You need to optimize muscle protein synthesis to see better results from your workouts and build muscle faster.
Muscle protein synthesis is the process of building new muscle tissue. The higher your rates of MPS, the more muscle you’ll be able to build and maintain.
Whether your goal is to gain lean mass or maintain the muscle you have as you age, it is crucial to maximize protein synthesis.
In this post, we’ll break down the science-backed strategies you can use to increase protein synthesis and boost muscle growth.
Let’s Dive In!

- What Is Muscle Protein Synthesis
- The Role of MPS in Muscle Building and Repair
- 10 Effective Ways To Improve Muscle Protein Synthesis
- 1. Proteins For Muscle Repair
- 2. Strength Training and Muscle Protein Synthesis
- 3. Creatine Monohydrate
- 4. Adequate Sleep
- 5. Increase Leucine
- 6. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- 7. Protein Timing
- 8. Balance Macronutrient Consumption
- 9. Consuming Sufficient Calories
- 10. Manage Stress Levels
- Conclusion
What Is Muscle Protein Synthesis
Muscle protein synthesis (MPS) is the process by which our bodies build new muscle tissue. It is a fundamental process in muscle growth and repair.
MPS is a process where amino acids are made into new muscle proteins. Proteins are composed of amino acids obtained from dietary protein sources.
When we consume protein, our bodies break down it into individual amino acids, which are absorbed into the bloodstream.
Then, they are transported to muscle cells. Here, they are used to synthesize new muscle proteins through a process called translation.
The Role of MPS in Muscle Building and Repair
MPS plays a critical role in both muscle building and repair. We create microscopic tears in our muscle fibers when we engage in resistance training.
After a workout, the body initiates a series of biological responses and cellular processes to repair muscle fibers and replenish energy stores. One of them is MPS.
MPS is responsible for repairing damaged muscle fibers and building new muscle tissue, which leads to muscle growth.
10 Effective Ways To Improve Muscle Protein Synthesis
Based on current scientific research, here are the top 10 ways to increase muscle protein synthesis. With these tips, you can improve your training program and get better results.
Let’s learn how to accelerate your muscle growth using strategies and tips.
1. Proteins For Muscle Repair
Exercising, especially during weight lifting or high-intensity training, creates microscopic tears in your muscle fibers.
Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS) is the process your body uses to repair and rebuild muscle fibers that are damaged during exercise. Consuming enough protein provides amino acids that stimulate MPS, leading to recovery and muscle growth.
Leucine is one amino acid that is especially important for initiating MPS after a workout.
Studies show that eating 20–40 grams of protein maximizes muscle growth.
Many experts recommend eating 0.14–0.23 grams of protein per pound of body weight within 1–2 hours after training for optimal recovery.
High-protein food sources include eggs, meat, fish, dairy, beans, nuts, and protein shakes.

2. Strength Training and Muscle Protein Synthesis
When we lift heavy weights, we damage the cells in the muscle fibers, which signals the body to increase protein synthesis rates to repair the damage.
A study has shown that the rate of MPS in humans is elevated by 50% at 4 hours following a bout of heavy resistance training and by 109% at 24 hours following training.
The intensity (amount of weight lifted) and volume (total number of repetitions and sets) of strength training can significantly influence the extent of MPS. Higher intensity and volume usually lead to a more substantial MPS response.

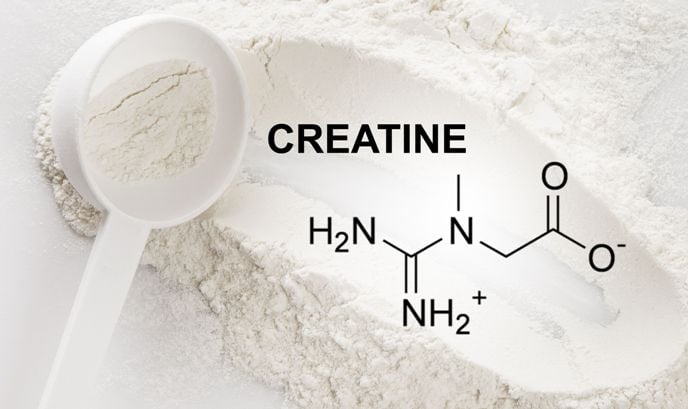
3. Creatine Monohydrate
This study has demonstrated that creatine significantly increases muscle protein synthesis (MPS) and muscle growth.
Creatine monohydrate is a popular sports supplement that has been shown to improve athletic performance and recovery.
It provides energy to cells, particularly muscle cells, during high-intensity, short-duration activities like weightlifting or sprinting.
Creatine can also be obtained through diet, primarily from animal products such as red meat and fish, and the body also produces it.
Studies have shown that it increases muscle strength, size, and endurance and improves exercise performance.
The recommended dose of creatine is 3–5 grams per day. You can take creatine in powder form or in capsules.
4. Adequate Sleep
Adequate sleep is a critical component of muscle growth and recovery, yet it is often overlooked. Its role in enhancing muscle protein synthesis is multifaceted.
A study found that sleep helps the body recover its physiological, psychological, musculoskeletal, immune, metabolic, and endocrine systems. These systems are all needed for the body to adapt to training stress.
Growth hormone, which plays a key role in muscle growth and repair, is released during deep sleep. This hormone boosts MPS and aids in the repair and regrowth of muscle tissue.
Sleeping enough helps regulate cortisol, a stress hormone that can cause muscle loss when overproduced.

5. Increase Leucine
Leucine is known for its ability to directly activate the mTOR pathway, a key regulator of MPS. This activation signals the body to initiate the process of muscle repair and growth.
A study has shown that adding 4–5 grams of leucine to regular meals can help muscles make more protein.
- Leucine is a key nutrient for building muscle mass and strength.
- Endurance athletes can also benefit from leucine’s role in muscle maintenance and recovery.
Leucine-Rich Foods:
- Animal Proteins: High-quality animal-based proteins such as whey, eggs, dairy products, beef, and chicken are rich in leucine.
- Plant-Based Options: For those following a plant-based diet, foods like soybeans, lentils, and pumpkin seeds are good sources of leucine.
- Supplements: Leucine supplements, often found in BCAA blends, can also be used, especially for those with dietary restrictions or who need additional intake.
Leucine has been shown to stimulate MPS and help prevent muscle protein breakdown.
6. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Research has shown that omega-3 fatty acids can stimulate MPS, especially in combination with factors like resistance training and sufficient protein intake.
Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids may increase the rate of MPS in older adults, potentially serving as a therapeutic agent for sarcopenia.
How do omega-3 fatty acids affect MPS?
- Reduce inflammation that impairs MPS.
- Improve insulin sensitivity and nutrient uptake in muscles
- Increase anabolic signals like mTOR activation
The available research shows that omega-3 fatty acids’ dosages vary widely, ranging from 0.16 to 2.6 g/day of EPA and from 0 to 1.8 g/day of DHA.
Best dietary sources
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines
- Chia seeds, walnuts, flaxseeds
- Omega-3 supplements like fish oil

7. Protein Timing
Consuming protein at the right times can significantly boost muscle regrowth and repair.
People have been studying how much protein to eat before, during, and after exercise for a long time. A widely discussed “anabolic window” post-exercise is believed to be a prime time for protein intake.
A meta-analysis found that consuming protein supplementation within 1 hour before and/or after resistance training effectively enhances gains in muscle mass.
While research on protein timing is still evolving, here are some general suggestions:

Pre-workout protein
- 10-20g protein 30–60 minutes before training
- Provides amino acids to muscles
- Whey or casein protein options
Post-workout protein
- 20-30g protein within 60–90 minutes after training
- Replenishes amino acids for MPS
- Quickly digesting whey protein is ideal.
Daily Protein Distribution
- Spreading out protein intake (every 3 hours)
- Provides muscles with continual amino acids
- Prevents periods of muscle breakdown
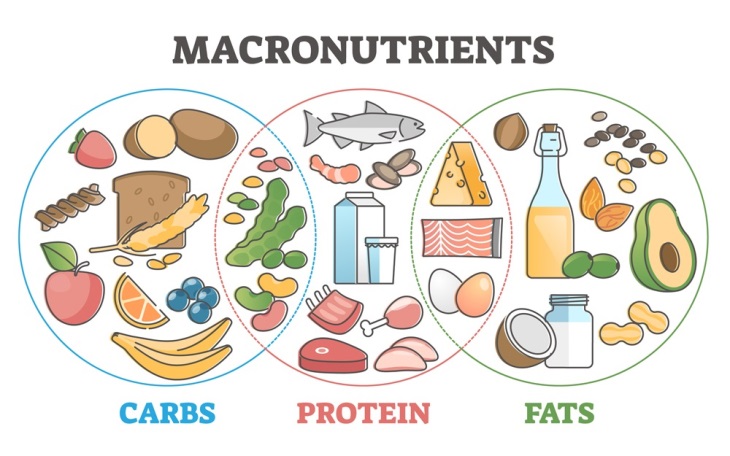
8. Balance Macronutrient Consumption
Proteins often get the spotlight when it comes to building muscle, but carbs and fats are just as important.
Protein: The Building Block of Muscle
Protein provides amino acids, the building blocks necessary for MPS. Adequate protein intake is essential for muscle repair and growth.
High-quality proteins with essential amino acids, particularly leucine, are essential. The recommended amount varies based on individual factors like body weight and activity level.
Want to take your gains to the next level? Discover your daily calorie needs with our free TDEE calculator.
Carbohydrates: Fueling Muscle Growth and Recovery
Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for high-intensity workouts. A healthy carb intake ensures energy availability for training and supports recovery. Carbs help replenish glycogen stores in muscles.
Even though carbs don’t directly increase MPS, they help by reducing muscle protein breakdown and helping to keep the body in a positive energy balance.
Fats: Essential for Overall Health
Fats play a key role in hormone production, including hormones like testosterone. It gives you a steady boost of energy, especially during slower, longer workouts.
Dietary fats are necessary for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins, which are essential for overall health and muscle function.
Balancing Macronutrient Intake for MPS
The right amount of certain nutrients depends on your goals for exercise and how you eat. However, a general guideline for healthy adults includes:
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of total calories
- Protein: 15-25% of total calories
- Fats: 20-35% of total calories
9. Consuming Sufficient Calories
When we consume too few calories, our bodies experience a negative energy balance, where energy expenditure exceeds energy intake. In this state, our bodies break down muscle tissue for fuel, which hinders muscle growth and repair. Eat enough calories to support MPS and build up muscle.
The most important thing you can do to gain weight is to create a calorie surplus, which means you eat more calories than your body needs.
Aim to add around 500 calories to your daily diet, which should help you gain around 1 pound (0.45 kg) per week.
Focusing on nutrient-dense foods rather than just increasing calorie intake indiscriminately is important.
Know More Weight Gain Calories: Use Our Free Calculator
10. Manage Stress Levels
Research has shown that muscle loss increases with prolonged inactivity and high stress levels due to reduced muscle protein synthesis.
Chronic stress leads to elevated levels of cortisol, a stress hormone. High cortisol levels can impede MPS and increase muscle protein breakdown, hindering muscle growth and recovery.
Stress can also reduce the levels of anabolic hormones like testosterone and growth hormone.
How to Manage Stress Levels and Increase Muscle Protein Synthesis:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Massages
- Maintain work/life balance
- Foster social connections
- Laugh and use humor
- Prioritize sleep
- Mindfulness and being present
- Ashwagandha
Getting a massage is an excellent way to help your body recover faster. It eases soreness and stiffness by boosting muscle circulation and blood flow. Studies show regular massage reduces inflammation and helps rebuild muscle tissue.

Conclusion
Muscle protein synthesis is the key biological process that allows your muscles to grow and strengthen. Optimizing MPS means building lean muscle mass more efficiently through training and nutrition.
Several key strategies can effectively boost MPS:
- Engage in regular resistance training.
- Consume adequate protein
- Prioritize protein timing
- Balance macronutrient intake
- Manage stress levels and many more.
Experiment with the MPS-boosting strategies discussed, finding the optimal combination that suits your needs. Our muscles constantly break down and require repair—give them what they require to recover, stronger than before.
Please let me know your favorite strategies in the comments.
References
- MacDougall JD, Gibala MJ, Tarnopolsky MA, MacDonald JR, Interisano SA, Yarasheski KE. The time course for elevated muscle protein synthesis following heavy resistance exercise. Can J Appl Physiol. 1995 Dec;20(4):480-6.
- White GE, West SL, Caterini JE, Di Battista AP, Rhind SG, Wells GD. Massage Therapy Modulates Inflammatory Mediators Following Sprint Exercise in Healthy Male Athletes. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2020 Jan 29;5(1):9.
- Volpi E. Is leucine content in dietary protein the key to muscle preservation in older women? Am J Clin Nutr. 2018 Feb 1;107(2):143-144.

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.

