Grip strength is the ability of your hands and forearms muscles to generate force (crushing power) and maintain a secure hold on objects. Poor grip strength can make it hard to hold on weights and cause injuries.
A strong grip is essential for everyday tasks like lifting boxes, moving furniture, cooking, and sports such as cricket, golf, tennis, and rugby. It is also important for weightlifting and strength training.
Don’t worry. This guide will assist you in strengthening your grip, no matter what your objective, and provide you with highly effective exercises.

- How To Train For Grip Strength
- 1. Focus on Improving Muscular Strength
- 2. Neural Adaptation
- 3. Improve Wrist Mobility
- 4. Train For All Types of Grip Strength
- 5. Hand Size and Structure
- Best Weighted Grip Strengthening Exercises
- 1. Plate Pinch
- 2. Hand Gripper
- 3. Reverse Curl
- 4. Farmer’s Walk
- 5. Wrist Rollers
- 6. Rope Climber
- 7. Wrist Curl
- 8. Barbell Reverse Wrist Curl
- 9. Fat Grip Barbell Curl
- 10. Barbell Holds
- Bodyweight Exercises To Improve Grip Strength
- 11. Dead Hangs
- 12. Finger Push Up
- 13. Towel Pull-Ups
- 14. Monkey Bar
- 15. Crab Walk
- Best Stretches Exercises for Grip Strength
- 16. Finger Spread (Extension)
- 17. Wrist Flexor Stretch
- 18. Wrist Extensor Stretch
- 19. Wrist Circles
- 20. Supinator Stretch
- 21. Wrist Side to Side
- 22. Rice Gripping
- 23. Clenched Fists
- 24. Tennis Ball squeeze
- 25. Thumb Stretch
- Grip Strengthening Training Routines
- 1. Select No. Of Sets
- 2. Frequency
- 3. Beginner Grip Strength Workout Routine
- Intermediate Grip Strengthening Workout Routine
- Conclusion
- References:
How To Train For Grip Strength
Grip strength can be affected by many factors. Understanding these factors will help you identify areas for improvement and optimize grip strength training.
1. Focus on Improving Muscular Strength
The muscles in your hands, fingers, and forearms are the powerhouses of your grip. Building strength in these muscles through targeted exercises is essential. Think of it like any other muscle group you train – stronger muscles equal a stronger grip.
2. Neural Adaptation
It’s not just about the muscles themselves but how well your brain can communicate with them. This is called neural adaptation.
Consistent practice helps your brain improve how it activates those muscles and leads to better grip strength over time.
3. Improve Wrist Mobility
If your wrists are stiff and immobile, your grip strength will suffer. Good wrist flexibility allows for a wider range of motion and a better grip position on objects. Regular stretching and mobility exercises for your wrists and hands are a must.
4. Train For All Types of Grip Strength
There are four primary gripping forms, each of which requires unique training techniques for muscle groups.
- Crushing Grip: Squeeze or close your hand around an object forcefully, such as when gripping a dumbbell or shaking hands. It primarily engages the muscles of your fingers and palm.
- Pinch grip: Ability to hold or pinch objects using your thumb and fingers, without the support of your palm. Examples include gripping a pen or holding a weight plate between your fingers.
- Support Grip: This is your endurance or how long you can hold onto something. It is crucial for exercises like dead hangs, pull-ups, and hanging from a bar.
- Extension Grip: The action of opening the fingers and thumb away from each other to create a wider hand span.
- Wrist Strength: While not specifically a grip strength, wrist strength works the synergistic muscles involved in grip and maintains a healthy muscle balance in the hands and wrists.
5. Hand Size and Structure
Hand size, finger length, and even bone density are things we’re mostly born with. These factors can naturally influence your grip strength.
But remember, everyone has the potential to improve, regardless of their genetics. Targeted training can help you reach your personal best.
Best Weighted Grip Strengthening Exercises
1. Plate Pinch
The Plate Pinch is a great way to strengthen the muscles in the fingers, hands, and forearms, improving their strength and dexterity.
The plate pinch is like what it sounds like. It is easy to learn and perform; simply hold a single-weight plate with your fingers and thumb.
You can also do the same with two weight plates. Hold them together with your fingers and thumb like you’re pinching something.
Hold this isometric contraction, I try to keep the time it takes to hold the pinch under 20–30 seconds.
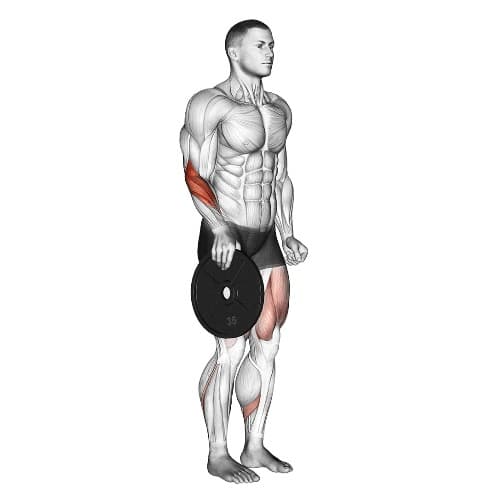
How To Do
- If you’re new to this, start with a lighter plate (5-10 pounds) suitable for more advanced lifters.
- You can always increase your weight as you get stronger.
- Rest the plate on the floor or a bench.
- Wrap your fingers around the edge of the plate, like you’re forming a C shape with your hand. Your thumb should be on one side of the plate, and your fingers should be on the other side.
- Lift the plate off the surface and squeeze your fingers and thumb together as hard as possible.
- You should keep your wrist straight and arm straight by your side, avoiding using your shoulder muscles.
- Hold the pinch for 10–20 seconds, or as long as possible with good form.
- Rest for a moment, then repeat with the other hand. Try to do 3-4 sets.
2. Hand Gripper
Hand gripper exercises are specifically designed to target forearm and improve grip strength. They engage the muscles of the hands, fingers, and forearms. It enhances the strength of grip and hand dexterity.
Hand grippers are compact and portable, making them convenient for use anywhere, whether at home, the office, or while traveling.
They provide a quick and effective way to work on grip strength without requiring a full gym setup.

How To Do
- Choose a hand gripper with an appropriate resistance level.
- Beginners may start with a lower resistance gripper.
- Hold the hand gripper in one hand, ensuring a firm grip on the handles.
- Squeeze the handles together using your fingers and thumb, applying steady and controlled force.
- Hold the gripper in the squeezed position for a few seconds,
- Then slowly release it back to the starting position.
3. Reverse Curl
The barbell reverse curl is a non-negotiable component of a barbell arm workout that primarily targets the muscles of the forearm, particularly the brachioradialis.
This helps make your wrists stronger and more flexible. This is helpful for doing things like turning, turning, and controlling things with your hands and wrists.
Other ways to do reverse curl strengthen your grip and build up forearm mass.
- Dumbbell Reverse Curl
- Cable Reverse Curl
- One Arm Reverse Curl
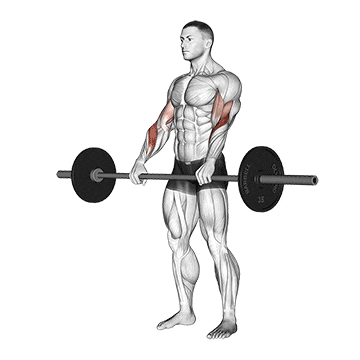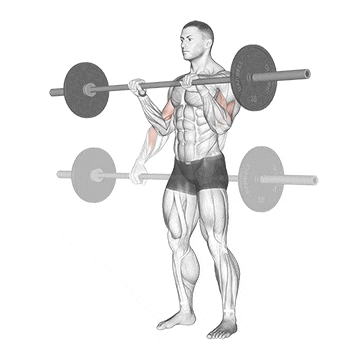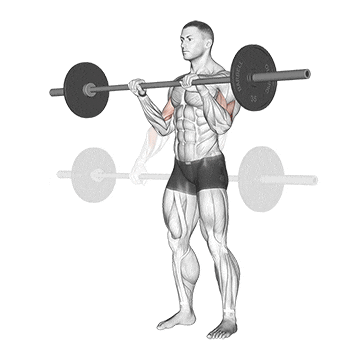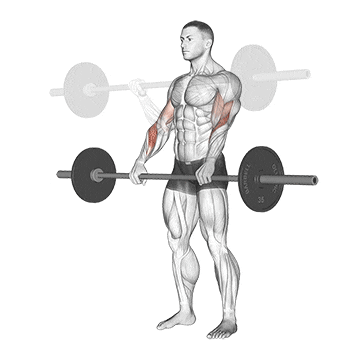
How To Do
- Grab the bar with a shoulder width grip with your hands on top of the bar (pronated grip)
- Curl the bar up to shoulder level by bending your elbows.
- Lower the bar back down to the arms’ extended position.
- Repeat for desired reps.
4. Farmer’s Walk
The farmer’s walk, also called the farmer’s carry, is a strength and conditioning exercise in which you hold a heavy load in each hand while walking for a designated distance.
It is good for your entire body. It strengthens the muscles in your biceps, triceps, forearms, shoulders, upper back, trapezius, quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, lower back, obliques, transverse abdominis, and rectus abdominis.
It is relatively simple to perform, simply hold a pair of heavy dumbbells at your sides and walk with them for a set distance or time.
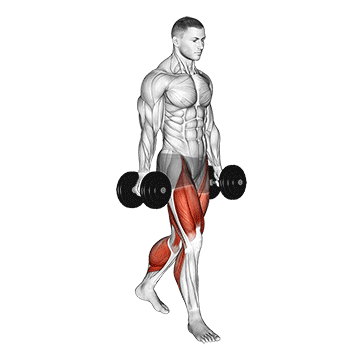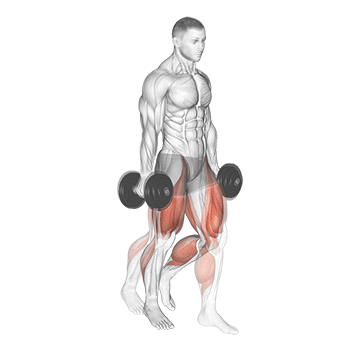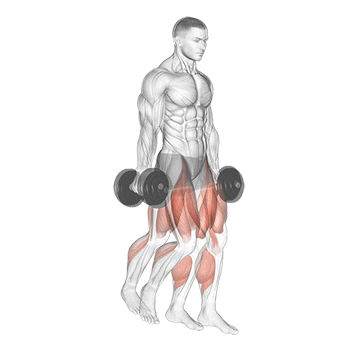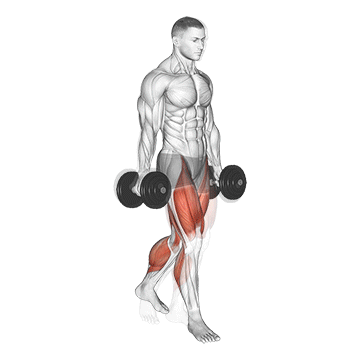
How To Do
- Start by selecting a pair of heavy dumbbells, which are challenging but still manageable to hold.
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart and your knees slightly bent.
- Take a dumbbell in each hand and let them hang at your sides.
- Keep your back straight and your core engaged throughout the exercise.
- Begin walking forward, keeping a steady pace and maintaining good form.
- Walk for the desired distance or time, then release the weight and rest for a moment before repeating.
5. Wrist Rollers
The wrist roller has a cylindrical handle and a rope attached to the center exercise. At the other end of the rope, weights are attached. You roll the device to work out the muscles in your wrists and forearms.
Rotating the wrist roller in both directions ensures balanced development of both forearm flexors (muscles responsible for wrist flexion) and extensors (muscles responsible for wrist extension).
Rolling motion strengthens the supporting muscles and tendons in the wrist, improving joint stability and range of motion.
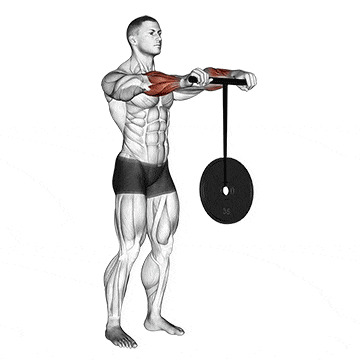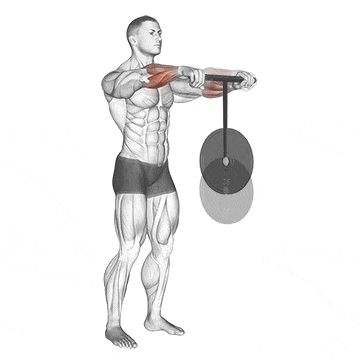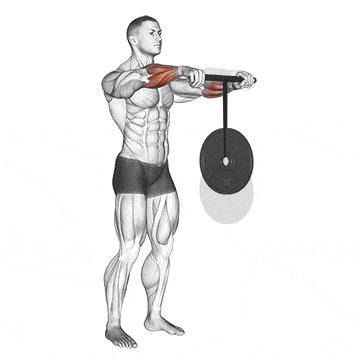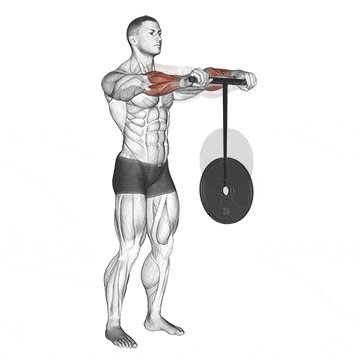
How To Do
- Start by attaching the desired weight to the end of the rope or cord.
- Hold the bar or rod with both hands, palms facing down.
- Keep your elbows slightly bent as you extend your arms in front of you.
- To begin rolling the wrist roller, move your hands forward and let the weight go up toward the bar.
- Continue to roll until the weight reaches the bar
- Then, turn around and roll it back up to where you started.
6. Rope Climber
Rope climbs require you to use your arms and upper body strength to climb a vertical rope while using your legs for support and balance.
It is a full-body exercise that primarily targets the muscles in the upper body, including the forearms, back, and shoulders.
Since rope climbs rely heavily on gripping the rope, they effectively improve grip strength and endurance.
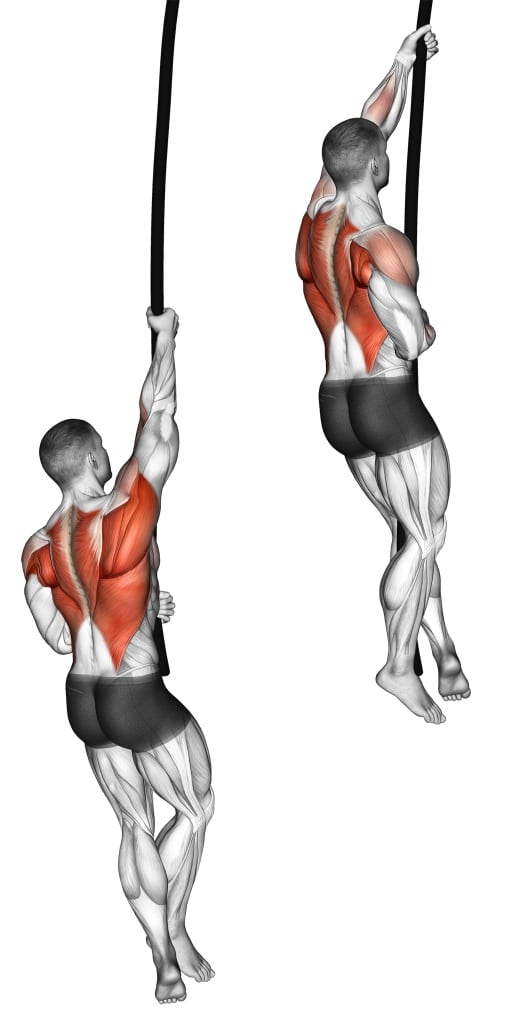
How To Do
- First, make sure you have a strong rope that can hold your weight.
- Reach up and grab the rope with both hands.
- You can begin the climb by using your arms to pull yourself upward while simultaneously pushing with your legs.
- Use a hand-over-hand technique, alternating your hands and legs to move up the rope.
- Maintain a strong grip on the rope and continue climbing until you reach your desired height or the top.
- To descend, either reverse the climbing motion or use a controlled descent technique, such as wrapping your legs around the rope and sliding down.
7. Wrist Curl
Barbell wrist curls are an isolation exercise that targets the flexor muscles in your forearms, the muscles responsible for gripping and wrist flexion. This exercise is great for improving grip strength and forearm size and definition.
According to the study, a 12-week periodized forearm training program can enhance wrist and forearm strength, as well as bat-end velocity, in baseball players.
Other ways to do wrist curl to improve forearm size and grip strength
- Dumbbell Wrist Curl
- Cable Wrist Curl
- Single Arm Wrist Curl
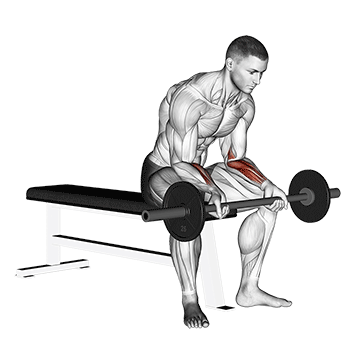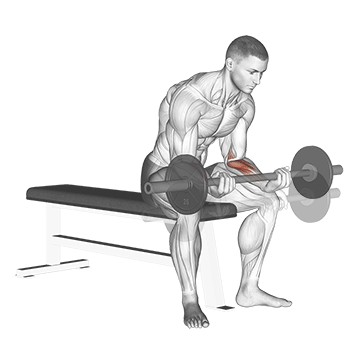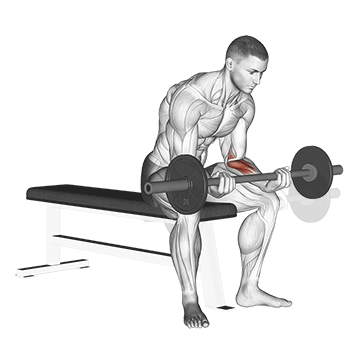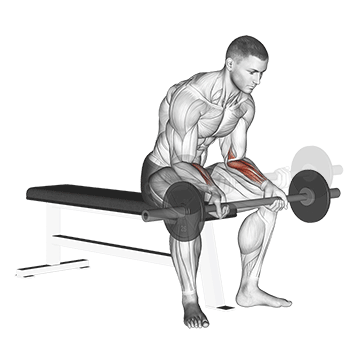
How To Do
- Grasp the barbell with an underhand grip.
- Rest your forearms on the bench with your palms facing up and the backs of your wrists resting on the bench/Quads.
- Slowly lift the barbell by flexing your wrists, keeping your forearms flat on the bench.
- Pause at the top of the movement, then slowly lower the barbell back down to the starting position.
8. Barbell Reverse Wrist Curl
Barbell Reverse wrist curls are similar to regular wrist curls, but with a reversed hand position. It primarily targets the forearm muscles, particularly the brachioradialis and wrist extensors.
Strong extensor muscles contribute to better grip stability and control. This can be beneficial in activities that require a firm grip, such as weightlifting, racket sports, and manual labor.
Other ways to improve forearm size and strength with a reverse wrist curl are:
- Reverse Dumbbell Wrist Curl
- Cable Reverse Wrist Curl
- Single Arm Reverse Wrist Curl
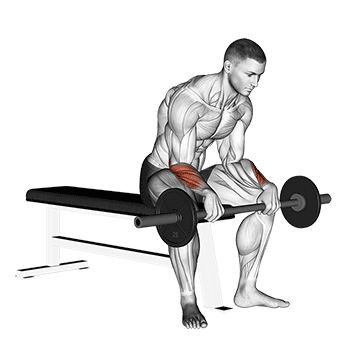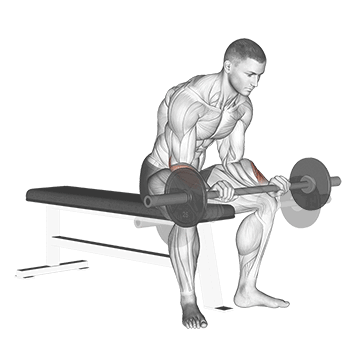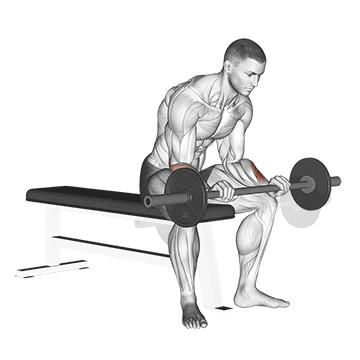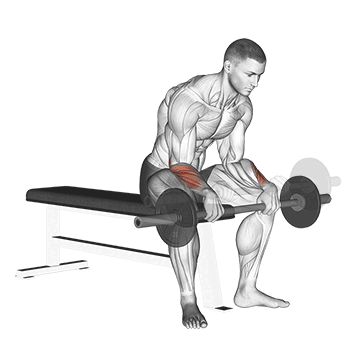
How To Do
- Grab a barbell with an overhand grip.
- Lift the barbell up by flexing your wrists and raising your hands towards your forearms.
- Slowly lower the weight back to the starting position by straightening your wrists.
- Remember that the hand should be fully free to move up and down unhindered.
- Do 12–15 reps and 3–4 sets.
9. Fat Grip Barbell Curl
It is a variation of the traditional bicep curl exercise where a thick grip attachment is added to the barbell.
This modification increases the diameter of the bar, which will challenge your grip strength and activate additional muscles in your forearms.
Fat Grip is one of the greatest investments I’ve ever made. My forearms got bigger by an inch after two months. The only downside is that you only feel them in pulling movements.

How To Do
- Attach the Fat Grip to a regular barbell.
- Hold the barbell with hands shoulder-width apart.
- Exhale, and slowly curl the barbell towards your shoulders.
- Hold for a moment and squeeze your biceps at the top.
- Then, slowly lower the barbell back to the starting position.
10. Barbell Holds
During Barbell holds, you must grip and hold a loaded barbell for a specified duration without any additional movement.
During the hold, the forearm muscles, including the flexors and extensors, are contracted for a long time.
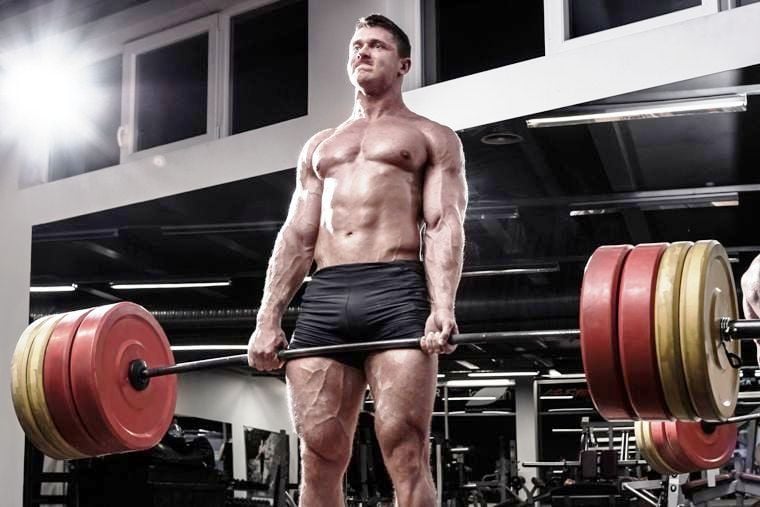

How To Do
- Stand up straight with your feet shoulder-width apart and your knees slightly bent.
- Grip the barbell with an overhand or mixed grip.
- Lift the barbell off the rack or from the ground with your arms fully extended.
- Hold the barbell in a static position for the desired duration.
- Focus on keeping a tight grip and staying engaged throughout the exercise.
- After completing the hold, lower the barbell back to the starting position.
Bodyweight Exercises To Improve Grip Strength
11. Dead Hangs
Dead hangs are a simple yet effective exercise that involves hanging from a bar or any elevated surface with an overhand grip.
The study has shown that dead hanging is an effective exercise to improve grip strength, improving climbing performance.
It also promotes scapular retraction and depression, which helps improve shoulder stability and posture.
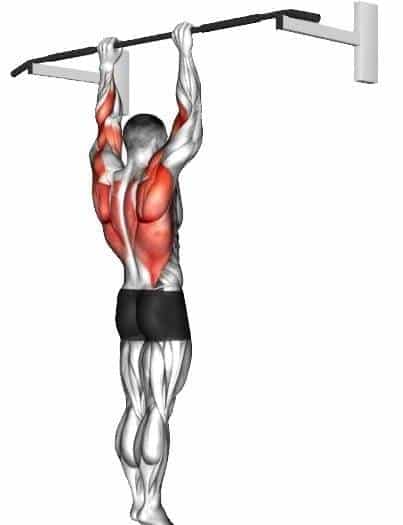
How To Do
- Find a sturdy bar or similar elevated surface that can support your body weight.
- Stand beneath the bar, reach up, and grab it with an overhand grip (palms facing away from you).
- Your hands should be slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Hang freely from the bar, allowing your body to fully extend.
- Hold the position for a designated amount of time.
- Release the grip and lower yourself down gently to finish the exercise.
12. Finger Push Up
Finger push ups emphasize the fingers, hands, and forearms while engaging the chest, shoulders, tricep. It also challenges your core muscles to keep your body balanced.
It’s also an efficient exercise to increase your grip for basketball, bodybuilding, or rock climbing.
It also keeps your wrists straight, making it an excellent way to eliminate wrist pain from the 90-degree bend when your palms are flat on the floor.
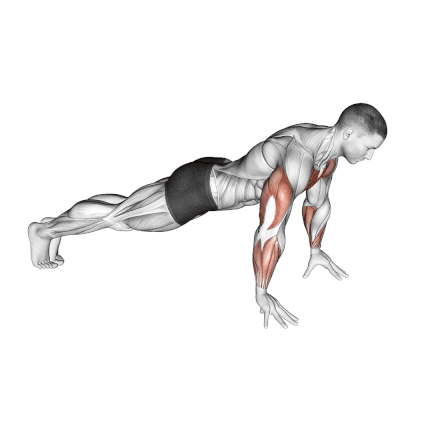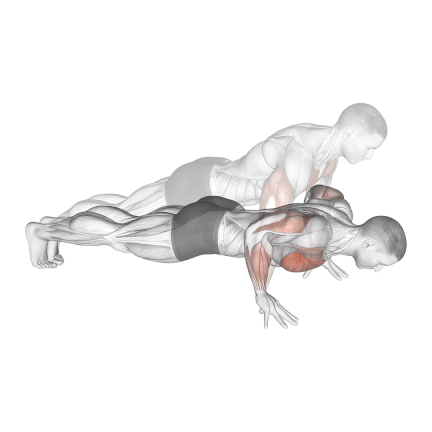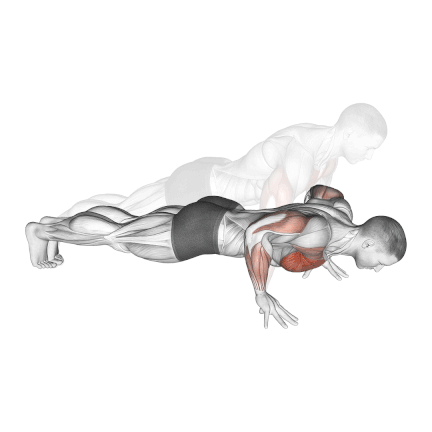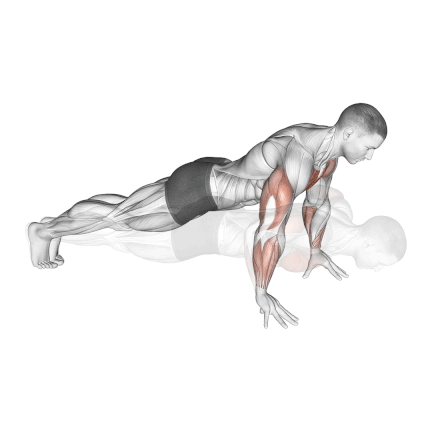
How To Do
- Take a standard push-up position, your fingertips are in contact with the ground.
- Position your fingers so that your fingertips are the only parts of your hand in contact with the ground.
- Engage your core muscles to maintain a straight line from your head to your heels.
- Bend your elbows, keeping them close to your sides, and lower your body until your chest almost touches the ground.
- Push yourself back up by extending your arms and returning to the starting position.
Know More: 20 Different Types Of Push Ups For Mass And Strength
13. Towel Pull-Ups
The Towel pull-ups are a harder version of the traditional pull-up exercise that uses towels as grips.
It helps increase muscle activation and strength in the upper body, especially in the biceps and back, and improves grip strength and endurance.
It places a significant demand on your grip strength, as you need to squeeze the towels tightly to maintain your hold.
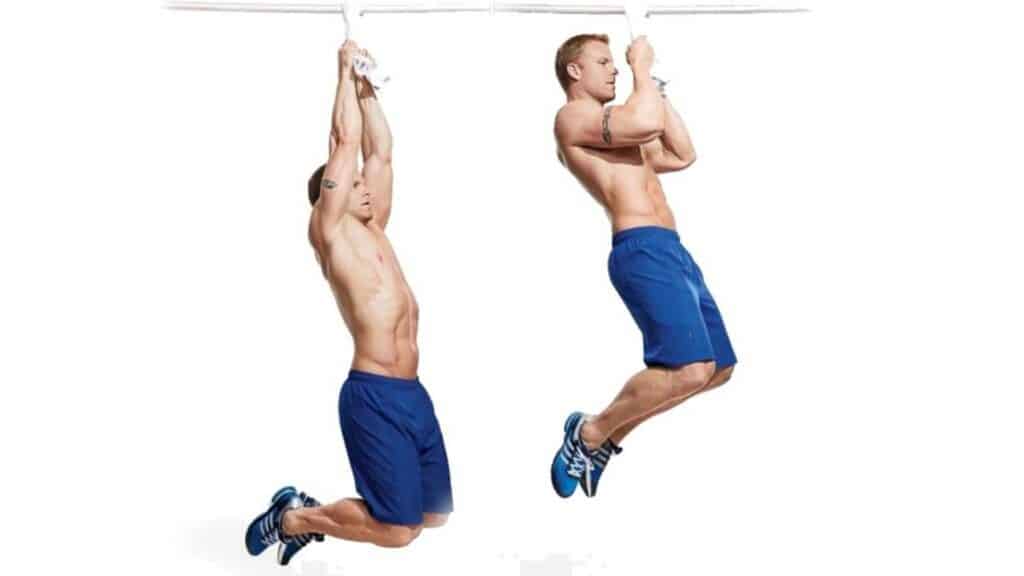

How To Do
- Stand beneath the bar and reach up to grab the ends of the towel.
- Hang freely from the towels, keeping your body straight and engaging your core.
- Bend your elbows and squeeze your shoulder blades together until your chin touches or clears the bar.
- Slowly lower yourself back down to the starting position with control.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
14. Monkey Bar
The monkey bars exercise relies heavily on grip strength, as you need to maintain a firm grip on the bars while traversing. This helps to strengthen the muscles of the hands, fingers, and forearms.
It would be best to use your core muscles to balance and move through the monkey bars. This helps strengthen your core and lower back muscles.
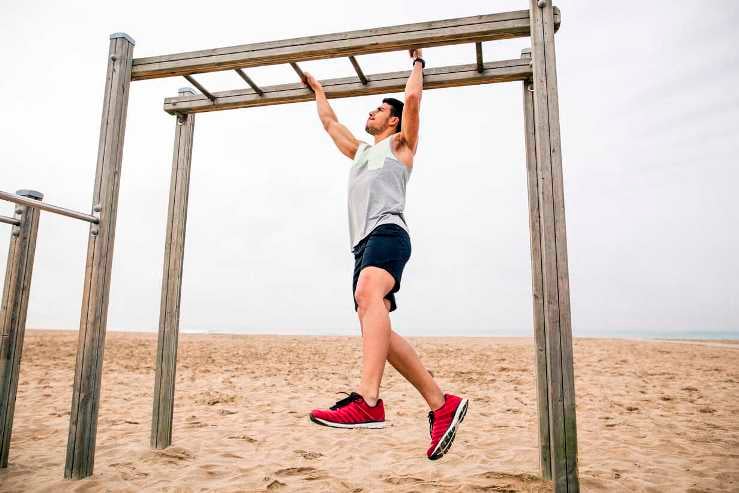

How to Do
- Stand under the bars and ensure enough space for you to hang free.
- Reach up and grab the first bar with your hands slightly wider than your shoulders.
- Start moving your body forward, generating momentum.
- Start by moving your hands one at a time to the next bar.
- Keep swinging and transferring your hands as you go through the bars until you reach the end of the structure, or do the number of repetitions you want to do.
- Once finished, safely dismount from the bars. Ensure a safe landing.
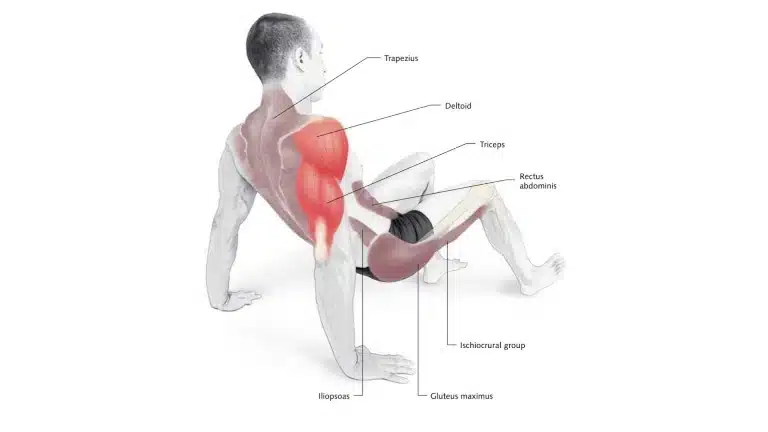
15. Crab Walk
The crab walk is a compound exercise that targets various muscle groups simultaneously. It primarily works the upper body’s muscles, including the arms, shoulders, and core, while also engaging the glutes, quadriceps, and hamstrings.
During the crab walk, supporting your body weight with the arms and hands helps develop upper body and grip strength.
How To Do
- Place your hands behind you, with fingers pointing backward, towards your feet.
- Lift your hips off the ground, supporting your weight with your hands and feet. Your body should resemble a tabletop position.
- Begin by stepping your left hand and right foot to the side, followed by your right hand and left foot.
- Continue moving in the crab walk pattern for a set distance or time.
Best Stretches Exercises for Grip Strength
To strengthen your grip, you can do different stretching exercises. These stretches can help you become more flexible and move more freely, making it easier to hold objects.
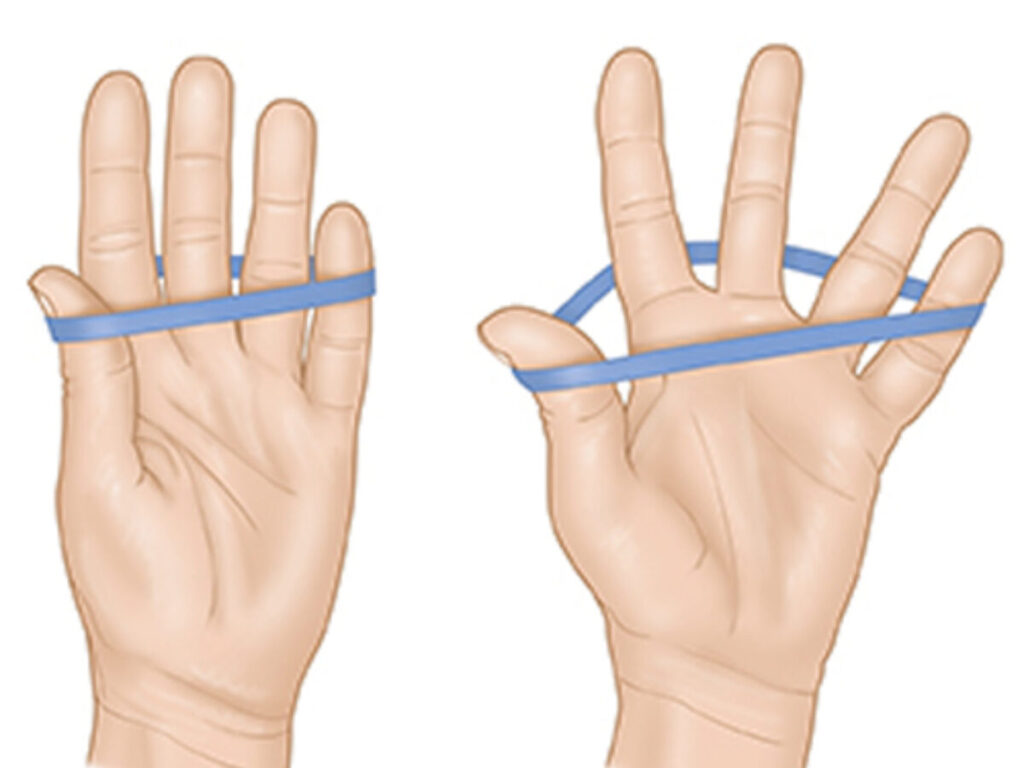
16. Finger Spread (Extension)
This might sound basic, but trust me, it packs some serious benefits for your hand health and grip strength.
Think of this as giving your fingers a wider range of motion. This can be especially helpful if you spend a lot of time typing, gripping tools, or playing instruments. Improved mobility means better finger control and dexterity.
This stretch helps to stretch the muscles in your fingers. To do this stretch, spread your fingers as wide as you can and hold for 30 seconds.
17. Wrist Flexor Stretch
Regular stretching of the wrist flexors can enhance grip strength and endurance, reduce finger flexor muscle tightness, and improve joint health.
Stretching the finger flexors can make it easier to reach more notes on a piano or handle small components when assembling electronics.
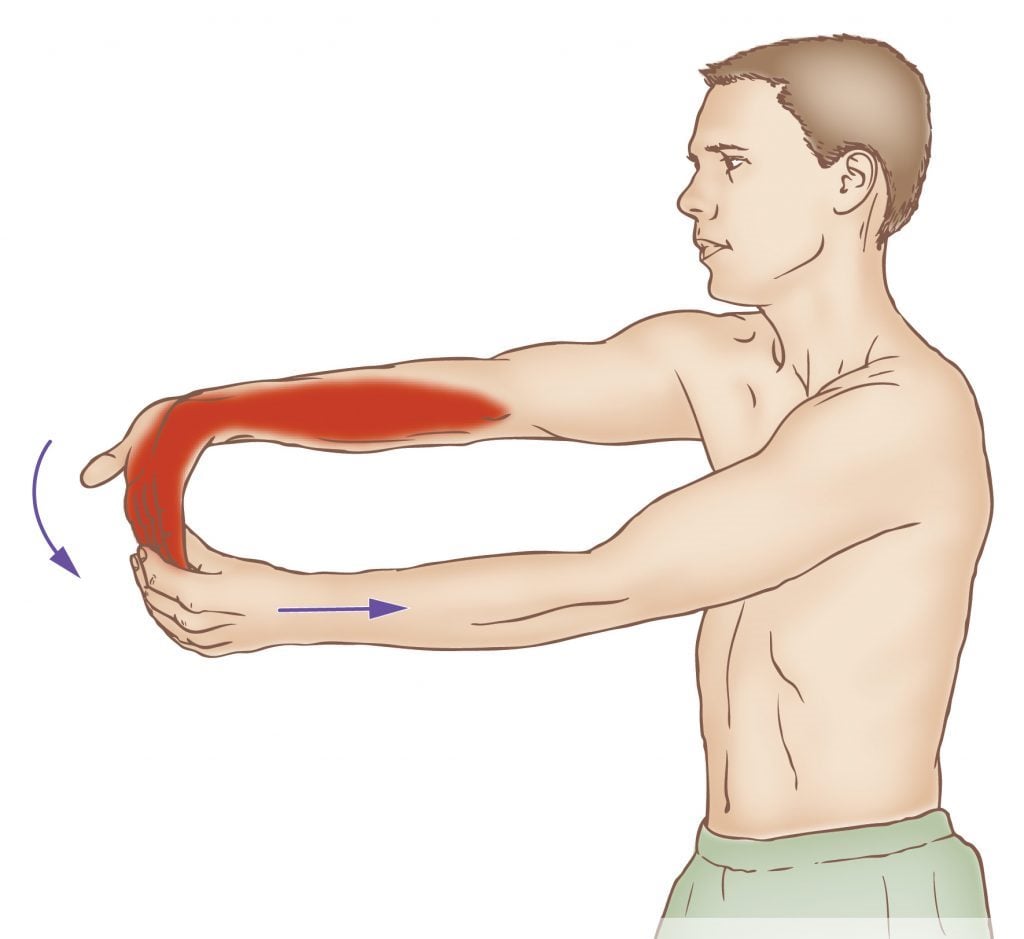
- Extend one arm in front of you, palm facing away.
- Use the other hand to pull back the fingers, stretching the muscles in the palm and fingers.
- Hold for 15-30 seconds and repeat on the other hand.
18. Wrist Extensor Stretch
This stretch specifically targets the extensor muscles, improving their flexibility and range of motion. This improves the ability to open your hand and extend your fingers fully.
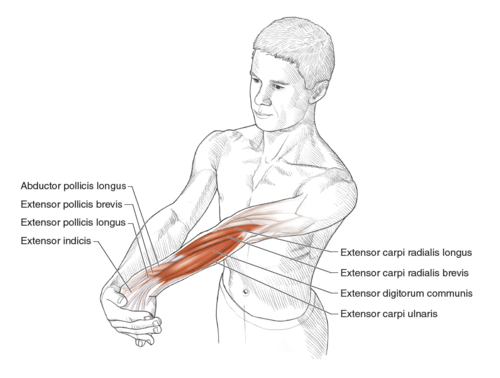
- Extend one arm in front of you, palm facing toward you.
- Use the other hand to gently bend the fingers backward, feeling a stretch in the top of the hand and fingers.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds and repeat on the other hand.
19. Wrist Circles
It’s easy to think of wrist circles as a quick warm-up, but they’re way more than that. These small movements can greatly affect your wrist health, grip strength, and hand function.
Wrist circles are an excellent way to prepare your wrists for exercise or activity and to help them cool down afterward.
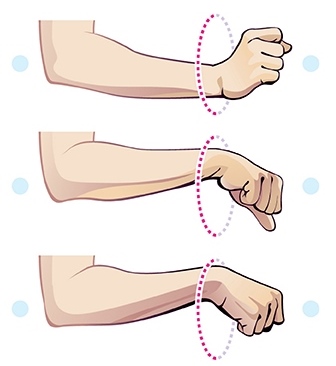
- Stand or sit comfortably with your arms extended in front of you.
- Make circular motions with your wrists, rotating them clockwise and counterclockwise.
- Perform 10-15 circles in each direction.
20. Supinator Stretch
The supinator stretch focuses on one specific motion, supination, to increase your movement capacity and mobility threshold.
- Start with your right palm facing down.
- Using your left hand, help turn the right forearm up, so the palm is facing up by using the pressure of your left hand.
- Then, once you reach your limit, hold the tension for 1 minute and switch hands.
21. Wrist Side to Side
Wrist side-to-side exercises, also called radial and ulnar deviation, are important for keeping the wrist flexible and preventing pain or stiffness.
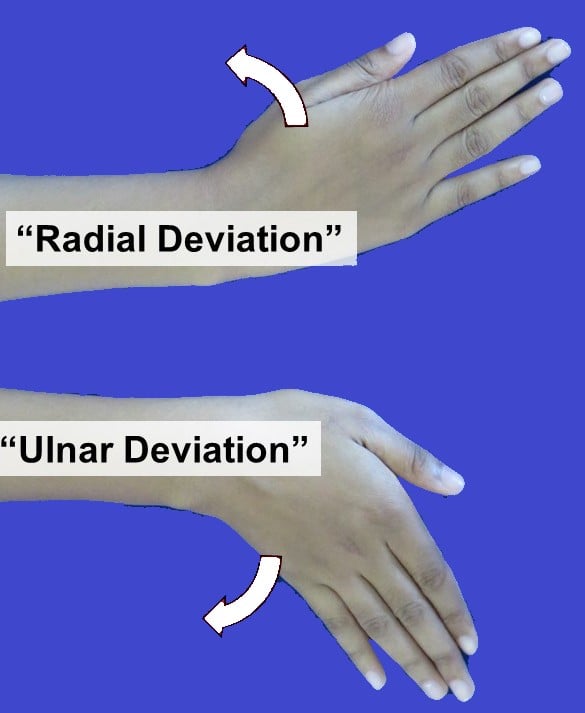
- Extend your arm out in front of you.
- Slowly bend your wrist from side to side, moving your hand toward your thumb (radial deviation) and then toward your pinky (ulnar deviation).
22. Rice Gripping
It might sound strange, but this simple method has unique benefits that go beyond those of traditional grip exercises.
The feeling of the rice grains moving against your skin provides valuable sensory feedback to your hands and fingers. This can improve proprioception (your sense of where your body is in space) and enhance your ability to control and coordinate your grip.
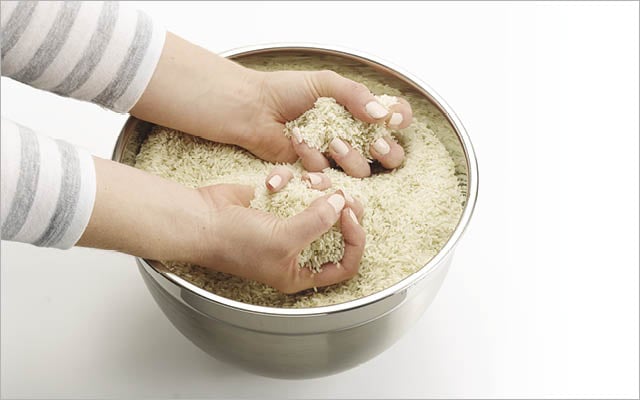

- Fill a bucket or container with uncooked rice.
- Submerge your hand in the rice up to your wrist.
- Perform gripping motions, such as opening and closing your hand, making a fist, or twisting at the wrists.
- Experiment with different movements and grips to target different muscle groups.
23. Clenched Fists
A clenched fist signifies strength, determination, and even defiance. When you clench your fist, you activate a network of muscles and nerves in your hand, forearm, and upper arm. This can help improve coordination, dexterity, and overall hand strength.
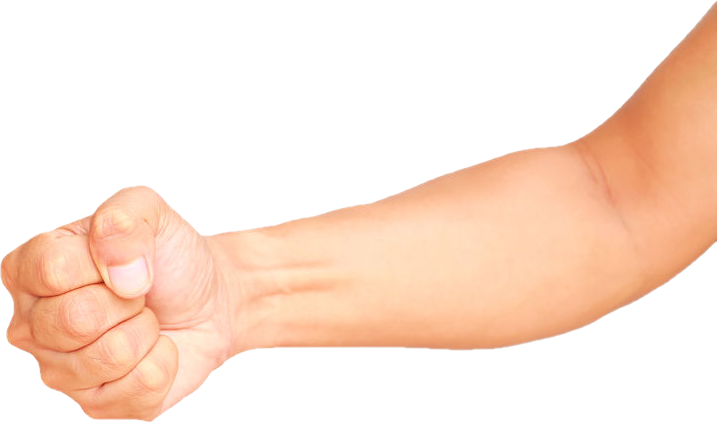

- While seated, place your hands on your things with palms up.
- Close your fists and, with your forearms touching your legs, raise your fists off of your body, bending at the wrist.
- Hold for 10-20 seconds.
24. Tennis Ball squeeze
The tennis ball squeeze is a simple but effective exercise that works your wrist and finger flexors, improves your crush grip, and strengthens and builds endurance in your forearm muscles.
Take a regular tennis ball (or a similar-sized soft rubber ball) and squeeze as hard as possible. Hold for a few seconds, release, and repeat.

25. Thumb Stretch
We often take our thumbs for granted, but they’re incredibly versatile and essential for countless daily tasks. From texting to opening jars to gripping a steering wheel, our thumbs are constantly in motion.
A strong and flexible thumb allows for a greater range of motion and a better distribution of forces across your hand when you’re gripping an object.
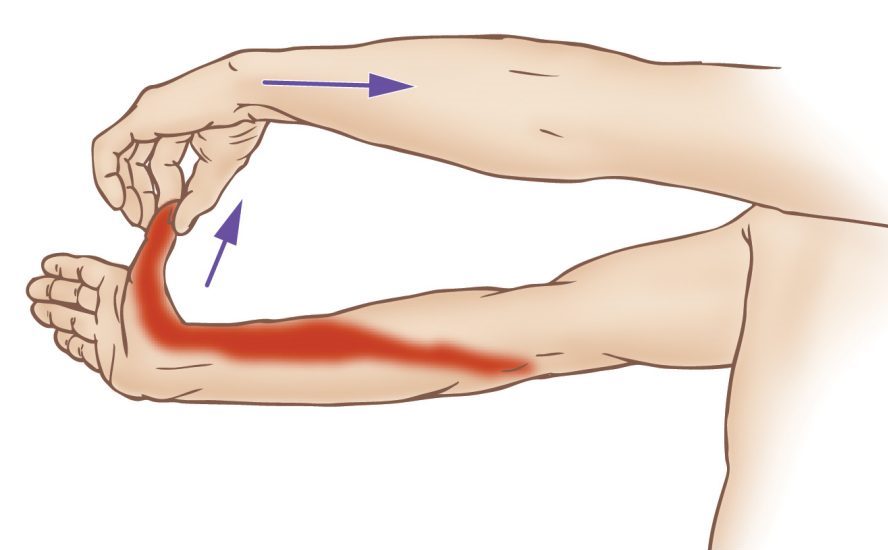
- Gently grasp your thumb with the opposite hand and pull it backward, away from your fingers, until you feel a stretch in the base of your thumb.
- Hold for 15-30 seconds and switch to the other hand.
Grip Strengthening Training Routines
Grip strengthening exercises should be performed at a frequency that is appropriate for your fitness level, goals, and recovery ability.
Nevertheless, there are some general guidelines to help you get started.
1. Select No. Of Sets
- Beginners: Start with 2-3 sets per exercise.
- Intermediate: Aim for 3-4 sets per exercise.
- Advanced: Perform 4-5 sets per exercise.
2. Frequency
- Beginners: Start with 1–2 weekly workouts, allowing ample recovery time between sessions.
- Intermediate: Aim for 2–3 weekly workouts, with at least two days of rest in between.
- Advanced: Perform 2–3 workouts per week, incorporating variety in exercises and intensity levels.
3. Beginner Grip Strength Workout Routine
These grip strength workouts for beginners offer a structured regimen comprising specific exercises, sets, and durations/reps to aid individuals in gradually enhancing their grip strength.
Remember to change the weights, duration, or reps according to your fitness level and increase the intensity over time.
Workout #1
| Exercise | Sets | Duration/Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Farmer’s Carry | 3 | 30 seconds |
| Dead Hangs | 3 | 30 seconds |
| Fingertip Push-Ups (on knees) | 3 | 10 reps |
| Hand Gripper | 3 | 10 closes/hand |
Workout #2
| Exercise | Sets | Duration/Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Dead Hangs | 3 | 30 seconds |
| Plate Pinches | 3 | 1 minute |
| Reverse Grip Dumbbell Curls | 3 | 10 reps |
| Dumbbell Twists | 3 | 10 reps |
Intermediate Grip Strengthening Workout Routine
Workout #1
| Exercise | Sets | Duration/Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Farmer’s Carry | 5 | 30 seconds |
| Plate Pinches | 5 | 1 minute |
| Towel Pull-Ups | 3 | 5 reps |
| Hand Gripper | 3 | 10 closes/hand |
Workout #2
| Exercise | Sets | Duration/Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Dumbbell Twists | 5 | 20 reps |
| Reverse Grip Barbell Curls | 5 | 20 reps |
| Plate Pinches | 5 | 1 minute |
| Dead Hangs | 3 | Till failure |
Conclusion
Grip strength is an essential component of our physical abilities, and it plays a vital role in various activities we engage in every day.
Improving our grip strength offers numerous benefits beyond simply enhancing our ability to grip objects. It can reduce the risk of conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, tendinitis, and arthritis.
Exercises like Farmer walk, Reverse curl, dead hangs, hand gripper training, and plate pinches are good for strengthening the muscles involved in grip.
It is also important to maintain flexibility and mobility in the hands, wrists, and forearms. Stretching exercises like wrist extensions, flexion, finger stretches, and forearm stretches can help keep your muscles strong, avoid accidents, and indirectly boost grip strength.
References:
- Mathiowetz, V., et al. (2004). Grip and Pinch Strength: Norms for 6- to 19-Year-Olds. The American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 58(2), 97-104.
- Stasinopoulos, D., & Johnson, M. I. (2007). Cyriax Physiotherapy for Tennis Elbow/lateral Epicondylitis. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 41(11), 639-642.
- Mark D Peterson. et al Low Normalized Grip Strength is a Biomarker for Cardiometabolic Disease and Physical Disabilities Among U.S. and Chinese Adults. Multicenter Study J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci2017 Oct 12;72(11):1525-1531. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx031.
- Fanchini M, Violette F, Impellizzeri FM, Maffiuletti NA. Differences in climbing-specific strength between boulder and lead rock climbers. J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27:310–314. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182577026 –

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
