Zig Zag Calorie Cycling Calculator
Generate a personalized 7-day calorie shifting plan based on your TDEE and goals
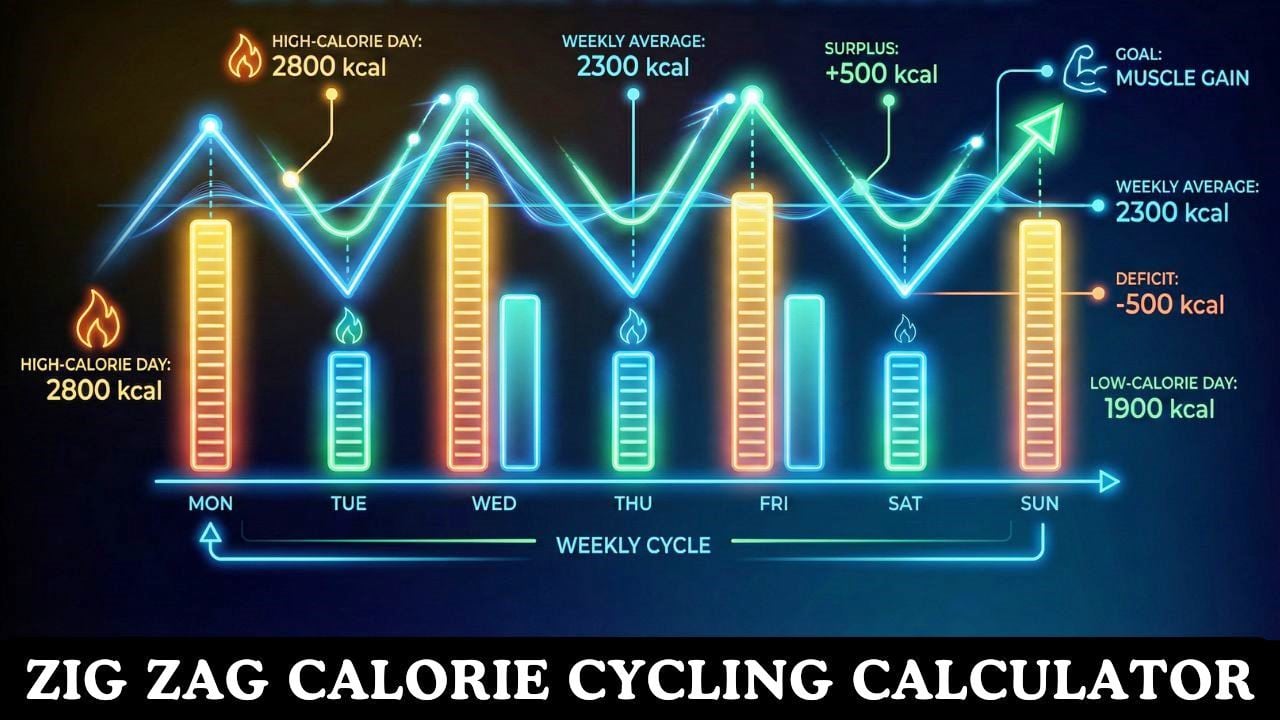
📈 Your Personalized Calorie Cycling Plan
📅 Your 7-Day Calorie & Macro Plan
🥗 Macro Distribution by Day Type
💡 Tips for Successful Calorie Cycling
- Plan high calorie days around your most intense workouts
- Focus on protein intake consistency across all days
- Use high days for social events or when cravings are strongest
- Stay hydrated regardless of calorie intake
- Track your weekly average, not daily fluctuations
What is Zig Zag Calorie Cycling?
Zig zag calorie cycling (also called calorie shifting) is a nutrition strategy where you alternate between higher and lower calorie days throughout the week while maintaining the same weekly average. Instead of eating the same number of calories every day, you strategically vary your intake to potentially avoid metabolic adaptation.
For example, if your target is 1,800 calories per day for gradual fat loss, a calorie cycling approach might have you eating 2,100 calories on high days and 1,500 on low days—but your weekly total remains the same as eating 1,800 daily. This approach is popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts who want more flexibility in their nutrition while staying on track with their goals.
Learn more about the benefits of combining proper nutrition with exercise at Fit Life Regime.
The Science Behind This Calculator
This calculator uses two scientifically validated formulas to determine your calorie needs before creating your cycling plan:
Person: 30-year-old male | 70 kg | 170 cm | Moderately active
BMR: (10 × 70) + (6.25 × 170) – (5 × 30) + 5 = 700 + 1,062.5 – 150 + 5 = 1,618 calories
TDEE: 1,618 × 1.55 = 2,508 calories/day
For fat loss (-500/day): Average target = 2,008 calories/day
High day (+20%): 2,410 cal | Low day (-20%): 1,606 cal
The Mifflin-St Jeor equation is considered the most accurate BMR formula according to research, with an accuracy rate of approximately 80-90% for most individuals when combined with accurate activity factors.
Activity Level Multipliers
Your activity level significantly impacts your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE). Here’s how each level is defined:
| Activity Level | Multiplier | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sedentary | 1.2 | Little or no exercise, desk job |
| Lightly Active | 1.375 | Light exercise 1-3 days/week |
| Moderately Active | 1.55 | Moderate exercise 3-5 days/week |
| Very Active | 1.725 | Hard exercise 6-7 days/week |
| Extra Active | 1.9 | Very hard exercise, physical job |
For best results, be honest about your activity level. Most people overestimate their activity, which can lead to slower progress than expected.
Cycling Pattern Options Explained
This calculator offers 10 preset patterns plus a fully customizable option. Choose based on your training schedule and lifestyle:
| Pattern | Structure | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Classic | 2 high, 2 medium, 3 low days | Balanced approach, good for beginners |
| Weekend Boost | 5 low weekdays, 2 high weekend days | Social flexibility, dining out |
| Alternating | High/low every other day | Consistent training schedule |
| 3 On / 4 Off | 3 high training days, 4 low rest days | 3-day training splits (PPL, Full Body) |
| 5:2 Pattern | 5 moderate days, 2 very low days | Intermittent restriction style |
| Push-Pull | 2 high, 1 med, 2 high, 2 low | Push/Pull/Legs training splits |
| Gradual Rise | Low→high progression through week | Building toward weekend workouts |
| Pyramid | Low→high→low (peak mid-week) | Mid-week intense training |
| Reverse | High→low progression through week | Front-loading weekly energy |
| Custom | You choose each day’s type | Complete flexibility for any schedule |
Benefits of Calorie Cycling
- Psychological Flexibility: High days make sticking to your plan easier long-term
- Social Adaptability: Plan high days around social events or dining out
- Training Alignment: Match higher calories to intense workout days
- Reduced Monotony: Varying intake can feel less restrictive than fixed daily targets
- Potential Metabolic Benefits: Some research suggests varying intake may help maintain metabolic rate
- Hunger Management: Low days may enhance fat utilization while high days satisfy appetite
Combine your calorie cycling plan with a solid home workout routine for optimal results.
Understanding Macro Distribution
This calculator provides complete macro breakdowns (protein, carbs, fats) for each day type. The key principle is keeping protein consistent while varying carbohydrates and fats:
| Macro Preference | Protein | Carbs | Fats | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balanced | 30% | 40% | 30% | General fitness, beginners |
| High Protein | 35% | 35% | 30% | Muscle building, fat loss |
| Lower Carb | 35% | 25% | 40% | Fat loss, insulin sensitivity |
| Higher Carb | 25% | 50% | 25% | Endurance athletes, high activity |
| Keto-Style | 30% | 10% | 60% | Very low carb approach |
Important: Protein remains fixed based on your body weight (1.6-2.2g per kg) regardless of the day type. This ensures muscle preservation during fat loss or optimal growth during muscle building phases. Learn more about muscle recovery and protein timing at Fit Life Regime.
Training Day Alignment
The Training Day Selector feature lets you mark which days you exercise. This helps you:
- Fuel Workouts: Higher calories on training days provide energy for performance
- Support Recovery: Extra carbs post-workout help replenish glycogen stores
- Optimize Fat Loss: Lower calories on rest days when energy needs are reduced
- Visual Planning: See at a glance which days are training vs rest
For effective training programs to pair with your nutrition plan, explore back workouts for strength and shoulder exercises at Fit Life Regime.
How to Use Your Calorie Cycling Plan
- Track Weekly, Not Daily: Focus on your weekly total rather than stressing over daily variations
- Prioritize Protein: Keep protein intake consistent (around 1.6-2.2g per kg bodyweight) across all days
- Schedule Strategically: Align high days with hard training or social events
- Adjust Carbs and Fats: Vary mostly carbohydrates and fats, not protein
- Stay Flexible: You can swap days if needed—just maintain the weekly balance
- Re-evaluate Monthly: Adjust your TDEE as your weight and activity change
Sample Meal Structure by Day Type
| Day Type | Protein | Carbs | Fats | Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Day | Same | Higher | Moderate | Add carbs around training |
| Medium Day | Same | Moderate | Moderate | Balanced macros |
| Low Day | Same | Lower | Moderate | Focus on protein + veggies |
For effective workouts to pair with your nutrition plan, explore leg exercises for strength and chest workouts at Fit Life Regime.
Frequently Asked Questions
Calorie cycling works for fat loss because the fundamental principle remains the same: you need to be in a caloric deficit over time. The cycling aspect doesn’t magically burn more fat, but it can make the deficit more sustainable by providing psychological relief on high days and potentially helping maintain metabolic rate. What matters most is your weekly average intake relative to your expenditure.
Start with “Moderate” (±20%) if you’re new to calorie cycling. This provides noticeable variation without extreme swings. If you have a higher calorie target (2,500+), you can handle “Aggressive” variance more easily. Choose “Mild” if you prefer consistency, or “Extreme” if you respond well to feast/fast patterns. Adjust based on how you feel after 2-3 weeks.
Many people find it beneficial to schedule high calorie days on their most intense training days, particularly for strength training or HIIT. The extra calories (especially carbohydrates) can fuel performance and support recovery. However, this isn’t mandatory—the weekly total matters more than day-to-day alignment. Choose what fits your lifestyle best.
Absolutely! The plan is a guideline, not a rigid rule. If a social event falls on a scheduled low day, swap it with a high day earlier or later in the week. The key is maintaining your weekly calorie target. Just avoid having multiple high days consecutively, as this defeats the purpose of cycling and can lead to overeating.
The Mifflin-St Jeor formula used in this calculator is considered the most accurate available, typically within ±10% for most individuals. However, TDEE varies based on genetics, body composition, and daily activity variations. Treat the result as a starting point, then adjust based on real-world results over 2-3 weeks. If you’re not seeing expected changes, adjust by 100-200 calories.

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
