
Weight Gain Calculator
Calorie Needed To Gain Weight:
_____ Calories/day
| Weight Gain Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Current Weight | |
| Goal Weight | |
| Goal Time (In days) | |
| To Maintain Weight (calorie/day) | |
| Calorie Surplus (calorie/day) |
Many people seek weight gain to gain muscle or improve their health. However, determining the optimal weight gain and calorie intake can be challenging. That’s where weight gain calculators come in.
Weight gain calories calculator tells you how many calories you need to eat to gain the weight you want.
What Is Weight Gain?
Weight gain refers to an increase in body weight due to increased body fat or muscle mass. It naturally occurs when people consume more calories than their bodies burn.
Since the body must store the leftover energy as some form of fuel, it generally stores it as fat or helps to build muscles.
You should increase your calorie surplus to 300–500 calories above your maintenance level to slow the gain.
You could try eating another 700-1,000 calories daily to gain weight.
Some may benefit from weight gain, including those who intend to gain muscle, become more assertive, or recover from a disease. To others, unwholesome food intake and excessive sitting around can be risky.
Understanding what contributes to weight gain is essential for making thoughtful choices that help you maintain a healthy weight.
Calorie calculators may not be precise, but they can still be helpful.
Related Calculator: Weight Loss Calculator
How To Calculate Calories Requirement To Gain Weight
1. Determine Your BMR
Use an online BMR calculator or the Mifflin-St Jeor Equation to estimate your BMR based on age, gender, weight, and height.
- For men: BMR = (10 x weight in kg) + (6.25 x height in cm) – (5 x age in years) + 5
- For women: BMR = (10 x weight in kg) + (6.25 x height in cm) – (5 x age in years) – 161
2. Estimate Your Activity Level
You should calculate how many calories you burn based on your daily routine and exercise habits.
There are several ways to do this, but a standard method is to use an activity multiplier:
Activity Level
- Sedentary (little or no exercise): BMR x 1.2
- Lightly active (1-3 days of exercise per week): BMR x 1.375
- Moderately active (3-5 days of exercise per week): BMR x 1.55
- Very active (6-7 days of exercise per week): BMR x 1.725
- Extra active (very intense exercise or physical job): BMR x 1.9
3. Calculate Your TDEE:
- TDEE = BMR + Activity Level
4. Calculator Calories For Weight Gain
Once you have calculated your TDEE, you can adjust your calorie intake to achieve your desired weight gain.
- You must create a calorie surplus by consuming more calories than your TDEE to gain weight.
- A daily surplus of 500–1000 calories is recommended for safe and sustainable weight gain.
- Keep track of your calorie intake and make gradual changes.
- 1 kg of body fat contains approximately, 7700 calories.
- One pound of body fat contains approximately, 3500 calories.
Gain Weight Weekly Calories Requirement
To Gain Weight 0.25 Kg/Week
- = (0.25 kg x 7700 calories/kg ÷ 7 days/week).
- You need a 275-calorie surplus per day.
- If your TDEE is 2000 calories daily, you should consume 2275 calories daily (2000 + 275) to gain 0.25 kg/week.
To Gain Weight 0.5 Kg/Week
- = (0.5 × 7700 ÷ 7).
- You need a 550-calorie surplus per day.
- If your TDEE is 2000 calories daily, you should consume 1450 calories daily (2000 + 550) to gain 0.5 kg/week.
To Gain Weight, 1 Kg/Week
- = (1 × 7700 ÷ 7).
- You require an 1100-calorie surplus per day.
- If your TDEE is 2000 calories daily, you should consume 3100 calories daily (2000 + 1100) to gain 1 kg/week.
5. Calculate Zig Zag Calories
To calculate Zigzag calories, you must determine your weekly calorie target and alternate between high and low-calorie days to meet that target.
- Determine your weekly calorie target based on your weight gain.
- Daily Calorie Target = Weekly Calorie Target / 7
- Alternate between low and high-calorie days to create a calorie surplus for weight gain.
- On low-calorie days, consume 300–500 calories less than your daily target,
- On high-calorie days, consume 100–300 calories more than your daily target.
6. Track Your Calories
Many user-friendly smartphone apps help you monitor calorie intake, exercise, and progress. Counting calories isn’t for everyone, as gauging food portions can be difficult.
Track calorie content to estimate intake without weighing food. Alternatively, use an Excel spreadsheet or journal for manual tracking.
Counting calories may not suit everyone, as it can be challenging to gauge food proportions and the number of calories they contain.
However, by tracking and measuring the calorie content of some of your regular meals, you can quickly learn to estimate calorie intake without weighing or measuring your food each time.
Alternatively, you may prefer to track your progress manually using an Excel spreadsheet or a pen-and-paper journal, both of which are viable options.
Keynote:
It’s important to note that achieving a healthy weight gain requires a proper diet and regular exercise. While increasing your calorie intake drastically to gain weight quickly may be tempting, it is not recommended.
Gaining weight too quickly can adversely affect your body. Aiming to gain 1 pound (0.45 kg) a week would add roughly 500 calories to your daily weight maintenance calorie needs.
Maintaining a healthy diet while increasing calorie intake is essential for supporting the body’s metabolic processes and replenishing itself.
Therefore, monitoring calorie and nutrient intake, including fiber, is essential to ensure the body receives all necessary nutrients to maintain balance and overall health.
If you’re gaining weight at a rate of 1 pound (0.45 kg) or more per week, consult a doctor.
How Many Calories Do I Need To Gain Weight?
Getting the right amount of calories is so important for healthy weight gain, but remember, everyone has different needs! Things like your age, weight, height, gender, activity level, and overall health all play a role in figuring out what’s best for you.
A young athlete exercising vigorously daily needs more calories than a sedentary office worker of the same age and gender. The athlete requires extra energy for physical demands and optimal health, while the office worker needs fewer calories for essential functions.
According to the 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, daily calorie requirements for weight gain may range from 2,000 to 3,000 calories for men and 1,600 to 2,400 calories for women.
You must consume more calories than your total energy expenditure (TDEE) to gain weight.
Generally, a healthy weight gain is between 0.5 and 1 pound per week, meaning you must eat 250 to 500 calories daily.
Several factors, including your basal metabolism, metabolic response to food, physical activity, and physiological state, determine your TDEE.
- You can calculate your basal metabolism using the Mifflin-St. Jeor equation in a BMR calculator
- Then, you can learn about your maintenance calories by adding activity levels with BMR.
- Once you have determined your daily caloric needs, you must consume excess calories to gain weight.
- Typically, you require approximately 3850 kcal to gain 0.5 kg or 1.1 lbs weekly.
- This means consuming an additional 550 kcal daily should result in a weight gain of 0.5 kg (1.1 lbs) within a week.
If you haven’t already, refer to our weight gain calorie calculator. It estimates your daily energy expenditure, giving you a more profound understanding of how many calories you must consume daily to gain weight.

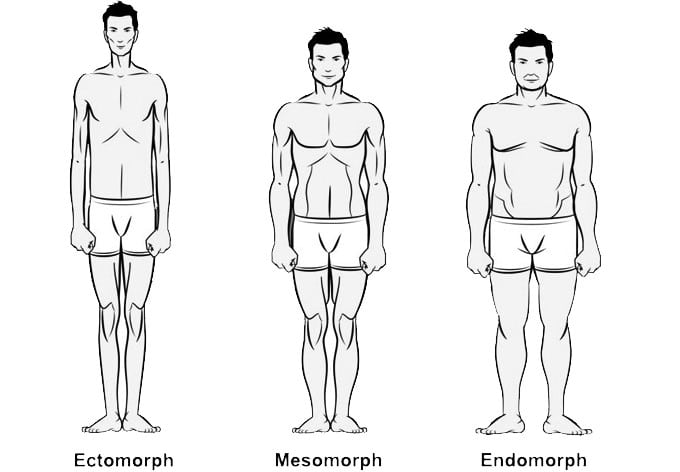
Macronutrient Ratios For Weight Gain
To gain lean muscle mass, you should consume more protein calories. Mike Roussell recommends the following baseline macronutrient ratios.
Note that these ratios are based on the overall percentage of calories consumed.
| Body Type | Fat % | Carbohydrate % | Protein % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ectomorph (skinny) | 20-30% | 50-60% | 20-30% |
| Mesomorph (muscular & athletic) | 15-25% | 40-50% | 30-40% |
| Endomorph (broad & thick) | 25-35% | 30-40% | 30-40% |
It is important to note that the ratios presented are general guidelines and may require adjustment based on your specific needs and objectives.
FAQs
How can I gain weight healthily?
To gain weight healthily, it is recommended to increase calorie intake gradually and focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods such as lean protein, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Resistance training can also help build muscle mass.
How much weight can I realistically expect to gain per week?
A healthy weight gain is between 0.5 and 1 pound per week. This can vary based on individual factors such as age, gender, height, weight, and level of physical activity.
How do you calculate weight gain?
To calculate weight gain, determine the total caloric surplus required to achieve your weight goal. Calculate your daily caloric needs to promote weight gain, and then add an appropriate surplus of calories.
How much does it take to gain 1 kg?
It takes about 7,700 calories to gain 1 kg of body weight. This means that if you eat 7,700 calories more than you burn each week, you will gain about 1 kg of weight.
Eating a healthy diet rich in calories is essential if you are trying to gain weight. You should also exercise regularly, as this will help you build muscle.
Can I gain 5 kg in a month?
It is possible to gain 5 kg in a month, but it is not recommended. The rapid gain of weight can result in health issues such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
A safe and healthy rate of weight gain is 1-2 pounds (0.45-0.91 kg) per week. This means you would gain about 5 kg in 12 weeks or 3 months.
How many kg should I gain?
A good starting point is gaining 1-2 pounds (0.45-0.91 kg) weekly. It is also essential to be patient and realistic when gaining weight. It takes time to see results, so don’t get discouraged if you don’t see changes immediately.
What is the maximum weight gain per month?
The maximum safe monthly weight gain is 2 pounds (0.91 kg) for women and 3 pounds (1.36 kg) for men. Any more than this, you risk gaining too much fat, which can lead to health problems.
Rapid weight gain beyond this range can be unhealthy and may lead to issues like metabolic disturbances or nutrient imbalances. Focusing on gradual and sustainable weight gain is essential for long-term health and well-being.
Sources
- How much protein you need everyday? Harvard Health Publishing, Harvard Medical School. https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/how-much-protein-do-you-need-every-day-201506188096
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2015 – 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 8th Edition. December 2015.
- Mifflin MD, St Jeor ST, Hill LA, Scott BJ, Daugherty SA, Koh YO. “A new predictive equation for resting energy expenditure in healthy individuals“ The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (February 1990).
- Prevalence of Underweight Among Adults Aged 20 and Over: United States, 1960–1962 Through 2017–2018.
- Nathaniel F Watson, Kathryn Paige Harden, Dedra Buchwald, Michael V Vitiello, Allan I Pack, David S Weigle, Jack Goldberg Sleep duration and body mass index in twins: a gene-environment interaction.

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.

This weight gain calculator is super helpful! I never realized how important it is to know my calorie requirements. It’s great that it breaks down the numbers so clearly. I’m excited to start tracking my intake and seeing results! Thanks for this valuable resource!
This calculator is really helpful! I’ve always struggled with knowing how many calories I need to gain weight effectively. The step-by-step guide made it easy to understand. Can’t wait to start my weight gain journey with this tool!
Ads are a major problem when using social media. But Honista blocks all these ads, so we can browse ads-free. Ads will not disturb you while using this app, which is a useful feature of the Honista app download.
Really helpful calculator! I’ve always wondered how many calories needed for healthy weight gain, especially when combining app-based tracking and fitness wearables.