
Body Fat Calculator
Your Body Fat: [ ]
Fat Mass: ______ Lean Mass: ______
American Council on Exercise
Body Fat Categorization
| Classification | Women | Men |
|---|---|---|
| Essential Fat | 10-13% | 2-5% |
| Athletes | 14-20% | 6-13% |
| Fitness | 21-24% | 14-17% |
| Acceptable | 25-31% | 18-24% |
| Obese | >32% | >25% |
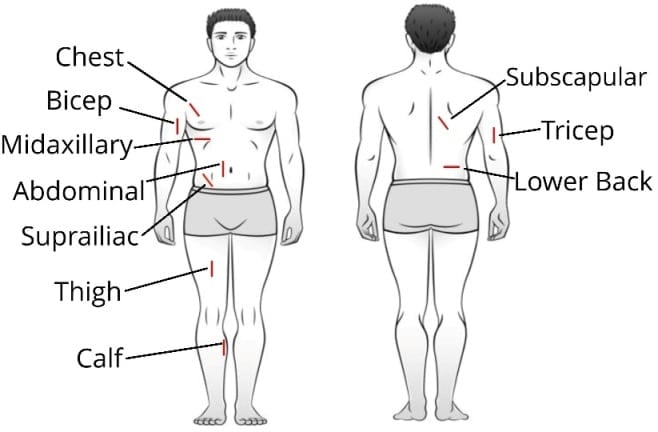
(Note: To determine the precise locations of measurement sites, please refer to the information below)
What is Body Fat Percentage
Body fat, or ‘adipose tissue,’ serves multiple functions, including energy storage, hormone secretion, and cushioning and insulation.
Body fat percentage measures the amount of fat in the body relative to total body weight. It represents the proportion of fat mass to lean body mass.
Body fat percentage is a more accurate indicator of overall health and fitness than measuring body weight or body mass index (BMI) alone.
A healthy body fat percentage can vary depending on age, gender, and activity level. Generally, men have a lower body fat percentage than women.
According to the American Council on Exercise, the recommended body fat percentage ranges are as follows:

7 Ways to Measure Body Fat
- Skinfold Calipers Method
- Bioelectrical Impedance Method
- Hydrostatic Weighing Method
- Air displacement plethysmography (ADP)
- DEXA Scan Method
- 3-D Body Scanners
Related Calculator: Weight Loss Calculator
Popular Method To Calculate the Body Fat Percentage
The body fat percentage calculators are a popular tool for fitness enthusiasts, athletes, and anyone interested in tracking their health progress.
Some body fat percentage calculators have stood out due to their ease of use, accuracy, or additional features, even though they are available online like Ours.
Here are several methods for calculating body fat percentage,
1. US Navy Method Body Fat Calculator
- Based on the U.S. Navy method
- Requires measurements like height, neck circumference, and waist circumference (hip circumference is also required for women)
- Widely available online
2. Caliper Method Body Fat Calculators
- Based on skinfold measurements taken with callipers at different sites on the body
- Sites often include the tricep, supra iliac, thigh, and more, depending on the method (3-site, 7-site, etc.)
3. Parrillo Caliper Method
- Utilizes a 9-point skinfold measurement.
- Known for being detailed and thorough but requires some expertise for accurate results.
4. Durnin and Womersley Caliper Method
- Utilizes 4-site skinfold measurements.
- It is commonly used and backed by research but requires skilled hands for accurate results.
How To Use Calipers To Measure The Sites Accurately

1. Chest
Take a diagonal fold halfway between the nipple and upper armpit.
2. Midaxillary
Take a horizontal fold directly below the armpit at a point on the midaxillary line
3. Biceps
Take a vertical fold on the front of the upper arm, midway between the shoulder and the elbow.
4. Triceps
Take a vertical fold on the back of the upper arm, midway between the shoulder and the elbow.
5. Subscapular
Take a diagonal fold directly below the shoulder blade.
6. Abdominal
Take a vertical fold about 2 cm to the right of the navel.
7. Suprailiac
A diagonal fold should be taken above the iliac crest.
8. Thigh
Take a vertical fold on the front of the thigh, midway between the hip and the knee, with the foot flat on the ground.
9. Lower back
Take a diagonal fold at the level of the iliac crest, slightly to the right of the spine.
10. Calf
Take a vertical fold on the inside of the leg, at the broadest part of the calf muscle.
Percent Body Fat Norms for Men and Women
It’s essential to understand the optimal amount of body fat you should have to maintain good health and fitness. Women tend to have a higher body fat percentage than men, primarily due to hormonal fluctuations and the physiological demands of childbearing, and this percentage increases with age.
The following table shows the ideal body fat percentage for men and women based on age and gender
| Classification | Women | Men |
|---|---|---|
| Essential Fat | 10-13% | 2-5% |
| Athletes | 14-20% | 6-13% |
| Fitness | 21-24% | 14-17% |
| Acceptable | 25-31% | 18-24% |
| Obese | >32% | >25% |
Skinfold Body Fat Calculator
There are several methods for calculating body fat using skinfold measurements, which assess subcutaneous fat thickness at specific body locations.
The most commonly used methods for calculating skinfold body fat include:
- Jackson-Pollock 3 Site Caliper Method
- Jackson-Pollock 4 Site Caliper Method
- Jackson-Pollock 7 Site Caliper Method
- Parrillo Caliper Method
- Durnin And Womersley Caliper Method
Jackson-Pollock 3 Site Skinfold Calculator
The 3-site Jackson-Pollock skinfold formula is one of the most commonly used because it’s easy, quick, and reliable.
The Jackson-Pollock method uses skin folds to measure body fat percentage. This one uses skin folds from 3 different points.
Measurement Locations for Males
- Chest (mm)
- Abdomen (mm)
- Thigh (mm)
Measurement Locations for Females
- Tricep (mm)
- Suprailiac (mm)
- Thigh (mm)
Record the measurements in millimeters (mm) and add them together.
3 Site Body Fat Formula (Males)
- Body Density = 1.10938 – (0.0008267 x sum of skinfolds) + (0.0000016 x square of the sum of skinfolds) – (0.0002574 x age)
3 Site Body Fat Percentage Formula (Females)
- Body Density = 1.0994921 – (0.0009929 x sum of skinfolds) + (0.0000023 x square of the sum of skinfolds) – (0.0001392 x age)
Note: age should be in years.
Use the body density to calculate the body fat percentage using the Siri equation:
- Body Fat Percentage = ((4.95 / body density) – 4.50) x 100
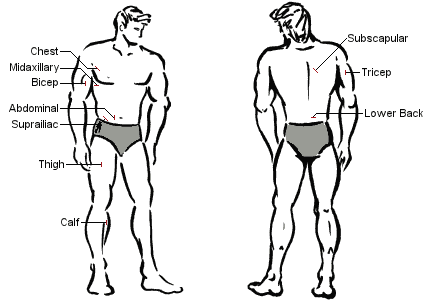
Jackson-Pollock 4 Site Skinfold Calculator
The 4-site Jackson-Pollock skinfold formula is about as accurate as the 3-site formula but also tends to slightly underestimate the body fat percentage of relatively lean people (men under 15% body fat and women under 25%).
Thus, it’s best used for people with more body fat than this.
Four skinfold measurement locations (Men & Female)
- Abdominal (mm)
- Thigh (mm)
- Tricep (mm)
- Suprailiac
Note: Each skinfold measurement is taken three times, and the average is calculated for each location.
4 Site Body Fat Formula for Males:
- Body Density = (0.29288 x sum of skinfolds) – (0.0005 x square of the sum of skinfolds) + (0.15845 x age) – 5.76377
4 Site Body Fat Formula for Females:
- Body Density = (0.29669 x sum of skinfolds) – (0.00043 x square of the sum of skinfolds) + (0.02963 x age) + 1.4072
Use the body density to calculate the body fat percentage using the Siri equation:
- Body Fat Percentage = ((4.95 / body density) – 4.50) x 100
Jackson-Pollock 7 Site Skinfold Calculator
The 7-site Jackson-Pollock skinfold formula is no more accurate than the 3-site formula, is more cumbersome, and tends to slightly underestimate the body fat percentage of relatively lean individuals (men with body fat levels under 15% and women with body fat levels under 25%).
It is ideal for persons with moderate physical activity and young athletes.
We usually recommend using the 3-site method for the general population.
Seven skinfold measurement locations (Men & Female)
- Chest
- Abdominal
- Thigh
- Tricep
- Subscapular
- Suprailiac
- Midaxillary
7 Site Body Fat Formula for Males
- Body Density = 1.112 – (0.00043499 x sum of skinfolds) + (0.00000055 x square of the sum of skinfold sites) – (0.00028826 x age)
7 Site Body Fat Formula for Females
- Body Density = 1.097 – (0.00046971 x sum of skinfolds) + (0.00000056 x square of the sum of skinfold sites) – (0.00012828 x age)
Use the body density to calculate the body fat percentage using the Siri equation:
- Body Fat Percentage = ((4.95 / body density) – 4.50) x 100
Parrillo 9 Site Skinfold Calculator
The Parrillo Caliper Method is a body fat measurement method that was developed by John Parrillo, a well-known fitness expert and bodybuilder.
It is important to note that the accuracy of the measurements can be affected by factors such as the skill of the person taking the measurements and variations in the thickness and distribution of subcutaneous fat.
9 Skinfold Measurement Locations (Men & Women)
- Chest
- Biceps
- Triceps
- Subscapular
- Abdominal
- Suprailiac
- Thigh
- Lower back
- Calf
9 Sites Body Fat Formula for Men and Women
To calculate the percentage of body fat with the Parillo method, take the skinfold measurements (in millimetres) and perform the following equation, which applies to both women and men:
- The percentage of body fat (%) is calculated as follows: (27 x sum of all skinfolds) / body weight (lbs.)
Durnin and Womersley Caliper Method
Durnin and Womersley developed this method in the 1970s, and it is still widely used today.
The Durnin and Womersley caliper method assumes that the subcutaneous fat thickness at these four sites is representative of total body fat.
This assumption may not hold for everyone, as body fat distribution can vary widely based on factors such as age, sex, and ethnicity.
4 Skinfold Measurement Locations (Men & Female)
- Bicep (mm)
- Tricep (mm)
- Subscapular (mm)
- Suprailiac (mm)
Durnin and Womersley Caliper Fat Formula for Men and Women
(D= Body Density; L= Log of the sum of skinfolds)
Log(a + b + c + d) = log(a) + log(b) + log(c) + log(d)
| age (years) | equations for males | equations for females |
|---|---|---|
| < 17 | D = 1.1533 – (0.0643 X L) | D = 1.1369 – (0.0598 X L) |
| 17-19 | D = 1.1620 – (0.0630 X L) | D = 1.1549 – (0.0678 X L) |
| 20-29 | D = 1.1631 – (0.0632 X L) | D = 1.1599 – (0.0717 X L) |
| 30-39 | D = 1.1422 – (0.0544 X L) | D = 1.1423 – (0.0632 X L) |
| 40 -49 | D = 1.1620 – (0.0700 X L) | D = 1.1333 – (0.0612 X L) |
| > 50 | D = 1.1715 – (0.0779 X L) | D = 1.1339 – (0.0645 X L) |
- Body Fat Percentage (%) = (495 / Body Density) – 450
Navy Body Fat Calculator
The Navy Tape Measure Method, also known as the US Navy Circumference Method, is a straightforward technique used to estimate a person’s body fat percentage based on body measurements.
You can use the Navy tape measure method to estimate your body fat percentage by measuring your height, neck circumference, and waist circumference.
It is simple, fast, and reliable since you don’t need to use calipers.
Although this method is pretty accurate, it also tends to overestimate the body fat percentage of relatively lean people (men under 15% body fat and women under 25%).
It is, therefore, best used for people with more body fat than this.
Measurement Locations for Males
- Height (cm)
- Neck (cm)
- Abdomen (cm)
Measurement Locations for Females
- Height
- Neck (cm)
- Waist (cm)
- Hips (cm)
How To Measure the Locations
- Height: Stand up straight against a wall with your back and head touching the wall. Look straight ahead with your chin parallel to the ground.
- Neck: Measure the circumference of your neck just below the larynx. The tape should be snug but not compressing the skin.
- Waist: Measure the circumference of your waist at the narrowest point, usually at or above the navel.
- Hip: Measure the circumference of your hips at the widest point, typically at the level of the buttocks.
- Abdomen: Place a measuring tape around your abdomen at the level of your belly button.
Navy Tape Body Fat Percentage Calculator Formula for Males
- Body Fat Percentage (%) (USC Units (inch):= 86.010 x log10 (abdomen – neck) – 70.041 x log10 (height) + 36.76
- Body Fat Percentage (%) (SI, Metric Units (cm):) = 495 / (1.0324 – 0.19077 x log10(waist – neck) + 0.15456 x log10(height)) – 450
Navy Tape Body Fat Percentage Formula for Females
- Body Fat Percentage (%) (USC Units (inch):) = 163.205 x log10 (waist + hip – neck) – 97.684 x log10 (height) – 78.387
- Body Fat Percentage (%) (SI, Metric Units (cm):= 495 / (1.29579 – 0.35004 x log10(waist + hip – neck) + 0.22100 x log10(height)) – 450
To Know Your TDEE Click Here
FAQs
How lean do you need to be to get great abs?
The level of leanness required to get great abs can vary depending on a person’s body composition and genetics. However, a body fat percentage of around 10-12% for men and 16-20% for women is typically necessary to achieve visible abs.
It is essential to note that achieving visible abs also requires a strong core muscle foundation, which can be developed through regular exercises such as planks, crunches, and other abdominal exercises.
A healthy and balanced diet and regular exercise are essential for six-pack abs.
How much body fat should I have
As a general guideline, a healthy range for men is considered to be 10-20% body fat, and for women, it is 20-30% body fat.
It is essential to recognise that having a body fat percentage that is too low can be just as detrimental to one’s health as having a body fat percentage that is too high.
A body fat percentage below 5% for men and below 12% for women is considered extremely low. It can lead to health problems, including weakened immune systems, hormonal imbalances, and decreased bone density.
How can I reduce my body fat percentage?
To reduce body fat percentage, it is essential to follow a healthy and balanced diet, engage in regular exercise, and get enough sleep.
Focusing on strength and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can also help increase muscle mass and reduce body fat percentage.
References
- Jackson, A. S., & Pollock, M. L. (1978). Generalized equations for predicting body density of men. British Journal of Nutrition, 40, 497-504.
- Jackson, A. S., Pollock, M. L., & Ward, A. (1980). Generalized equations for predicting body density of women. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 12, 175-182.
- Jackson A S, Pollock, M (1985) Practical assessment of body composition. Physician Sport Med. 13: 76-90
- J. Parrillo, Greenwood-Robinson. “High-performance bodybuilding” Berkeley Publishing group, New York,169-172, 1993.
- Durnin, J.V.G.A. and Womersley, J. (1974). Body fat assessed from the total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. British Journal of Nutrition, 32, 77-97.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Subcommittee on Military Weight Management. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2004.
- Peterson DD. “History of the U.S. Navy Body Composition program“ Military Medicine (January 2015)
- The association between body fat and musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
- Comparison of the Three-Site and Seven-Site Measurements in Female Collegiate Athletes Using BodyMetrix™.
- Siri W.E. Body Composition from Fluid Spaces and Density: Analysis of Methods. Nutr. Burbank Los Angel. Cty. Calif. 1993;9:480–491. – PubMed
- Tedford AG, Pribyslavska V, Bryant LG, Scudamore EM. A Comparative Analysis of Army Body Composition Standards for Women. Int J Exerc Sci. 2020 Sep 1;13(7):1275-1282. PMID: 33042386; PMCID: PMC7523900.
- Wilson, C. C., Harp, C. J., & Koch, A. J. (2010). Comparison of the US Army tape test to skinfold and underwater weighing measures of body composition. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 24(1), 1-8.

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.
