Interactive Muscle Chart & Exercise Guide
Master your fitness journey with comprehensive anatomy guide, personalized workout planner, and 500+ scientifically-backed exercises.
Complete Guide to Muscle Groups and Exercise Training
Master your fitness journey with our comprehensive muscle anatomy guide. This detailed resource covers all major muscle groups, their functions, anatomy, and the most effective exercises for building strength, size, and endurance. Whether you’re a beginner or advanced athlete, use this scientifically-backed information to optimize your training results.
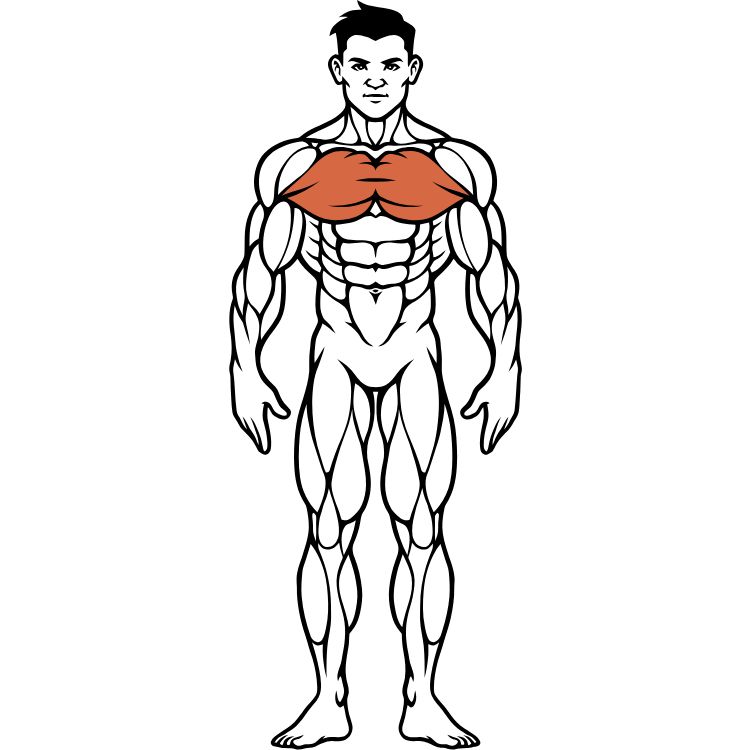
Chest Muscles (Pectorals)
The pectoralis major and minor are the primary chest muscles responsible for pushing movements, arm adduction, and internal rotation. These powerful muscles form the foundation of upper body strength and create the broad, defined chest appearance that many fitness enthusiasts strive for.
Chest Muscle Anatomy & Function
Location: The pectoralis major covers most of the upper chest, originating from the clavicle, sternum, and upper ribs, inserting into the humerus. The pectoralis minor lies beneath, connecting the ribs to the scapula.
Primary Functions: Horizontal adduction (bringing arms across the body), internal rotation of the arm, and flexion of the shoulder joint. Essential for all pushing movements in daily life and sports.
Muscle Fibers: Contains upper (clavicular), middle (sternal), and lower (costal) fibers, each activated differently by exercise angles and hand positions.
10 Best Chest Exercises for Maximum Development
1. Barbell Bench Press
King of chest exercises targeting all pectoral areas with maximum weight capacity. Learn technique
2. Incline Dumbbell Press
Targets upper chest fibers more effectively than flat pressing, essential for complete development.
3. Push-Ups
Fundamental bodyweight chest exercise, perfect for all fitness levels. Master variations
4. Chest Dips
Compound movement targeting lower chest, triceps, and front deltoids using bodyweight.
5. Cable Flys
Isolation exercise providing constant tension throughout movement. Explore variations
6. Incline Cable Fly
Targets upper chest with perfect isolation and constant tension. Master technique
7. Decline Dumbbell Press
Emphasizes lower chest fibers for complete pectoral development and strength.
8. Machine Chest Press
Safe, controlled movement perfect for beginners or high-intensity training. Learn technique
9. Dumbbell Pullovers
Unique exercise stretching and strengthening chest while engaging lats and serratus anterior.
10. T-Push-Ups
Advanced push-up variation adding rotation and core engagement. Master technique
Benefits of Strong Chest Muscles
- Enhanced Upper Body Power: Improved performance in pushing movements and sports
- Better Posture: Strong chest muscles help maintain proper shoulder alignment
- Functional Strength: Essential for daily activities like lifting, pushing, and carrying
- Aesthetic Appeal: Well-developed chest creates an impressive upper body silhouette
- Injury Prevention: Balanced chest strength protects shoulders and improves joint stability
Shoulder Muscles (Deltoids)
The deltoid muscles are the primary shoulder muscles, consisting of three distinct heads that provide the shoulders’ rounded appearance and enable complex arm movements. These muscles are crucial for overhead activities, lifting, and maintaining shoulder stability throughout daily activities and athletic performance.
Shoulder Muscle Anatomy & Function
Location: The deltoid is a triangular muscle covering the shoulder joint, originating from the clavicle and scapula, inserting into the humerus.
Primary Functions: Shoulder abduction (lifting arms to sides), flexion (lifting arms forward), extension (moving arms backward), and rotation. Essential for overhead movements and arm stability.
Three Heads: Anterior (front), lateral (middle), and posterior (rear) deltoids, each with specific movement patterns and training requirements.
10 Best Shoulder Exercises for Complete Development
1. Overhead Press (Military Press)
Fundamental shoulder exercise building overall deltoid mass and strength. Master techniques
2. Lateral Raises
Isolation exercise targeting lateral deltoid for shoulder width and definition.
3. Front Raises
Targets anterior deltoid, improves shoulder stability and forward pressing strength.
4. Rear Delt Flys
Essential for posterior deltoid development and shoulder balance. Learn variations
5. Arnold Press
Named after Arnold Schwarzenegger, targets all three deltoid heads with rotation.
6. Upright Rows
Compound movement targeting deltoids and traps simultaneously. Master technique
7. Pike Push-Ups
Bodyweight exercise mimicking overhead pressing motion, perfect for home workouts.
8. Single-Arm Lateral Raise
Unilateral training for improved muscle balance and core engagement. Perfect technique
9. Shoulder Press Machine
Controlled movement ideal for beginners or high-intensity training. Learn technique
10. Face Pulls
Excellent exercise for rear delts and shoulder health, improving posture and preventing injury.
Benefits of Strong Shoulder Muscles
- Enhanced Overhead Strength: Improved performance in pressing and lifting activities
- Shoulder Stability: Reduced risk of shoulder impingement and injury
- Better Posture: Strong deltoids help maintain proper shoulder alignment
- Athletic Performance: Essential for throwing, swimming, and overhead sports
- Functional Movement: Improved ability to reach, lift, and carry objects overhead
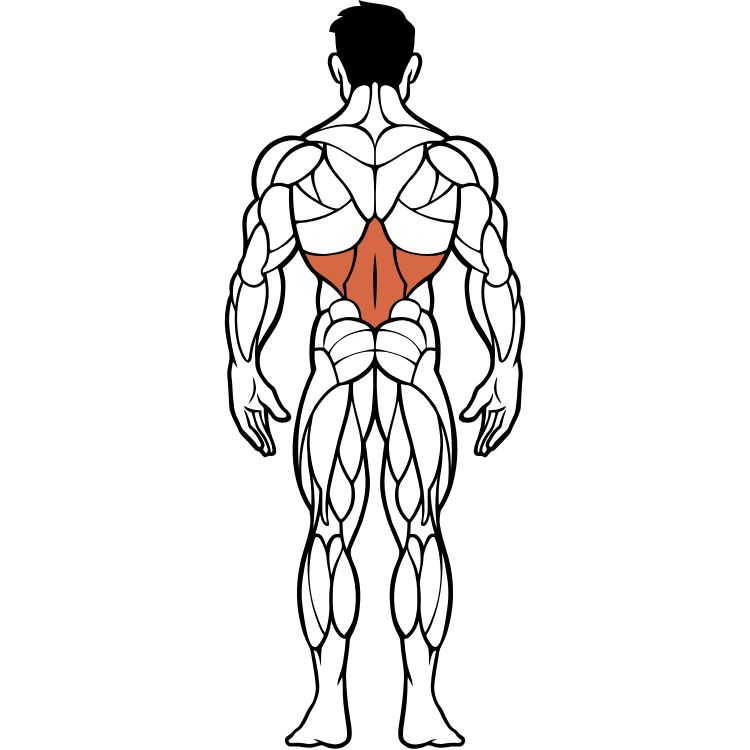
Back Muscles (Latissimus Dorsi & More)
The back muscles, including the latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, and middle traps, create the V-shaped torso and provide essential pulling strength. These muscles are crucial for posture, spinal stability, and overall upper body power.
Back Muscle Anatomy & Function
Location: The latissimus dorsi extends from the lower spine and pelvis to the upper arm bone, creating the broad back appearance. Supporting muscles include rhomboids, middle traps, and rear deltoids.
Primary Functions: Pulling movements, shoulder adduction, spinal extension, and maintaining posture. Essential for all rowing and pulling activities.
Muscle Groups: Lats (width), rhomboids (thickness), middle traps (posture), and lower traps (stability).
10 Best Back Exercises for Complete Development
1. Pull-Ups/Chin-Ups
Ultimate bodyweight back exercise building width and strength. Master variations
2. Barbell Rows
Compound movement targeting all back muscles with heavy resistance for maximum growth.
3. Lat Pulldowns
Machine-based exercise perfect for beginners to build lat strength. Learn techniques
4. Cable Rows
Seated rows targeting middle back and rhomboids with constant tension. Perfect form
5. T-Bar Rows
Excellent for building back thickness and overall pulling strength.
6. One-Arm Dumbbell Row
Unilateral exercise for balanced development and core engagement. Master single-arm rows
7. Face Pulls
Essential for rear delts and upper back health, improving posture significantly.
8. Deadlifts
The king of posterior chain exercises, building total back strength and power.
9. Reverse Flys
Isolation exercise for rear delts and rhomboids, crucial for shoulder balance.
10. Hyperextensions
Strengthens lower back and glutes, essential for spinal health and posture.
Benefits of Strong Back Muscles
- Improved Posture: Strong back muscles counteract forward head posture and rounded shoulders
- Reduced Back Pain: Strengthened posterior chain supports the spine and reduces injury risk
- Enhanced Pulling Power: Essential for all pulling activities in sports and daily life
- V-Shaped Physique: Well-developed lats create the coveted V-taper appearance
- Functional Strength: Improved ability to lift, carry, and pull objects safely
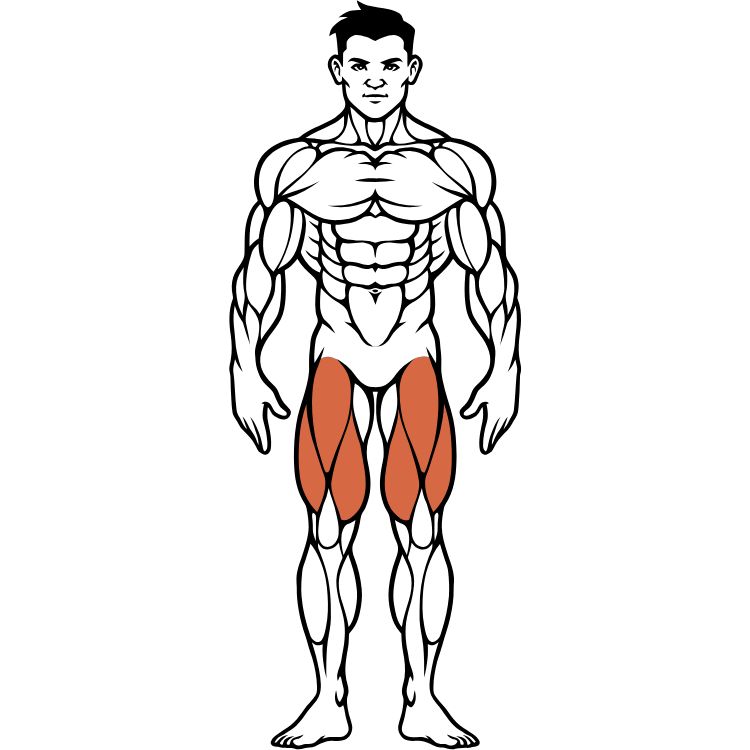
Leg Muscles (Quadriceps & Hamstrings)
The leg muscles, including quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, form the foundation of human movement. These powerful muscle groups enable walking, running, jumping, and provide the strength for all lower body activities.
Leg Muscle Anatomy & Function
Quadriceps: Four-headed muscle group at the front of the thigh responsible for knee extension and hip flexion. Essential for squatting, jumping, and climbing.
Hamstrings: Three muscles at the back of the thigh enabling knee flexion and hip extension. Critical for running speed and posterior chain strength.
Glutes & Calves: Glutes power hip extension and provide stability, while calves enable plantar flexion for walking and jumping.
10 Best Leg Exercises for Complete Development
1. Squats
King of leg exercises targeting quads, glutes, and core simultaneously. Master techniques
2. Deadlifts
Compound movement targeting hamstrings, glutes, and entire posterior chain with maximum weight.
3. Lunges
Unilateral exercise improving balance while targeting quads, glutes, and stabilizing muscles.
4. Leg Press
Machine-based exercise allowing heavy loading of quads and glutes safely. Explore machines
5. Romanian Deadlifts
Hamstring-focused variation emphasizing hip hinge movement pattern and posterior chain strength.
6. Bulgarian Split Squats
Advanced single-leg exercise challenging stability while building unilateral strength.
7. Leg Curls
Isolation exercise specifically targeting hamstrings for balanced leg development. Learn hamstring machine exercises
8. Calf Raises
Essential for calf development and lower leg strength. Build bigger calves
9. Hip Thrusts
Glute-focused exercise improving hip extension power and posterior chain activation.
10. Step-Ups
Functional exercise mimicking daily activities while building single-leg strength and power.
Benefits of Strong Leg Muscles
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Powerful legs improve running, jumping, and sports performance
- Functional Movement: Strong legs support daily activities like climbing stairs and lifting
- Injury Prevention: Balanced leg strength protects knees, hips, and lower back
- Metabolic Benefits: Large leg muscles burn more calories and boost metabolism
- Bone Health: Weight-bearing leg exercises strengthen bones and prevent osteoporosis
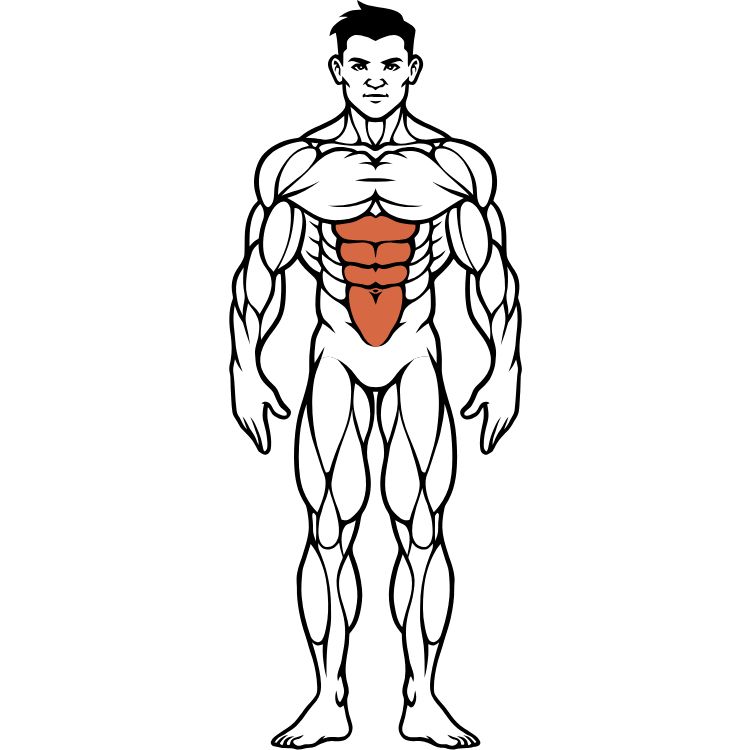
Core Muscles (Abdominals & Obliques)
The core muscles, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis, form the foundation of all movement. These muscles provide spinal stability, enable trunk flexion and rotation, and are essential for athletic performance and daily activities.
Core Muscle Anatomy & Function
Rectus Abdominis: The “six-pack” muscle running vertically along the front of the abdomen, responsible for trunk flexion and spinal stability.
Obliques: External and internal obliques located on the sides of the abdomen, enabling rotation and lateral flexion of the trunk.
Transverse Abdominis: The deepest core muscle acting like a natural weight belt, providing internal pressure and spinal stability.
10 Best Core Exercises for Complete Development
1. Planks
The ultimate core stability exercise, engaging all core muscles simultaneously for functional strength.
2. Dead Bug
Excellent for teaching core stability while moving limbs, perfect for beginners and rehabilitation.
3. Russian Twists
Dynamic exercise targeting obliques and rotational core strength with added resistance options.
4. Bicycle Crunches
Combines trunk flexion with rotation, effectively targeting both abs and obliques simultaneously.
5. Mountain Climbers
High-intensity exercise combining core stability with cardiovascular conditioning and coordination.
6. Leg Raises
Targets lower abs specifically while building hip flexor strength and core control. Focus on lower abs
7. Side Planks
Unilateral core exercise specifically targeting obliques and lateral core stability.
8. V-Ups
Advanced exercise combining upper and lower body movement for complete abdominal activation.
9. Wood Chops
Functional rotational exercise mimicking real-world movement patterns while strengthening obliques.
10. Hollow Body Hold
Advanced isometric exercise building incredible core strength and body awareness for athletes.
Benefits of Strong Core Muscles
- Spinal Stability: Strong core muscles protect the spine and reduce lower back pain risk
- Athletic Performance: Core strength transfers power between upper and lower body in sports
- Better Posture: Core muscles help maintain proper spinal alignment throughout the day
- Functional Movement: Essential for lifting, carrying, and rotational activities
- Injury Prevention: Strong core reduces risk of back injuries and improves movement quality
Essential Training Principles for Optimal Results
Progressive Overload
Gradually increase weight, reps, or sets to continuously challenge your muscles and promote growth. This is the fundamental principle of muscle building and strength development.
Proper Form & Technique
Maintain correct technique to maximize muscle activation, prevent injury, and ensure optimal results from every repetition. Quality always beats quantity.
Adequate Recovery
Allow 48-72 hours between training the same muscle groups to enable proper recovery, repair, and growth. Rest is when muscles actually grow.
Consistent Training
Regular, consistent workouts are more effective than sporadic intense sessions. Aim for 2-3 sessions per muscle group weekly for optimal results.
Balanced Programming
Train all muscle groups proportionally to prevent imbalances, reduce injury risk, and achieve optimal functional strength and aesthetics.
Mind-Muscle Connection
Focus on feeling the target muscle work during each exercise. This mental connection improves muscle activation and training effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Related
- Basketball Calories Burned Calculator
- Badminton Calories Burned Calculator
- Boxing Calories Burned Calculator
- Plank Calories Burned Calculator
- Burpee Calories Burned Calculator
- Crunches Calories Burned Calculator
- Sit-Up Calories Burned
- Zumba Calories Burned Calculator
- Pull Up Calories Burned Calculator
- Push-Up Calories Burned Calculator
- Home Activities Calories Burned Calculator
- Exercise Calories Burned Calculator
- Running Calorie Calculator
- Walking Calorie Burned Calculator

Manish is a NASM-certified fitness and nutrition coach with over 10 years of experience in weight lifting and fat loss fitness coaching. He specializes in gym-based training and has a lot of knowledge about exercise, lifting technique, biomechanics, and more.
Through “Fit Life Regime,” he generously shares the insights he’s gained over a decade in the field. His goal is to equip others with the knowledge to start their own fitness journey.