During my 10+ years fitness journey, I tested many quad exercises, analysed the research, and worked with many.
The truth is that most people waste time on ineffective movements while ignoring the exercises that actually build impressive quads.
In this guide, I share the 20 quad exercises that consistently outperform everything else for strength and hypertrophy.
These aren’t random picks—they’re backed by EMG studies showing maximum quadriceps activation and real-world results from serious lifters.
Here’s what makes these exercises different:
- They target all four quadriceps muscles (vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, and rectus femoris)
- They allow progressive overload—the proven key to muscle growth
- They work for beginners and advanced lifters alike
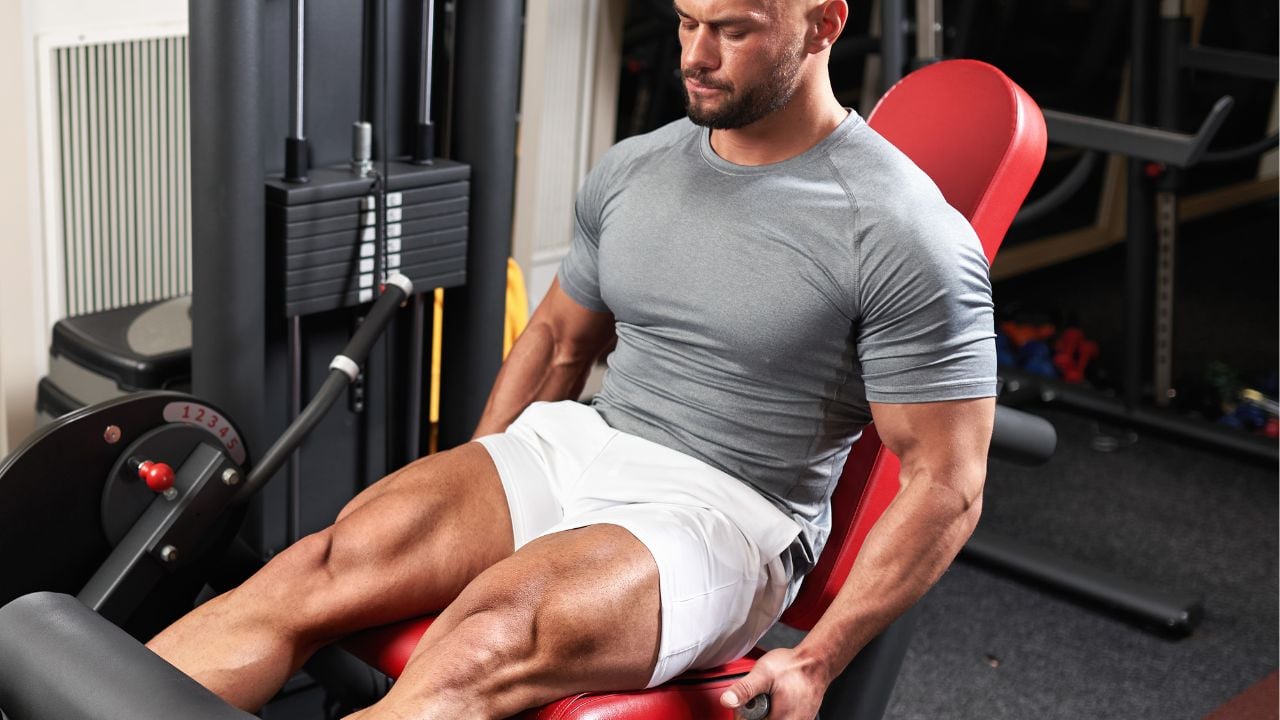

- 20 Best Exercises To Build Bigger Quads
- 1. Bodyweight Squat
- 2. Bodyweight Sumo Squat
- 3. Jump Squat
- 4. Sissy Squat
- 6. Resistance Band Split Squat
- 6. Dumbbell Squat
- 7. Dumbbell Split Squat
- 8. Dumbbell Sumo Squat
- 9. Dumbbell Step Up
- 10. Barbell Squat
- 11. Front Squat
- 12. Barbell Split Squat
- 13. Zercher Squat
- 14. Side Lunge
- 15. Jefferson Squat
- 16. Barbell Box Squat
- 17. Leg Press
- 18. Leg Extension
- 19. Hack Squat
- 20. Smith Machine Squat
- What Are the Quadriceps Muscles
- How To Build Quad Muscle Mass
- 1. Do Plenty Of Squats And Lunges
- 2. Go Heavy
- 3. Challenge Yourself With Drop Sets And Supersets
- 4. Follow Quad Training Weekly Volume, Sets And Reps
- 5. Beginner Quad Workout Plan
- References
20 Best Exercises To Build Bigger Quads
Let’s explore some excellent exercises to strengthen your quads. We’ll explore a mix of workouts using different kinds of fitness equipment and some great bodyweight exercises you can easily do at home.
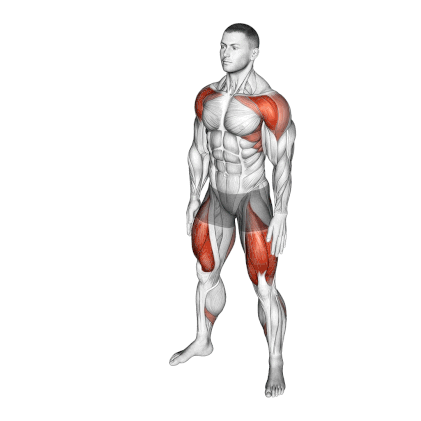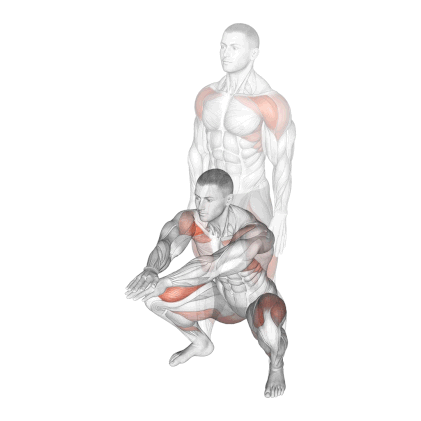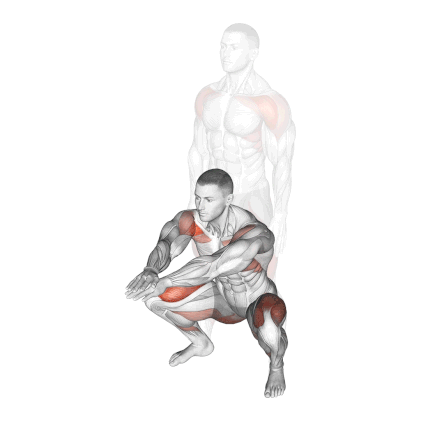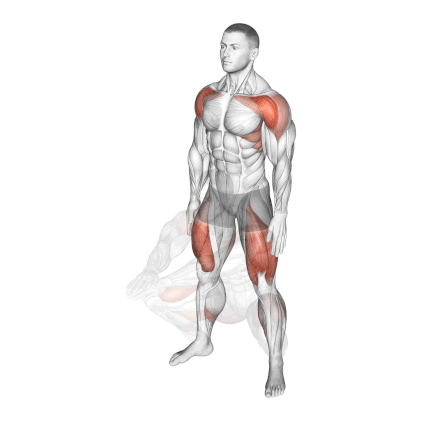
1. Bodyweight Squat
Bodyweight squats are among the best quad exercises to build mass and strength in your legs. You can perform it virtually anywhere, with no equipment and limited space.
It is a highly functional movement that works the major muscles of the legs. Beginners need to learn the bodyweight squat before progressing to weighted squats.
If you can’t correctly squat your bodyweight, adding extra weight just worsens things on top of a weak base.
Bodyweight squats can be executed in various ways.
- Jump Squats
- Pistol Squats
- Bulgarian Split Squats
- Wall Squat
- Squat Jumps with Rotation
How To Do
- Stand with your feet roughly shoulder-width apart. You can point your toes out 5 to 15 degrees. Find the angle that feels best for your hips and knees.
- Keep your chest up and shoulders back. To balance, you can extend your arms straight in front, cross them over your chest, or place them on your hips.
- Take a deep breath, engage your core, and push your hips back while bending your knees. Imagine you are sitting back in a chair that’s just behind you.
- Lower your body down in a controlled manner. Keep your torso relatively upright—don’t let your chest collapse forward.
- Make sure you keep your back straight and your spine neutral.
- Descend until your thighs are parallel to the floor, or even lower if your mobility allows. Don’t sacrifice form for depth.
- Exhale as you powerfully drive through your entire foot (don’t lift your heels or roll onto your toes). Push the floor away. Extend your knees and hips simultaneously, returning to the standing position.
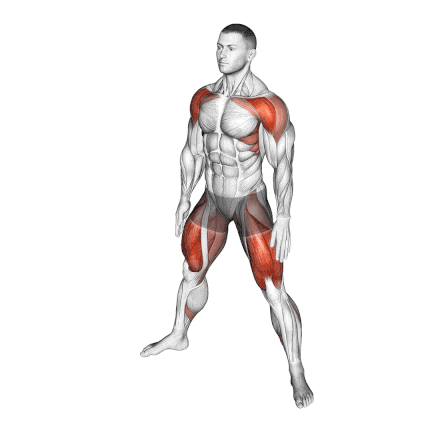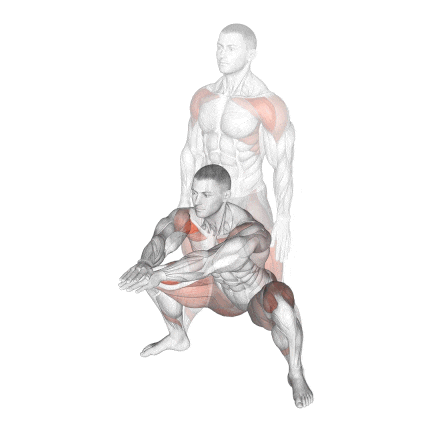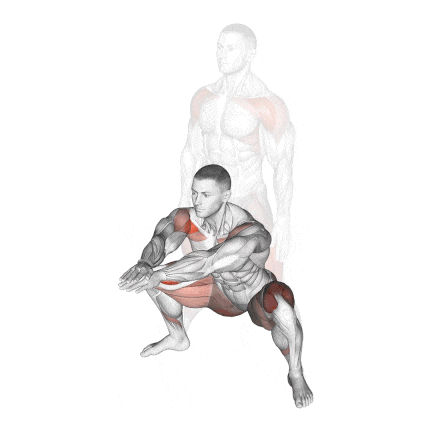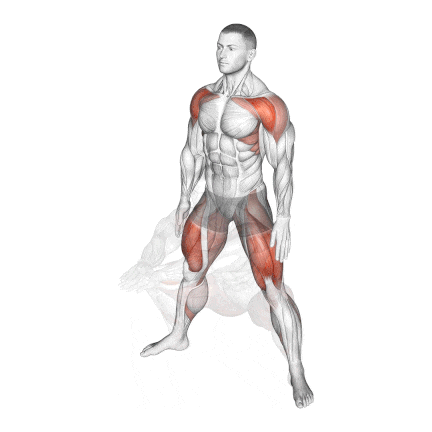
2. Bodyweight Sumo Squat
Regular squats are great for building your lower body, but the Sumo variation uses a wider stance and an outward foot angle to focus on the inner thighs (adductor muscles) and can help your quads get stronger.
It’s also a fantastic way to work on hip flexibility, which is key for deeper squats.
This setup reduces stress on the lower back and emphasises the gluteus maximus, adductors, and vastus medialis oblique (VMO) of the quads.
How To Do
- Stand with your feet significantly wider than shoulder width. Turn your toes outwards—experiment to find an angle where your knees can comfortably track outwards in line with your toes.
- Keep your chest up, shoulders back, and core braced. As with regular bodyweight squats, arms can be out front, crossed, or on the hips.
- Keep your torso upright, push your hips back and down simultaneously, bending your knees outwards.
- Lower your body down, focusing on driving your knees outwards over your toes. Your torso will remain more vertical than in a regular squat, where you might hinge more at the hips.
- Descend until your thighs are parallel to the floor or lower. At the bottom, you should feel a good stretch in your inner thighs.
- Focus on engaging your inner thighs as you come back to your starting position.
3. Jump Squat
Jump squats are the power-packed HIIT version of squats. Squat jumps help shed body fat, tone your butt and legs, and improve strength and balance.
Research has shown that Jump squats generate more explosive force than traditional squats, making them a valuable addition to any lower-body workout routine.
Including in-home quad workouts is a great exercise since they can be done in a small space without any equipment.
Studies also indicate that jump squats can improve vertical jump height, crucial for various sports and athletic activities.

How To Do
- Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart and your knees slightly bent.
- Quickly drop down by bending at the knees and hips, and let your glutes track backward to lower yourself into a squat.
- At the point where your thighs are parallel to the floor.
- Reverse direction, driving up through your heels and the balls of your feet to lift your body off the floor as high as possible.
- Land with soft knees and immediately lower into the next rep.
- Don’t perform this exercise with cold muscles. Do a cardio warm-up before it.
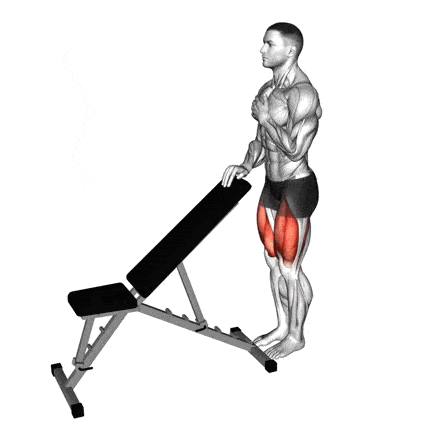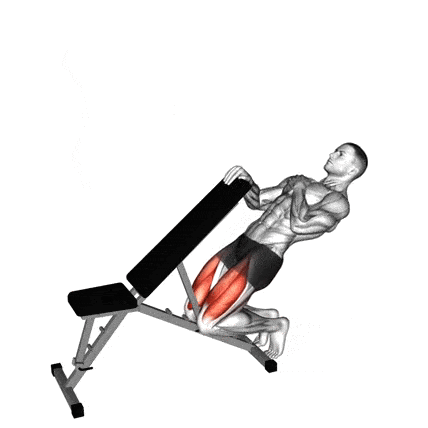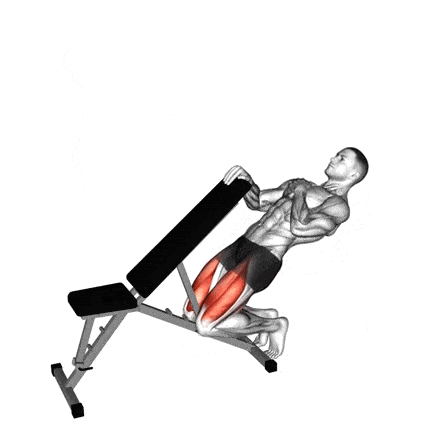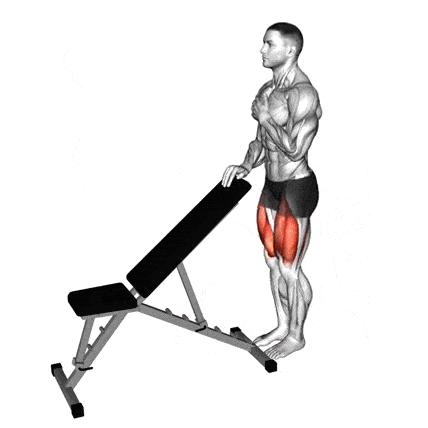
4. Sissy Squat
While squats typically involve sitting back and down, the Sissy Squat is the complete opposite. You’re leaning back and letting your knees travel far forward over your toes.
This drastically shifts the leverage and places almost all the tension directly onto the quadriceps, with minimal help from the hamstrings and glutes.
It’s a fantastic accessory movement or finisher for isolating quads for growth, especially Vastus Medialis and the top of the quad (Rectus Femoris).
To add resistance, hold a weight plate on your chest with the arm that is not stabilizing your body.
How To Do
- Stand upright and hold onto a stable support with one hand (like a squat rack upright, a sturdy pole, or a sissy squat machine if available). Your feet should be about hip-width apart.
- Keep your chest up and core braced, allow your hips to extend slightly so your body forms a relatively straight line from your knees up through your shoulders. You will feel your quads engage immediately.
- As you lower yourself, keep your body straight and bend your knees so they go over your toes. Simultaneously, you will lean your torso backwards.
- Lower yourself slowly and under control. Go as low as your knee mobility and strength. You should feel an intense stretch and burn in your quads.
- Powerfully contract your quads to extend your knees and pull yourself back up to the starting upright position. Drive through the balls of your feet.
6. Resistance Band Split Squat
It is a powerful unilateral exercise that targets the quads, glutes, and hamstrings. The instability introduced by the band also activates the core.
This is my go-to unilateral leg builder for at-home training or training the quads without loading the spine.
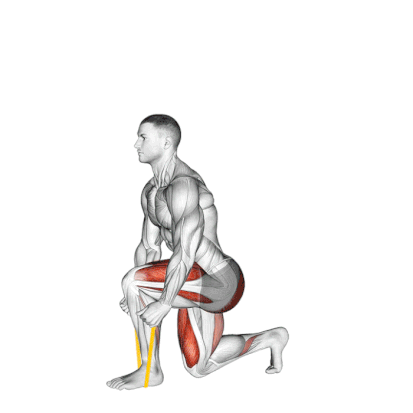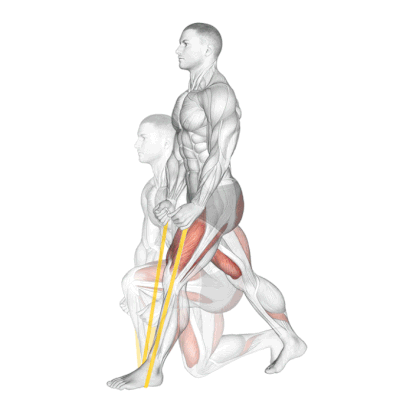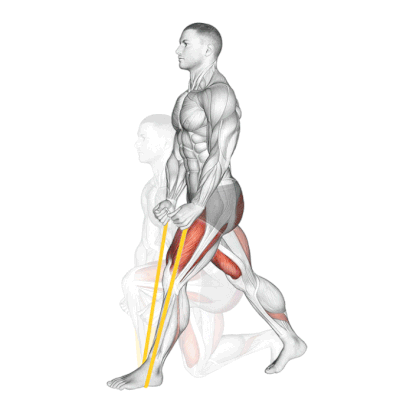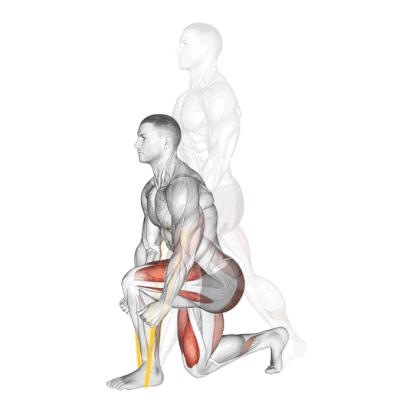
How To Do
- Stand tall, place a resistance band under your front foot, and maintain a posture that allows you to move freely.
- Your front foot is planted firmly – about 2-3 feet before your back foot.
- Keep your torso upright and confident. Your chest is up like you’re trying to show off a logo on your shirt.
- As you go lower, everything moves in harmony. Your front knee tracks over your toes like it’s on rails, and your back knee drops toward the ground.
- At the bottom position, your front thigh is parallel to the ground.
- Now drive back up with the front wheel. Push through it like you’re trying to leave a footprint in concrete. The band tension increases as you rise, challenging you most at the top when traditional squats would be easiest.
- The whole movement should feel smooth, controlled, and strong – like you’re moving through slightly thick honey.
6. Dumbbell Squat
The Dumbbell Squat is one of the most accessible and effective leg exercises for building strength, muscle mass, and joint stability—especially for those training at home, beginners, or even advanced lifters during deloads.
I start almost all my new clients with this before moving on to the more difficult barbell squat. It allows me to correct their depth, posture, and breathing under controlled load.
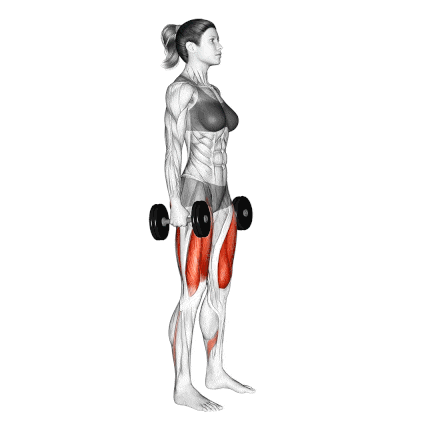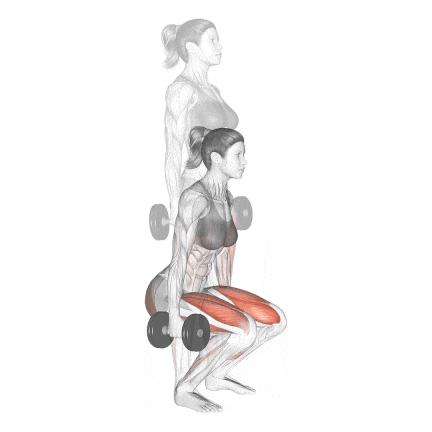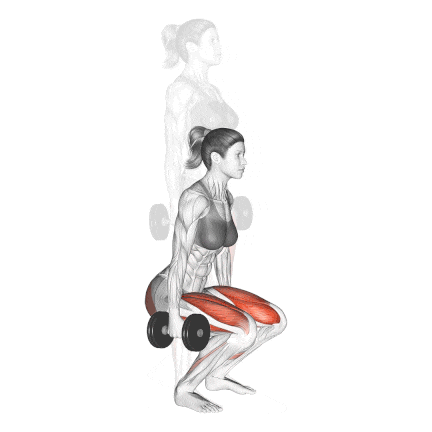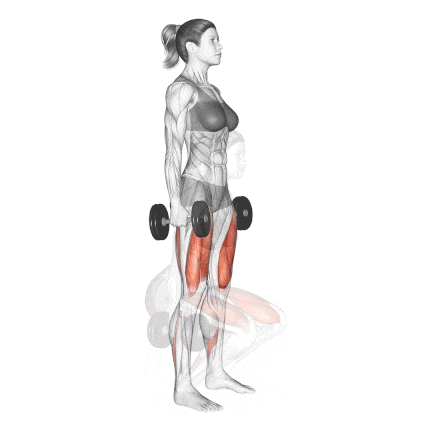
How To Do
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly out (your comfortable squat stance).
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand, arms hanging naturally by your sides, palms facing your body. Keep your chest up, shoulders back, and core braced.
- Take a breath, engage your core, and push your hips back and bend your knees simultaneously, just like the bodyweight squat.
- Lower under control, keeping your back straight and chest lifted. Allow your knees to track in line with your toes. Descend to at least parallel, or lower if comfortable with good form.
- Drive powerfully through your entire foot, extending your hips and knees to return to standing.
- Stand tall, hips and knees locked out.
7. Dumbbell Split Squat
The dumbbell split squat is a fundamental unilateral exercise essential for developing strong, balanced, and aesthetic legs. It should be included in nearly every individual’s workout routine.
It is an excellent exercise to build thigh muscles and glutes. Along with squats, lunges are highly recommended to build mass in your butt and quad muscles.
It calls for good balance, so if you struggle with it at first, try doing it without the weights.
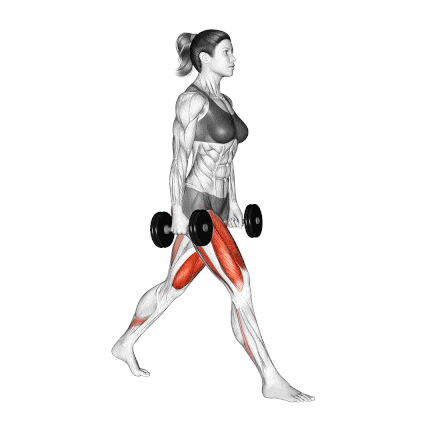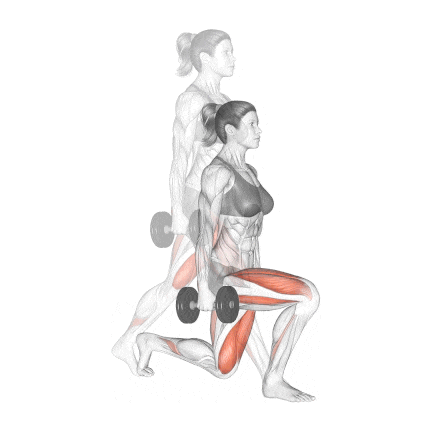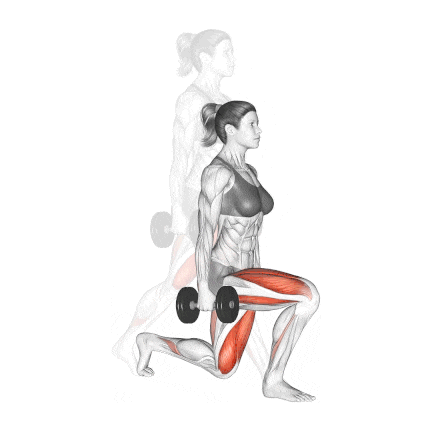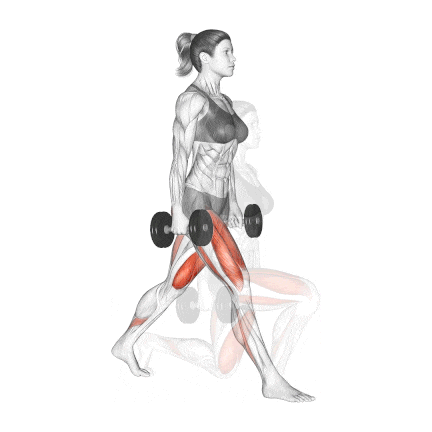
How To Do
- Start in a split stance with feet approximately hip-width apart, front foot flat and rear foot with heel elevated (ball of foot on ground). The optimal front foot position is typically 2-3 feet ahead of your rear foot.
- Hold dumbbells at your sides in a neutral grip position. This stance creates immediate stability challenges that enhance neuromuscular recruitment.
- Keep your torso upright with a very slight forward lean (5-10°)
- Position the front knee directly above or slightly behind the ankle at the bottom position
- Descend until the rear knee nearly touches the floor (about 1-2 inches clearance)
- Drive through your front leg’s midfoot while concentrating on your quadriceps contraction.
8. Dumbbell Sumo Squat
It’s a great variation for individuals who struggle with traditional squats due to hip mobility restrictions or lower back discomfort.
It is performed with a wider-than-shoulder-width stance, usually at a 30°–45° angle.
This position shifts some of the load away from the spine and places greater emphasis on the adductors and glutes, while still heavily engaging the quads.
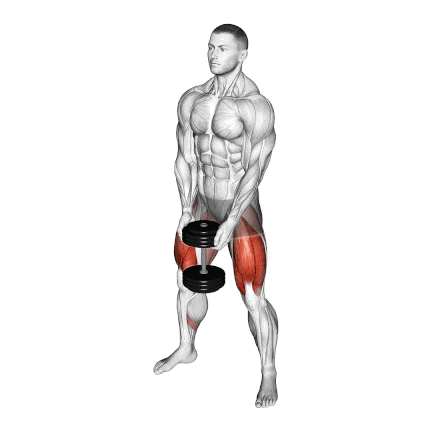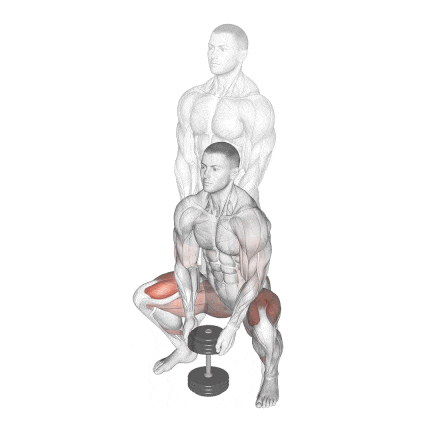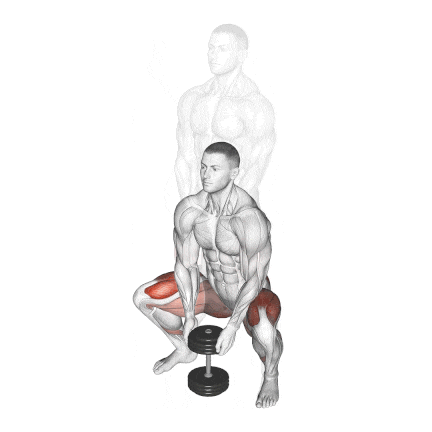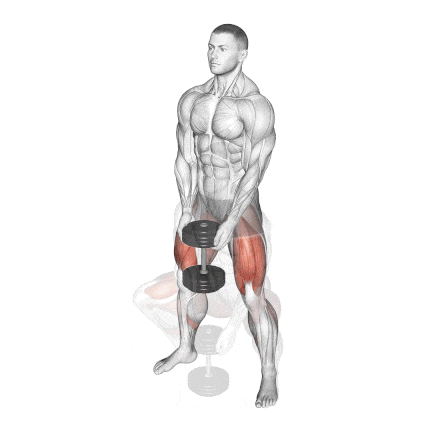
How To Do
- Stand with your feet slightly wider than hip-width apart and turn your feet out, externally rotating your hips.
- Hold a dumbbell with both hands in front of you (either goblet-style or hanging vertically like a kettlebell).
- Breathe in deeply, then push your hips back and lower your body into a squat.
- Pause, then exhale and ensure you’re pushing through your heels and engaging your inner thighs as you return to your starting position.
9. Dumbbell Step Up
It is an effective unilateral compound exercise that targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and hip abductors by imitating movements such as hiking or climbing stairs.
I use dumbbell step-ups as a staple in my clients’ programs to correct leg imbalances, enhance functional strength, and improve single-leg stability.
If you don’t have weights or want an easier variation, you can do a bodyweight step-up at home.
You can also try a lateral step-up.
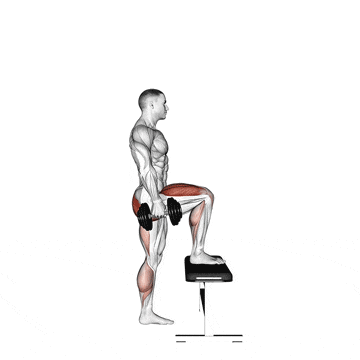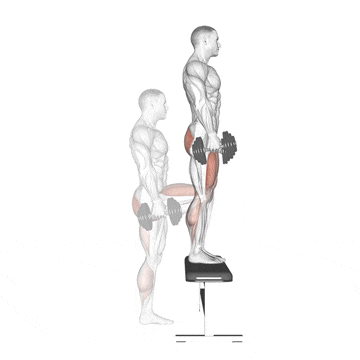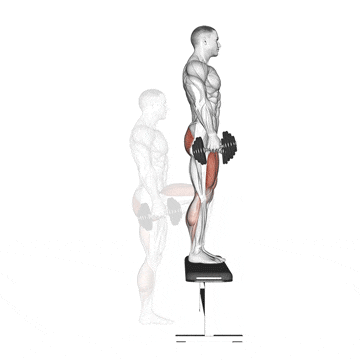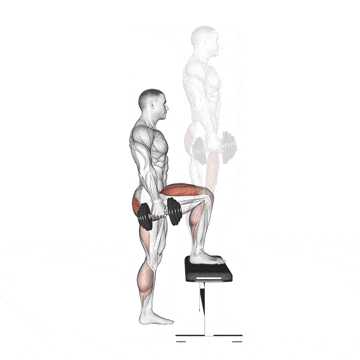
How To Do
- Place a knee-high box or bench in front of you.
- Grasp a dumbbell in each hand, or use just your body weight.
- Stand with your feet in a comfortable hip-width stance. Keep your back in a natural arch and your body upright.
- Step forward with one leg onto the step and drive through that thigh to bring your body upward.
- Bring the trailing leg to the top of the step and stand on the box. Then, step back with the opposite leg to the floor and lower yourself.
- Alternate legs with each rep.
10. Barbell Squat
The barbell squat is the king of all exercises, with the only challenger being the barbell deadlift. Nothing comes close to a squat workout for building muscle mass and toning the leg muscles.
Most people love this exercise because it strengthens the legs and core. Many research papers have investigated the effects of squats on testosterone levels.
In general, these studies have found that squats can lead to a significant increase in testosterone levels.

How To Do
- Adjust the barbell height in the rack so it’s roughly level with your mid-chest. This ensures you don’t have to stand on your toes to unrack or struggle to re-rack.
- Load the desired weight plates evenly on both sides of the bar. Use collars to secure the plates!
- Step directly in front of the bar. Place your hands on the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width. Grip the bar firmly.
- Duck under the bar. Position the bar securely on your upper back. For most people, this means creating a “shelf” with your upper traps and rear deltoids, just below the base of your neck (High Bar position).
- Lift the bar off the hooks by driving through your feet and standing tall.
- Take 1-2 steps back from the rack to clear the hooks. Adjust your foot stance to your comfortable squat width (shoulder-width or slightly wider, toes pointed slightly out).
- Take deep, bracing breath into your core. Push your hips back while bending your knees simultaneously. Imagine sitting down and back.
- Lower yourself down under control. Descend until your thighs are at least parallel to the floor. Allow your knees to track in line with your toes.
- Drive up powerfully through your entire foot. Think about pushing the floor away. Extend your hips and knees simultaneously, returning to the standing position.
11. Front Squat
The Back Squat is a fantastic exercise for building overall strength and targeting multiple muscle groups, but if you want to focus on your quads, the Front Squat is the way to go.
By shifting the bar from your back to the front of your shoulders, you change how your body works during the lift.
This position keeps your torso nice and upright, which challenges your quads. Plus, it also gives your core and upper back stabilisers a great workout.
The study also shown that front squats may be advantageous compared with back squats for individuals with knee problems such as meniscus tears, and long-term joint health.
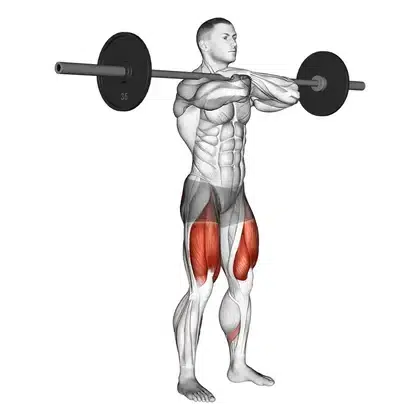
How To Do
- Adjust the bar height slightly lower than for a back squat, around clavicle height.
- Step up to the bar, chest up. Cross your arms and place your hands on the bar, gripping it lightly with your fingers (just enough to keep it from rolling).
- Let the bar rest across the front of your shoulders and clavicles. Elevate your elbows high, pointing them straight forward. Your arms form a shelf.
- Take 1-2 small steps back to clear the rack. Adjust your foot stance – often shoulder-width or slightly narrower than a back squat, with toes pointed slightly out.
- Keep your chest up and elbows HIGH. To start lowering, bend your knees and push your hips back a little. Descend to at least parallel, or deeper if your mobility allows.
- From this position, push yourself back to the starting point.
12. Barbell Split Squat
This exercise is a powerhouse for building serious single-leg strength, correcting imbalances between your legs, and stimulating significant muscle growth in your quads and glutes.
As you descend, the front quad and glute work eccentrically. The degree of quad vs. glute emphasis can be slightly shifted by stance length – a shorter stance places a bit more stress on the quad, while a longer stance can involve the glute more, but both are heavily recruited regardless.
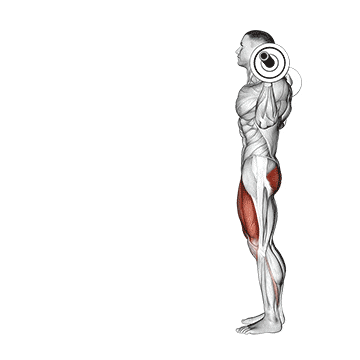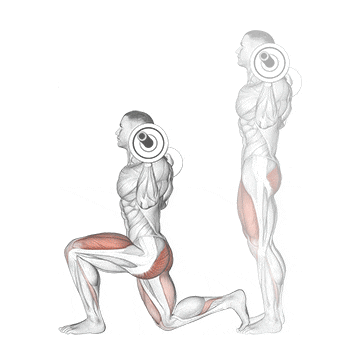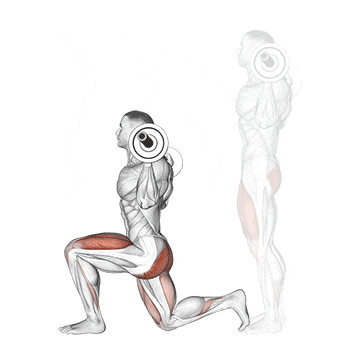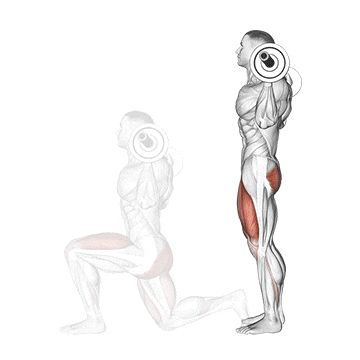
How To Do
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart and your toes pointing forward.
- Place a barbell across your back and rest it on your upper traps.
- Step forward with one leg and lower your body until both knees are bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Make sure your front knee does not extend past your toes.
- Exhale and drive powerfully up through your entire front foot, extending your front knee and hip to return to the starting position.
- Complete all desired reps on one leg before carefully returning to the rack to re-rack the bar. Then, switch legs and repeat the entire process.
13. Zercher Squat
The Zercher Squat is a unique and highly effective compound exercise in which the barbell is held in the crooks of your elbows in front of your torso. It’s an excellent squat variation for improving quad strength, core stability, and upper back endurance.
I often recommend the Zercher Squat to intermediate and advanced lifters who want to break through plateaus, develop real-world functional strength, or build mental toughness.
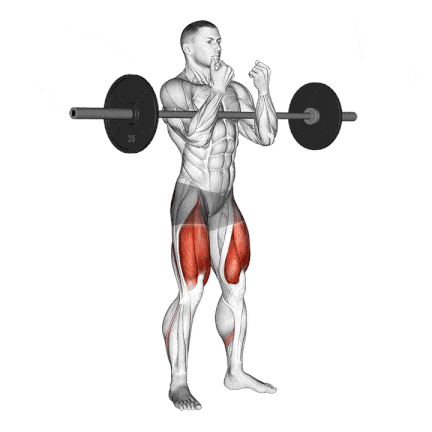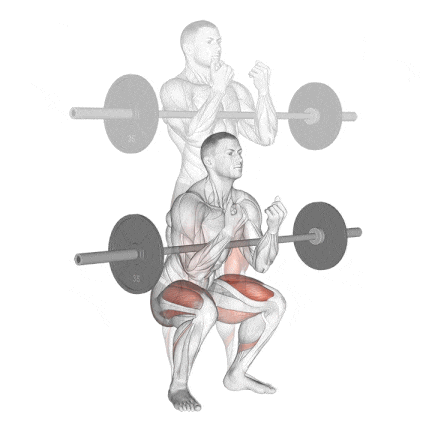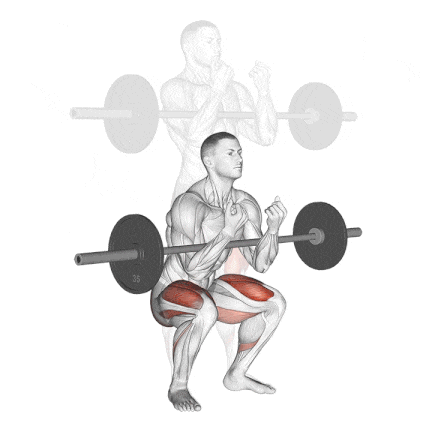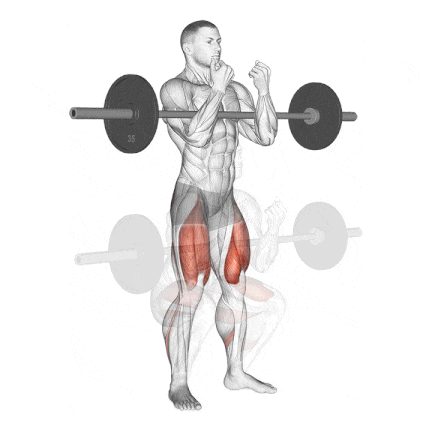
How To Do
- Stand with a shoulder-width grip. Hold a barbell at chest height in the crook of your crossed arms.
- Use elbow pads to decrease discomfort in your arms. Another option is placing two barbell pads for each arm on the bar.
- Step back from the rack and stand in a wide stance with your knees and feet pointed out diagonally in the same direction.
- Keep your back straight and body upright.
- Squat down until your thighs are parallel to the ground.
- It would be best if you paused when your thighs are parallel to the floor.
- Reverse direction and drive up through your heels to the standing position.
14. Side Lunge
The side lunge, aka lateral lunge, is fantastic because it targets muscles that don’t get as much direct work in traditional squats and lunges, particularly the inner and outer thighs (adductors and abductors).
It’s the best for improving hip mobility, building strength in unique ranges of motion, and correcting side-to-side imbalances. Plus, it still hits those quads and glutes
Other Variations:
- Bodyweight Lateral Lunge
- Dumbbell Lateral Lunge
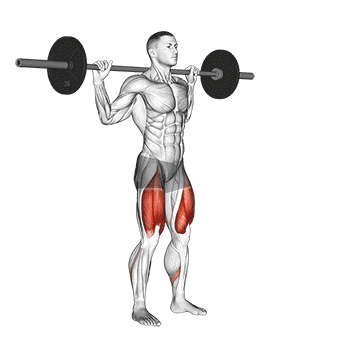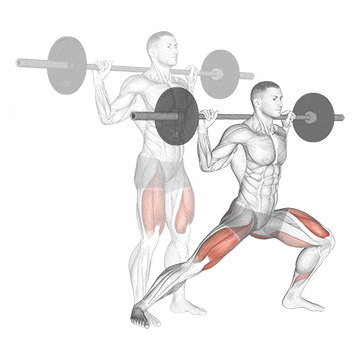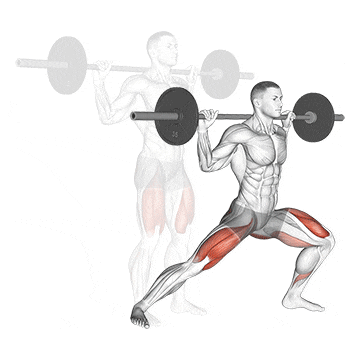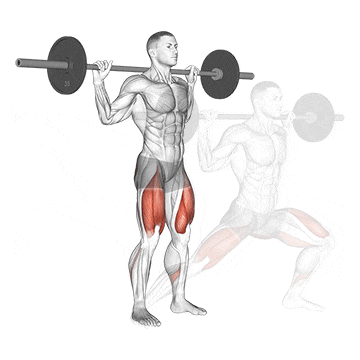
How To Do
- Place a barbell on your traps and stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart.
- Step out to your right as far as you can with your right foot.
- The forefoot should be turned out slightly as you plant it on the floor.
- Squat, shifting your weight to the left until your left leg is parallel with the floor.
- Do not lean the torso forward as you rise out of the bottom of the lunge.
- Extend your left leg back up to lift your body up.
- Repeat with your left leg in the same manner, alternating legs each rep until all reps are completed.
15. Jefferson Squat
This exercise is kind of a hybrid beast, sitting somewhere between a squat and a deadlift, performed with the barbell between your legs, straddled.
Because of the unique bar placement and stance challenges your body’s ability to resist rotation and puts your quads and hips under tension in a way traditional squats don’t.
It’s a favourite among old-school strength athletes—and it’s making a comeback in modern functional training programs.
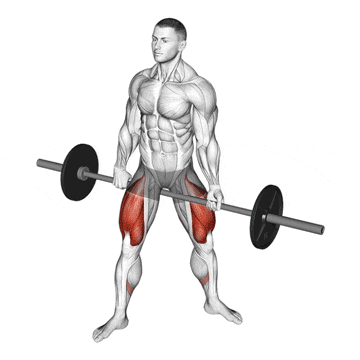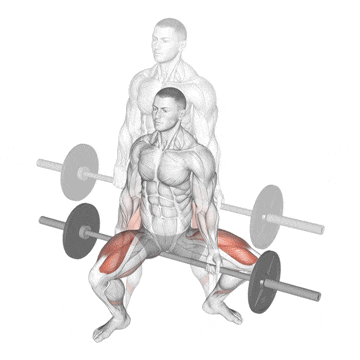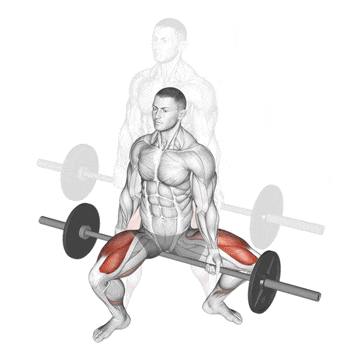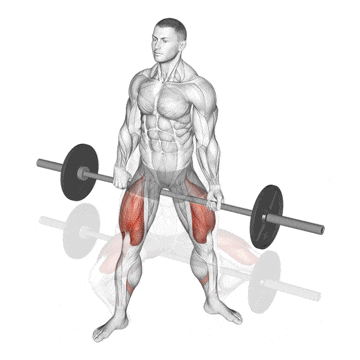
How To Do
- Straddle a loaded barbell placed on the floor and run sideways between your feet.
- Squat down to pick up the bar, grabbing it with one hand facing palm backwards and one hand facing palm forward.
- Hold the bar as you stand with a wider grip than shoulder-width. Ensure that the weight is evenly distributed between your two legs.
- Bend at the knees and hips, letting your glutes track backwards to lower yourself.
- When your thighs are parallel to the floor or the bar touches the floor, reverse direction and drive up through your heels to a standing position.
16. Barbell Box Squat
The box squat is a compound exercise that uses a barbell and a plyometric box to work the muscle groups throughout your body.
Box squats’ posture puts slightly less pressure on the knee joints than front or back squats.
This is a great workout for learning how to squat because it reinforces the sitting-back portion of the squat.
Other variation: Bodyweight Box Squat and Dumbbell Box Squat
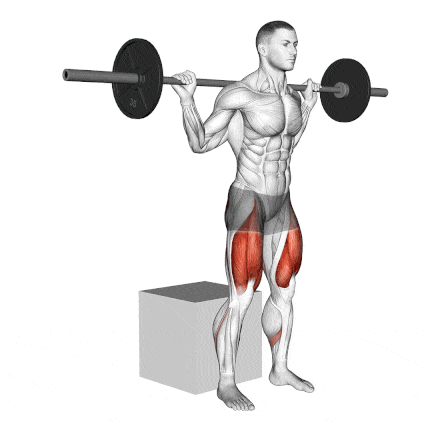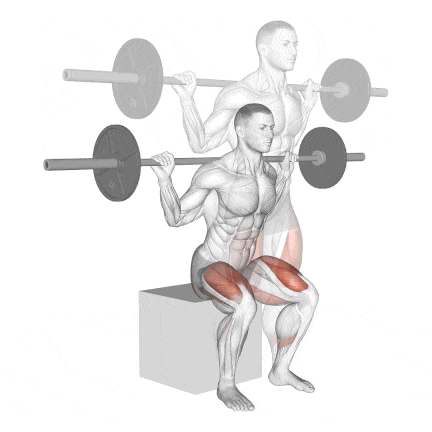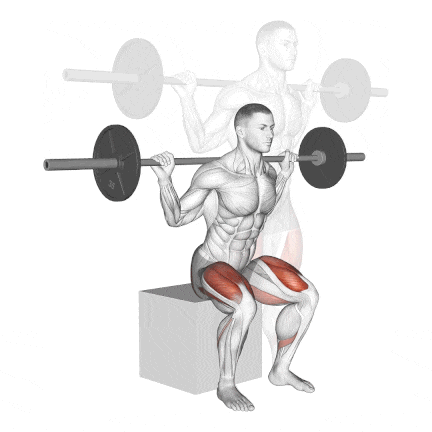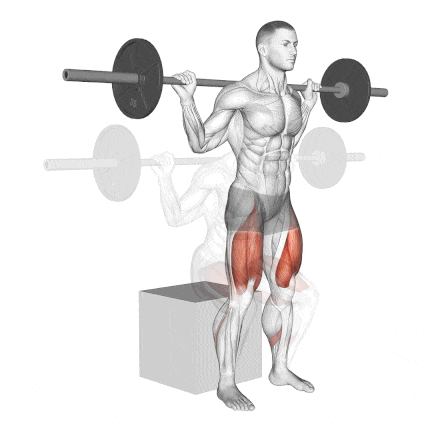
How To Do
- Place a box or bench that is about knee height behind you in the power rack or squat rack.
- Unrack the bar and move back so you are several inches ahead of the box or bench.
- Your posture should be tall, with your feet wider than hip-width apart and your knees slightly bent.
- Your shoulders should be directly over your hips, with your head and neck in a neutral position.
- Squat back and down until your glutes make contact with the box, and immediately explode back up by pressing through your heels until you’re back in the standing position. Do not “plop” or fully sit down on the box.
- Do not sit on the box and rock backwards, as this can compress your spine; pause and immediately raise.
Know More: 15 Best Barbell Leg Workout For Mass and Strength
17. Leg Press
If you have back problems or are concerned about lower back pressure, leg press exercises are the best thigh-building and toning workouts.
In comparison with the barbell squat, the seated leg press exercises reduce the axial load on your spine and reduce the risk of backache.
It’s an excellent tool for building pure muscle mass (hypertrophy) and strength in the quads and glutes, especially when you want to eliminate your core and lower back or push your legs to fatigue after heavier compound lifts.
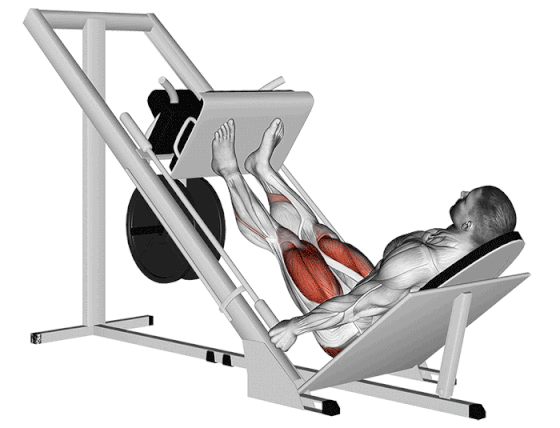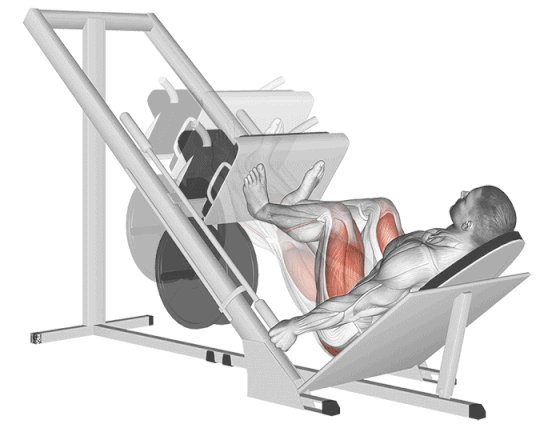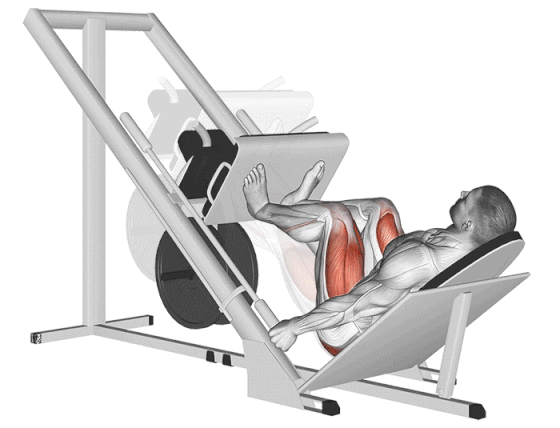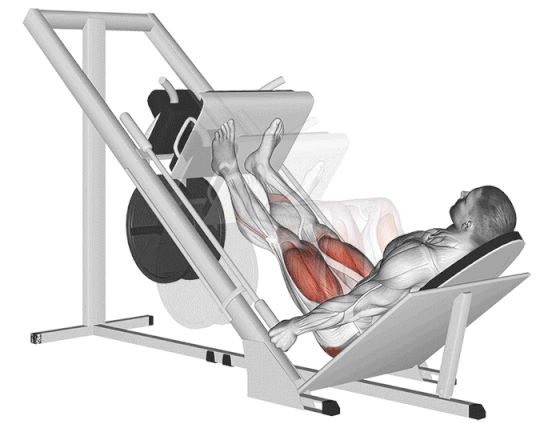
How To Do
- Adjust the seat back if possible to a comfortable angle (usually 45 degrees is standard).
- Sit in the machine with your back flat against the backrest.
- Place your feet on the platform in your preferred stance (start with standard/mid-platform, shoulder-width, toes slightly out).
- Push the platform away from you by extending your knees and hips until your legs are nearly fully extended (do not lock your knees out completely).
- Slowly lower the platform towards your body by bending your knees and hips. Keep your back flat against the pad – do NOT let your lower back round off the seat.
- Exhale and powerfully drive through your entire feet, pushing the platform back up by extending your knees and hips.
18. Leg Extension
Leg extension is one of the best quad-dominant exercises and a great way to build and shape your quad muscles.
Research has shown that range of motion (ROM) and leg rotation significantly affect muscle activation during leg extensions. The vastus medialis oblique is best targeted in the final ROM, while the rectus femoris is maximally activated with lateral rotation.
Different positions of the toes work different quad muscles.
- Pointing your toes directly upward hits all sections of the quadriceps equally,
- Toes inward, internally rotates the tibia to target the inner quad.
- Placing your toes outward externally rotates the tibia to hit the outer quad.
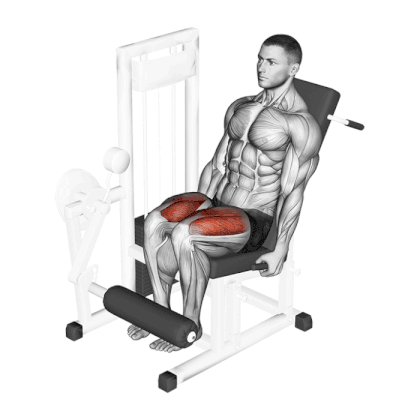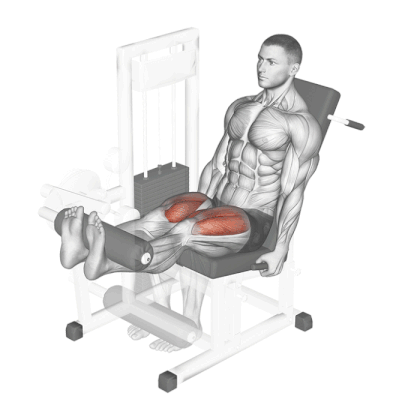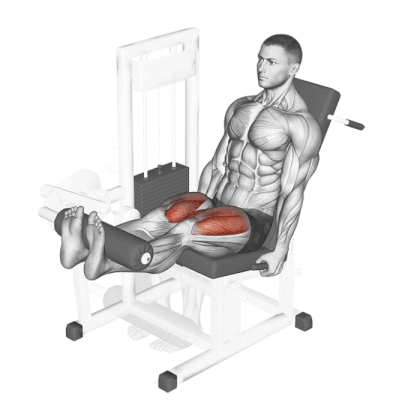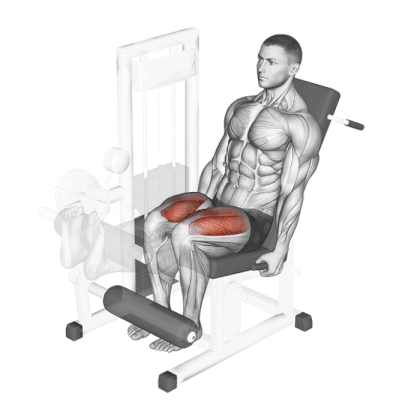
How To Do
- Sit on a Leg extension machine with your legs under the pad and with your back pressed firmly against the back pad.
- Grab the handles or the seat edges behind your hips and keep your upper body steady.
- Extend your legs as far as possible in a smooth movement until fully extended to get a maximum thigh contraction.
- Do not lock your knees when they are fully extended. This can put additional strain on the knee joint.
- Contract your quads at the top and slowly lower the weight under control to the starting position.
19. Hack Squat
The machine hack squat is a variation of the squat and an exercise used to build the muscles of the legs.
In particular, the hack squat targets Quadriceps, glutes, and hip flexors and also involves calves and hamstrings.
The difference between a barbell squat and a hack squat is that the barbell squat involves the core more.
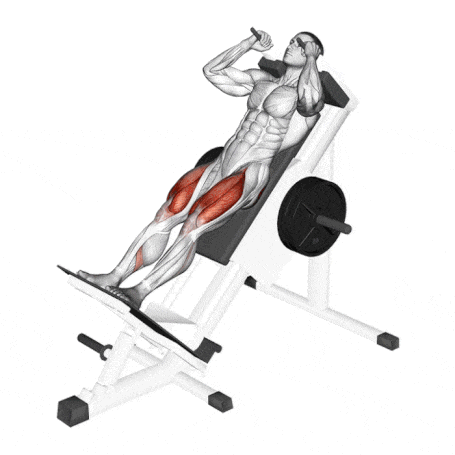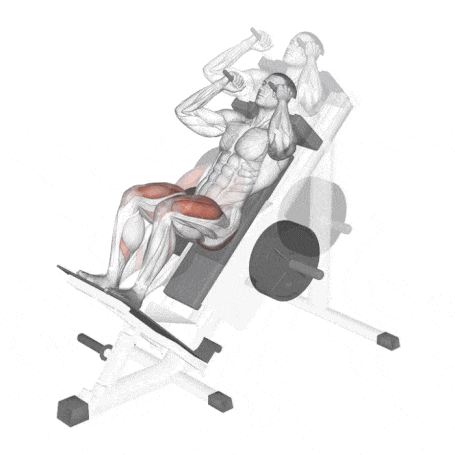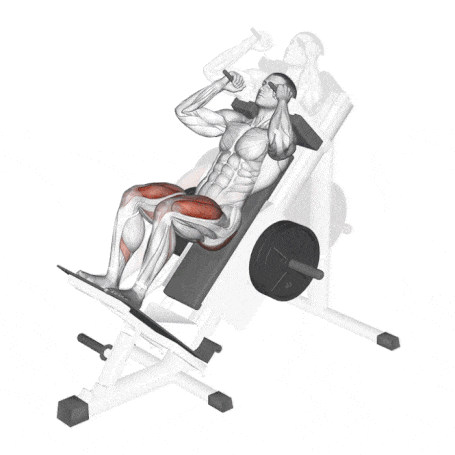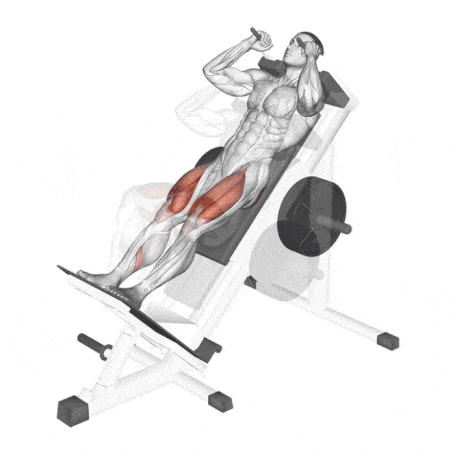
How To Do
- Get on a hack squat machine and place your back flat against the back pad of the and get your shoulders under the support.
- Grip the side handles of the machine and place your legs in a shoulder width stance with your toes pointed out slightly.
- Straighten your legs, but do not lock your knees. Bend your knees as you slowly lower the weight.
- Go down as low as possible, parallel to the floor. Hold for a count of one.
- Return to the start position by pushing down through your heels and extending your legs.
20. Smith Machine Squat
Smith machines are designed to stabilise your core and maintain your posture while you squat.
The Smith machine squat allows you to squat a heavy weight without a spotter safely. Just make sure that you use the safety pins. You must add this exercise to your quad workout to help you build mass and strength.

How To Do
- Stand in a smith machine so that the barbell is behind your shoulders and slightly below your neck, grasping it just outside your shoulders. Twist the bar to unrack it.
- Grasp the barbell with palms facing forward and hands wider than shoulder width apart.
- With your chest high, head forward, and back slightly arched, bend your knees and hips.
- Inhale as you slowly lower the barbell by getting into a squat position.
- When your thighs parallel the floor, exhale and push off with your legs to reverse the movement and return to the starting position.
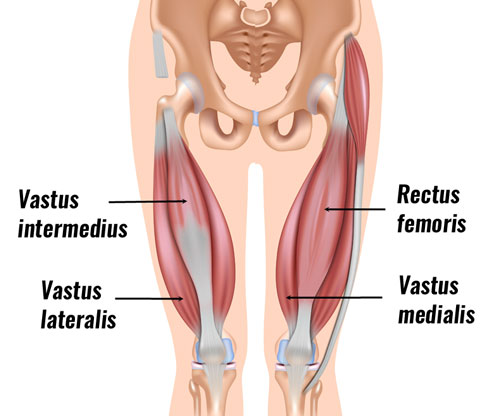
What Are the Quadriceps Muscles
The quads, or quadriceps femoris, located in front of the thigh. They are the largest and strongest muscles in the thigh, and they play an important role in extending the knee and flexing the hip.
The four muscles of the quadriceps are:
- Rectus femoris: the longest muscle in the quadriceps, and it runs along the front of the thigh.
- Vastus lateralis: This muscle is located on the outside of the thigh. It is responsible for giving the thigh its shape.
- Vastus medialis: This muscle is located inside the thigh and helps stabilize the knee joint.
- Vastus intermedius: This muscle is located in the middle of the thigh and helps extend the knee.
The four heads merge together, attach onto the patella (knee cap), and then insert via a single (patellar) tendon onto the tibia, just below the knee joint.
All four of these muscles help your knee joint extend, and due to the rectus femoris’ attachment to the ilium, it’s also a flexor of the hip. Hence, the muscle group is so important in walking, running, jumping, and squatting.
How To Build Quad Muscle Mass
You also need to consider other strategies and workouts. Here are the best tips for getting bigger and stronger quads fast.
1. Do Plenty Of Squats And Lunges
Squats and lunges are basic and ideal for building quad strength. As compound movements, they work the quads, hamstrings, glutes, and other muscles.
Another great thing is that you can make many variations and add weight to your progress. Start with the basics to get good form, and then try these:
- Weighted squat
- Jump Squat
- Weighted lunges
- Jumping lunges
2. Go Heavy
Fewer reps with heavier weights are always more effective and efficient when building muscle strength and size.
You will gain strength by lifting lighter weights and completing more repetitions, but you will eventually hit a wall. To see results, focus on loading up squats and other exercises while doing fewer reps.
3. Challenge Yourself With Drop Sets And Supersets
Take your leg workout to the next level with more challenging sets. A drop set is when you hit muscle failure, switch to a lighter weight and do more reps. Continue until you get to no weight.
To do a superset, plan a series of sets of quad strengthening exercises and do them all in a row with no rest until you have completed them all. Then do it again. Start small with just two sets of different moves. Add more as you progress.
4. Follow Quad Training Weekly Volume, Sets And Reps
The number of reps and sets will vary based on your fitness level, weekly workout frequency, and strength training goals to structure an effective quad workout to increase mass and strength.
Weekly Volumes
| Fitness Level | Working Sets per Week |
|---|---|
| Beginners | ~10 sets per week |
| Intermediate | ~15 sets per week |
| Advanced | ~20 sets per week |
Reps
- For strength gains, do 1 to 6 reps each exercise with a weight that is at least 85% of your one-repetition maximum (1rm). The fewer reps you perform, the closer to 100% of your 1rm you should strive for.
- If your goal is hypertrophy (muscle growth), perform 8 to 12 reps, using loads 70 to 85% of your 1RM.
- When training for endurance, it is usually recommended to use higher reps (15 to 20 repetitions) and moderate loads with a weight of at least 50 to 70% of your 1RM.
5. Beginner Quad Workout Plan
If you’re new to lifting weights, don’t worry. This beginner-friendly quad workout routine is a great place to start.
When this gets easy, choose a heavier free weight. After you’ve upped your weight several times and feel strong in the movements below, move on to the intermediate routine.
Until then, you can follow this beginner quad workout plan at home.
| Exercise | Sets | Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Bodyweight Squat | 4 | 8-15 |
| Lunges | 3 | 8-12 |
| Step-Up | 3 | 8-10 |
References
- Michal Krzysztofik,* Michal Wilk, Grzegorz Wojdała, and Artur Gołaś: Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec
- Thomas Linding Jakobsen, Markus Due Jakobsen, Lars Louis Andersen: Quadriceps muscle activity during commonly used strength training exercises shortly after total knee arthroplasty: implications for home-based exercise-selection. J Exp Orthop. 2019 Dec
- Donnelly DV, Berg WP, Fiske DM. The effect of the direction of gaze on the kinematics of the squat exercise. J Strength Cond Res. 2006;20:145–150.
- Desiana, Istingadah & Moeliono, Marina & Prabowo, Tertianto. (2017). Effects of Quadriceps Strengthening Exercise on Quadriceps Muscle Strength and Its Relation to Lower Extremity Lean Mass. International Journal of Integrated Health Sciences. 5. 84-88. 10.15850/ijihs.v5n2.1010.
- Mehls K, Grubbs B, Jin Y, Coons J. Electromyography Comparison of Sex Differences During the Back Squat. J Strength Cond Res. 2022 Feb 1;36(2):310-313. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003469. PMID: 32032232.
- Wirth K, Hartmann H, Sander A, Mickel C, Szilvas E, Keiner M. The Impact of Back Squat and Leg-Press Exercises on Maximal Strength and Speed-Strength Parameters. J Strength Cond Res. 2016 May;30(5):1205-12. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001228. PMID: 26439782.
- Muscle Activity in Single- vs. Double-Leg Squats
- Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Thigh Quadriceps Muscle

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
