The Bayesian curl is a must-try exercise to improve your bicep training. This challenging move targets the biceps and also engages forearm muscle groups.
In the Bayesian Curl, your arm is positioned behind your body at the start, which elongates the biceps and places them under a stretch. This stretch reflex, coupled with the curling motion, activates more muscle fibers, particularly in the long head of the biceps
Menno Henselmans originally popularized this exercise. We can modify it to emphasize the long head and create more striking peaks.
The behind-the-back cable curl provides several benefits, including increased muscle activation in the biceps and forearms. It also helps develop grip strength and can be an effective exercise for addressing muscle imbalances.
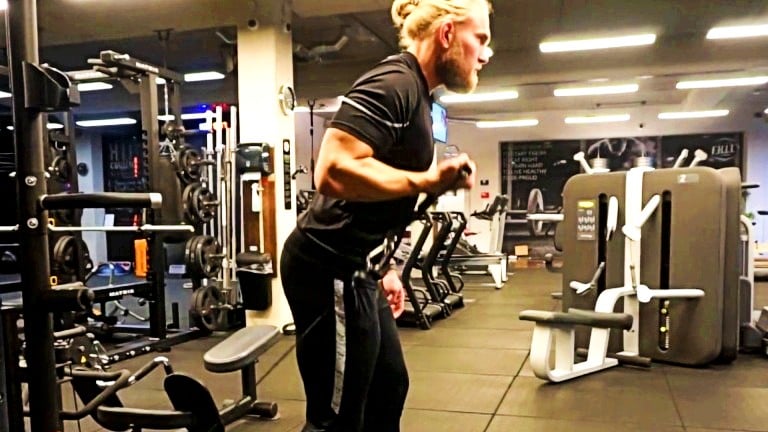

Bayesian Curl Muscles Worked
- The Bayesian curl primarily targets the biceps brachii muscle in the upper arms.
- Additionally, it also engages the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles.
- Some other muscles worked or played stabilizer muscles, including your Obliques and Rectus abdominis.
How To Do Bayesian Curl
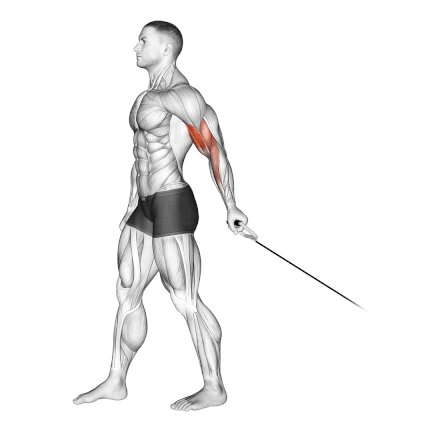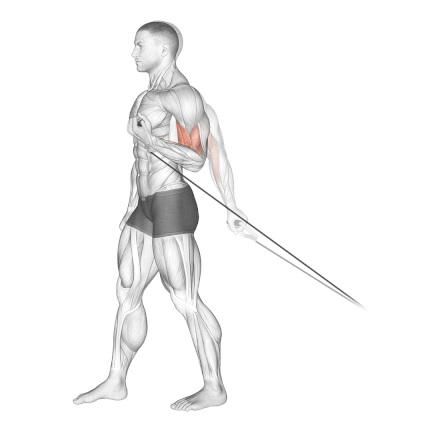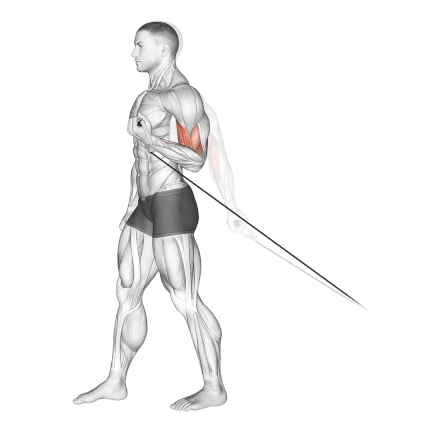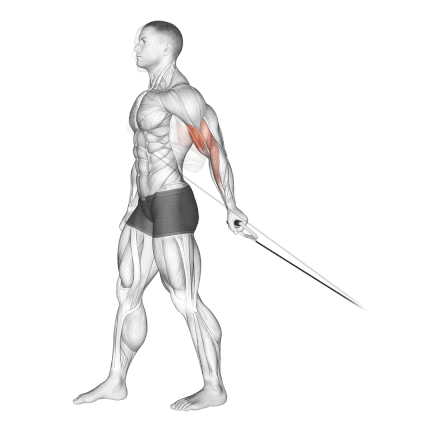
- Stand facing away from the cable machine with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Adjust the cable pulley to a low position and attach a single handle or a D-handle to the cable.
- Reach behind your back with the same-side arm and grasp the handle with an underhand grip.
- Keep your elbow close to your side and extend your arm fully downward.
- Engage your core for stability.
- Exhale and curl the cable handle up towards your shoulder.
- Squeeze your biceps at the top of the movement and hold briefly.
- Slowly lower the cable handle back to the starting position while inhaling.
- Repeat the movement for the desired number of repetitions.
- Switch arms and repeat the exercise on the other side.
Tips and Proper Form
- Avoid letting the weight drag your elbow back. Keep your elbow at your side to maintain tension on your biceps throughout the curl.
- When you curl, don’t let your elbows move forward or backward. Keep them locked in position by your sides.
- Avoid cheating or skimping on the range of motion (ROM). Focus on achieving a good stretch at the bottom and a strong contraction at the top of the movement.
- Engage your core muscles. This helps stabilize your torso and maintain proper alignment.
- Avoid using momentum to lift the weight. Instead, perform the curl in a slow and controlled manner.
- Ensuring a secure grip without excessive tension or strain in your hands and wrists.
- Keep your upper body upright and avoid leaning too forward.
- Inhale during the lowering phase and exhale during the lifting phase of the curl.
- Beginners do 3 sets per exercise; Intermediate: Aim for 3-4 sets per exercise; and advanced, do 3-5 sets per exercise.
- For muscle growth and hypertrophy, do 8-12 reps per set, and for endurance-focused training, higher reps (15+) with lighter weights may be required.
FAQs
Are Bayesian curls the same as incline curls?
No, Bayesian curls and incline curls are not the same exercise.
Bayesian cable curls are done with a cable machine that is placed behind your body. You grasp the handle and curl it upward towards your shoulders while keeping your elbows stationary.
Incline curls, on the other hand, are performed on an incline bench. You sit or lie on the bench with your upper arms resting on the incline, then curl weights.
Can I use other equipment besides a cable machine for Bayesian curls?
Yes, if a cable machine is not available, you can perform Bayesian curl with resistance band.
References:
- Staudenmann D, Taube W. Brachialis muscle activity can be assessed with surface electromyography. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 2015;25(2):199-204. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2014.11.003
- Schoenfeld, Brad J.1; Ogborn, Dan I.2; Vigotsky, Andrew D.3; Franchi, Martino V.4; Krieger, James W.5. Hypertrophic Effects of Concentric vs. Eccentric Muscle Actions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 31(9):p 2599-2608, September 2017. | DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001983

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
