Want to build a big, muscular back? The wide-grip lat pulldown should be at the top of your back workout routine.
The wide grip lat pulldown is a variation of the lat pulldown and a popular back exercise that targets the back muscles, particularly the lats and teres major. The compound pull exercise helps build a wide, V-shaped back and is a staple in many bodybuilders and fitness enthusiasts back workouts.
As the name suggests, it involves using a wide overhand grip on the pulldown bar, generally about 1.5 times shoulder width or wider.
The wide grip targets the latissimus dorsi muscles (outer lats) of the back more than a close-grip lat pulldown. It also allows for a wider range of motion and greater activation of the upper back muscles.
Want to take your gains to the next level? Discover your daily calorie needs with our free TDEE calculator

- Wide Grip Lat Pulldown Muscles Worked
- 1. Primary Muscles Worked
- 2. Secondary Muscles Worked
- 3. Stabilizing Muscles Worked Wide Grip Pulldown
- How To Do Wide Grip Lat Pulldown
- Wide Grip Lat Pulldown Form and Technique
- 1. Back Slightly Lean
- 2. Controlled Motion
- 3. Do Full Range Of Motion
- 4. Grip and Hand Position
- 5. Keep Your Elbow Close
- 6. Avoid Behind The Neck Pulldown
- Benefits of the Wide Grip Lat Pulldown
- FAQs
- What muscles do the wide-grip pulldown work?
- Is the wide-grip lat pulldown effective for building a V-shaped back?
- Conclusion
Wide Grip Lat Pulldown Muscles Worked
The Lat Pulldown primarily targets the upper back muscles, specifically the latissimus dorsi. However, the exercise also engages various other secondary and stabilizing muscles to some extent.
1. Primary Muscles Worked
- Latissimus Dorsi: The large, flat muscles that cover the middle and lower back. The lats help the shoulder joint move up and down, so they work a lot when doing a lat pulldown.
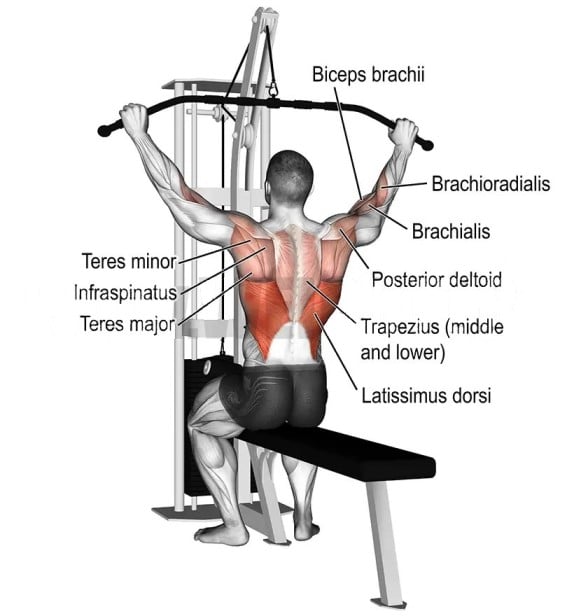
2. Secondary Muscles Worked
- Rhomboids aids in adduction and retraction of the scapulae. They assist the lats during pulldown.
- The trapezius supports scapular retraction and elevation. The mid and lower traps are engaged during pulldown.
- Posterior Deltoid (rear deltoid) is located on the backside of the shoulders.
- Levator Scapulae helps elevate the scapula and is engaged when pulling the bar.
- Teres Major is located near the lats and aids in shoulder adduction and medial rotation.
- Infraspinatus and Teres Minor are part of the rotator cuff muscles and are engaged for shoulder stabilization.
3. Stabilizing Muscles Worked Wide Grip Pulldown
- Biceps Brachii: involved in the elbow flexion part of the exercise.
- Brachialis: Located underneath the biceps, this muscle aids elbow flexion.
- Brachioradialis: This is a muscle of the forearm that assists in flexing the elbow.
- Serratus Anterior: This muscle helps with the movement and stability of the scapula, supporting it during the downward pull.
- Core Muscles: your core muscles engage to stabilize your torso during the exercise.
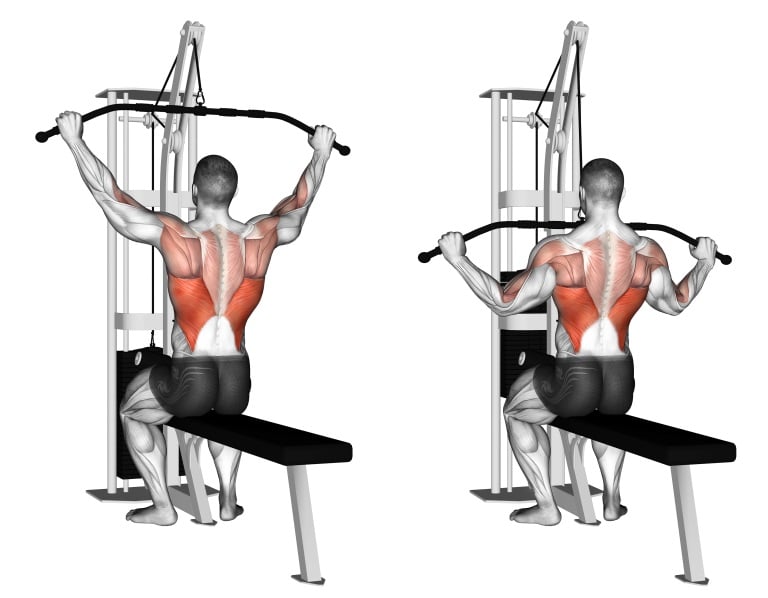
How To Do Wide Grip Lat Pulldown
- Set Up: Position yourself on a lat pulldown machine with a wide-grip bar attachment. Adjust the knee pad and seat height so that your thighs are securely placed and your feet are flat on the ground.
- Grip: Reach up and grasp the bar with a pronated (overhand) grip. Your hands should be positioned wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Initial Position: Sit down, secure your thighs under the pads, and let your arms fully extend. Your back should be straight, and your shoulders should be relaxed.
- Pull Phase: Initiate the pull by driving your elbows down and back. Aim to bring the bar towards your upper chest. Retract your shoulder blades and squeeze your lats as you lower the bar.
- Controlled Release: Slowly return the bar to the starting position.
- Repetitions: Perform the 3–4 sets and 8–12 repetitions.
Wide Grip Lat Pulldown Form and Technique
Even though the wide-grip lat pulldown exercise is very popular, many people make common mistakes when they do it. Here are some of the things you should avoid:
1. Back Slightly Lean
Excessively leaning back can disengage the latissimus dorsi and put unnecessary strain on your lower back. Maintain an upright posture, leaning slightly back just enough to prevent the bar from hitting your face.
2. Controlled Motion
Using body momentum to jerk the weight down makes the exercise less effective and increases the risk of injury. Instead, use a controlled, steady movement both while pulling the bar down and releasing it back up.
3. Do Full Range Of Motion
Not pulling the bar down low enough or not doing the top portion of the exercise can limit the effectiveness of the exercise.
Ensure you fully extend your arms at the starting position and pull the bar down at the upper chest level. Additionally, focus on squeezing the shoulder blades together at the bottom of the movement.
4. Grip and Hand Position
With an overhand grip, place your hands wider than shoulder-width apart on the bar. Your wrists should be in a neutral position, aligned with your forearms.
5. Keep Your Elbow Close
Flaring the elbows too far out or dragging them too far back can reduce lat engagement and put stress on the shoulders.
You should keep your elbows pointing downward and to the rear during the movement.
6. Avoid Behind The Neck Pulldown
This can put extra stress on the shoulder joints and make the exercise less effective at targeting the lats. Pull the bar down in front of you, towards your upper chest.
(Note: Some people can perform behind-the-neck pulldowns without issues, but it’s generally not recommended for most due to the risk of shoulder strain.)
Benefits of the Wide Grip Lat Pulldown
- Specifically, it works the latissimus dorsi, which helps to make a wide, V-shaped back.
- Strengthens the biceps and forearms as secondary movers.
- It targets the outer lats more directly than other grip widths for lat pulldowns.
- Improves pulling strength, which is good for swimming, climbing, and lifting activities.
- It helps retract the shoulder blades and straighten the upper back that help you improve posture.
- Engages core and stabilizer muscles for balance and support.
- Easily integrated into various workout routines, whether targeting strength, hypertrophy, or endurance.
To Stay Motivated: 150+ Gym Workout Motivational Quotes To Stay Fit
FAQs
What muscles do the wide-grip pulldown work?
The wide grip pulldown primarily works the latissimus dorsi (lats), the largest muscle in the back. It also works the rhomboids, trapezius, biceps, and forearms.
Is the wide-grip lat pulldown effective for building a V-shaped back?
Yes, the wide-grip lat pulldown exercise is good for building a wider back, which helps create a V-shaped torso.
Conclusion
The Wide grip at pulldown is a versatile and highly effective exercise for targeting the muscles in your back, particularly the latissimus dorsi. They also work the rhomboids, trapezius, biceps, and forearms.
Combining the wide grip variation with underhand and neutral grips will build a thicker, well-proportioned back. There’s no substitute for hard work and progressive overload over time.
References
- Andersen, V., Fimland, M. S., Wiik, E., Skoglund, A., & Saeterbakken, A. H. (2014). Effects of grip width on muscle strength and activation in the lat pull-down. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 28(4), 1135-1142. doi:10.1097/JSC.0000000000000232
- Lusk, S. J., Hale, B. D., & Russell, D. M. (2010). Grip width and forearm orientation effects on muscle activity during the lat pull-down. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 24(7), 1895-1900.
- Lehman, G. J., Buchan, D. D., Lundy, A., Myers, N., & Nalborczyk, A. (2004). Variations in muscle activation levels during traditional latissimus dorsi weight training exercises: An experimental study. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 18(3), 500-506.

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
