| Kiwi | 1 medium | 61 |
| Grapes | 1 cup | 104 |
| Papaya | 1 cup | 62 |
| Cherries | 1 cup | 97 |
| Apricot | 1 medium | 17 |
| Cantaloupe | 1 cup | 54 |
| Honeydew | 1 cup | 64 |
| Lemon | 1 medium | 24 |
| Lime | 1 medium | 20 |
| Pomegranate | 1 medium | 234 |
2. Calories In Vegetables
| Vegetable | Serving Size | Calories |
|---|---|---|
| Asparagus | 1 cup | 27 |
| Bell Pepper | 1 medium | 24 |
| Broccoli | 1 cup | 55 |
| Carrots | 1 cup | 52 |
| Cauliflower | 1 cup | 28 |
| Celery | 1 cup | 16 |
| Cucumber | 1 cup | 16 |
| Green Beans | 1 cup | 31 |
| Kale | 1 cup | 33 |
| Lettuce (romaine) | 1 cup | 8 |
| Mushrooms | 1 cup | 15 |
| Onion | 1 cup | 64 |
| Peas | 1 cup | 118 |
| Spinach | 1 cup | 7 |
| Sweet Potato | 1 medium | 103 |
| Tomato | 1 medium | 22 |
| Zucchini | 1 cup | 20 |
3. Calories in Nuts and Oil Seeds
| Nuts and Oil seeds | Serving Size | Calories |
|---|---|---|
| Almonds (raw) | 1 oz (23 nuts) | 164 |
| Brazil nuts (raw) | 1 oz (6 nuts) | 185 |
| Cashews (raw) | 1 oz (18 nuts) | 157 |
| Chia seeds | 1 oz (2 tbsp) | 138 |
| Flaxseeds | 1 oz (3 tbsp) | 150 |
| Hazelnuts (raw) | 1 oz (21 nuts) | 176 |
| Hemp seeds | 1 oz (2 tbsp) | 155 |
| Macadamia nuts (raw) | 1 oz (10-12 nuts) | 204 |
| Peanuts (roasted) | 1 oz (28 nuts) | 166 |
| Pecans (raw) | 1 oz (19 halves) | 193 |
| Pine nuts (raw) | 1 oz (167 nuts) | 191 |
| Pistachios (raw) | 1 oz (49 nuts) | 159 |
| Pumpkin seeds (roasted) | 1 oz (85 seeds) | 151 |
| Sesame seeds | 1 oz (3 tbsp) | 160 |
| Sunflower seeds | 1 oz (3 tbsp) | 164 |
| Walnuts (raw) | 1 oz (14 halves) | 185 |
4. Calories In Protein-Rich Foods
| Protein Food | Serving size | Calories |
|---|---|---|
| Chicken breast, skinless | 3 oz | 142 |
| Ground beef, 93% lean | 3 oz | 164 |
| Salmon, Atlantic, farmed | 3 oz | 155 |
| Tuna, canned in water | 3 oz | 100 |
| Shrimp, cooked | 3 oz | 84 |
| Turkey breast, skinless | 3 oz | 140 |
| Pork chop, center rib, boneless | 3 oz | 221 |
| Lentils, cooked | 1/2 cup | 115 |
| Chickpeas, cooked | 1/2 cup | 134 |
| Black beans, cooked | 1/2 cup | 114 |
| Tofu, firm, raw | 1/2 cup | 183 |
| Greek yogurt, plain, low-fat | 6 oz | 100 |
| Cottage cheese, low-fat | 1/2 cup | 81 |
| Egg, large, boiled | 1 large | 78 |
| Almonds, dry roasted | 1 oz | 170 |
| Peanut butter, creamy | 2 tbsp | 180 |
| Quinoa, cooked | 1/2 cup | 111 |
5. Calories In Snacks and Common Meals
| Snacks | Serving Size | Calories |
|---|---|---|
| Potato chips, plain, salted | 1 ounce | 155 |
| Bread, white | 1 slice (1 oz.) | 75 |
| Pretzels, hard, plain, salted | 1 ounce | 108 |
| Granola bar, chewy, with raisins | 1.5 oz bar | 193 |
| Graham cracker, plain, honey, or cinnamon | 1 cracker | 59 |
| Chocolate chip cookie (from packaged dough) | 1 cookie | 59 |
| Raisins | 1.5 oz | 130 |
| Hamburger | 1 sandwich | 250 |
| Cheeseburger | 1 sandwich | 285 |
| Corn | 1 cup | 132 |
| Pizza | 1 slice (14”) | 285 |
| Peanut butter, creamy | 2 tbsp | 180 |
6. Calories In Beverages and Dairy
| Beverages and Dairy | Serving Size | Calories |
|---|---|---|
| Almond Milk (unsweetened) | 1 cup | 30 |
| Beer (regular) | 12 oz | 153 |
| Coffee (black) | 8 oz | 2 |
| Cola | 12 oz | 136 |
| Fruit Juice (unsweetened) | 8 oz | 60-100 |
| Greek Yogurt (plain, non-fat) | 6 oz | 100 |
| Hot Chocolate (prepared with water) | 1 cup | 90 |
| Milk (2% fat) | 8 oz | 122 |
| Orange Juice (freshly squeezed) | 8 oz | 112 |
| Protein Shake (whey, vanilla) | 1 scoop (25 g) | 120 |
| Red Wine | 5 oz | 123 |
| Soy Milk (unsweetened) | 1 cup | 80 |
| Sparkling Water | 12 oz | 0 |
| Tea (black, brewed) | 8 oz | 2 |
| Water | 8 oz | 0 |
| White Wine | 5 oz | 121 |
Know Calories Burned During a 30-Min Activity To Calculate Weight Loss Calories
Harvard Medical School has compiled a list of calorie-burning estimates for various activities lasting 30 minutes. It’s worth noting that even activities like sitting and watching TV can burn calories, in addition to your basal metabolic rate (BMR).
| Activity | 125lb person | 155lb person | 185lb person |
| Walking: 3.5 mph (17 min/mi) | 120 | 149 | 178 |
| Weight Lifting: general | 90 | 112 | 133 |
| Stretching, Yoga | 120 | 149 | 178 |
| Weight Lifting: vigorous | 180 | 223 | 266 |
| Stair Step Machine: general | 180 | 223 | 266 |
| Hiking: cross-country | 180 | 223 | 266 |
| Rowing, Stationary: Moderate | 210 | 260 | 311 |
| Rowing, Stationary: moderate | 210 | 260 | 311 |
| Circuit Training: general | 240 | 298 | 355 |
| Rowing, Stationary: vigorous | 255 | 316 | 377 |
| Boxing: sparring | 270 | 335 | 400 |
| Rope Jumping | 300 | 372 | 444 |
| Swimming: laps, vigorous | 300 | 372 | 444 |
| Bicycling, Stationary: vigorous | 315 | 391 | 466 |
| Running: 7.5 mph (8 min/mile) | 375 | 465 | 555 |
FAQs
What is a weight loss calculator?
A weight loss calculator is a tool that estimates the number of calories a person should consume each day to achieve their desired weight loss goal.
It considers factors such as age, sex, weight, height, and activity level to determine the daily calorie intake required to lose weight.
How accurate are weight loss calculators?
Most weight loss calculators are accurate, but they should not be used as the only source of information for a weight loss plan. Their estimates are based on averages and do not account for individual differences in metabolism and body composition.
How many calories should I eat to lose weight?
The number of calories you need to eat to lose weight depends on several factors, including your age, sex, height, weight, and activity level.
Generally, women should consume between 1,200 and 1,500 calories per day, while men should consume between 1,500 and 1,800 calories per day.
Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian is essential to determine your calorie range.
Can I lose weight by simply reducing my calorie intake?
Yes, reducing the number of calories you consume can help you lose weight. It’s essential to ensure you get all the nutrients your body needs.
A balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats is essential for achieving long-term weight loss success.
How do I determine the number of calories I’m consuming?
Using a food diary or a food tracking app can help you track your daily calorie intake.
Many fitness and nutrition apps allow you to log your meals and snacks within the app and calculate the total number of calories you consume.
Is it safe to drastically reduce my calorie intake to lose weight quickly?
It is not recommended to lose weight quickly, as it can be detrimental to your health. Drastically reducing your calorie intake can lead to nutrient deficiencies, muscle loss, and other health problems.
Aiming for a gradual weight loss of 1–2 pounds per week is essential.
Should I exercise to lose weight?
Yes, exercise is an essential component of weight loss. Not only does it burn calories, but it also helps to build muscle and boost your metabolism.
Aim to get at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week for optimal weight loss results.
How long will it take to lose weight?
It takes a long time to lose weight, depending on the amount of weight you need to lose, the number of calories you consume, and the level of exercise you engage in.
A healthy rate of weight loss is 1 to 2 pounds per week. It is possible to achieve significant weight loss over several months with consistent effort.
Related Tools
- Basketball Calories Burned Calculator
- Badminton Calories Burned Calculator
- Boxing Calories Burned Calculator
- Plank Calories Burned Calculator
- Burpee Calories Burned Calculator
- Crunches Calories Burned Calculator
- Zumba Calories Burned Calculator
- Pull Up Calories Burned Calculator
- Push-Up Calories Burned Calculator
- Home Activities Calories Burned Calculator
- Exercise Calories Burned Calculator
- Running Calorie Calculator
- Walking Calorie Burned Calculator
References:
- Johnstone AM, Murison SD, Duncan JS, Rance KA, Speakman JR, Factors influencing variation in basal metabolic rate include fat-free mass, fat mass, age, and circulating thyroxine but not sex, circulating leptin, or triiodothyronine1. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82: 941-948.
- Schwarz, N. A., Rigby, B. R., La Bounty, P., Shelmadine, B., & Bowden, R. G. (2011). A Review of Weight Control Strategies and Their Effects on the Regulation of Hormonal Balance. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2011.
- Rossow, L. M., Fukuda, D. H., Fahs, C. A., Loenneke, J. P., & Stout, J. R. (2013). This Link Will Open A PDF DocumentNatural bodybuilding competition preparation and recovery: a 12-month case study. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 8(5), 582–592.
- Muller, M. J., Enderle, J., Pourhassan, M., Braun, W., Eggeling, B., Lagerpusch, M., … Bosy-Westphal, A. (2015). Metabolic adaptation to caloric restriction and subsequent refeeding: the Minnesota Starvation Experiment revisited. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 102(4), 807–819.
- Davoodi SH, Ajami M, Ayatollahi SA, Dowlatshahi K, Javedan G, Pazoki-Toroudi HR. Calorie shifting diet versus calorie restriction diet: a comparative clinical trial study. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(4):447–456.
- Burke L. E., Wang J., Sevick M. A. (2011). Self-monitoring in weight loss: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 111, 92–102.

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
